Abstract
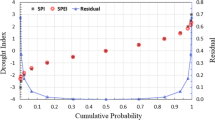
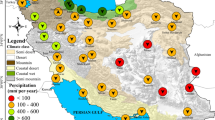
Precise analysis of spatiotemporal trends of temperature, precipitation and meteorological droughts plays a key role in the sustainable management of water resources in the given region. This study first aims to detect the long-term climate (monthly/seasonally and annually) trends from the historical temperature and precipitation data series by applying Spearmen’s Rho and Mann-Kendall test at 5 % significant level. The measurements of both climate variables for a total period of 49 years (1965–2013) were collected from the 11 different meteorological stations located in the Songhua River basin of China. Secondly, the two well-known meteorological drought indices including the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) and Reconnaissance Drought Index (RDI) were applied on normalize data to detect the drought hazards at 3, 6, 9 and 12 month time scale in the study area. The analysis of monthly precipitation showed significant (p < 0.05) increasing trends during the winter (November and December months) season. Similarly, the results of seasonal and annual air temperature showed a significant increase from 1 °C to 1.5 °C for the past 49 years in the basin. According to the Sen’s slope estimator, the rate of increment in seasonal temperature slope (0.26 °C/season) and precipitation (9.02 mm/season) were greater than annual air temperature (0.04 °C/year) and precipitation (1.36 mm/year). By comparing the results of SPI and RDI indices showed good performance at 9 (r = 0.96, p < 0.01) and 12 (r = 0.99, p < 0.01) month drought analysis. However, the yearly drought analysis at over all stations indicated that a 20 years were under dry conditions in entire study area during 49 years. We found the extreme dry and wet conditions in the study region were prevailing during the years of 2001 and 2007, and 1994 and 2013, respectively. Overall, the analysis and quantifications of this study provides a mechanism for the policy makers to mitigate the impact of extreme climate and drought conditions in order to improve local water resources management in the region.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexandersson H, Moberg A (1997) Homogenization of Swedish temperature data. Part I: homogeneity test for linear trends. Int J Climatol 17(1):25–34
Banimahd SA, Khalili D (2013) Factors influencing Markov chain predictability characteristics, utilizing SPI, RDI, EDI and SPEI drought indices in different climatic zones. Water Resour Manag 27:3911–3928
Blain GC (2013) The Mann-Kendall test: the need to consider the interaction between serial correlation and trend. Acta Scientiarum. Agronomy 35(4):393–402
Bonaccorso B, Bordi I, Cancelliere A, Rossi G, Sutera A (2003) Spatial variability of drought: an analysis of the SPI in Sicily. Water Resour Manag 17(4):273–296
Brunsell NA (2010) A multiscale information theory approach to assess spatial–temporal variability of daily precipitation. J Hydrol 385:165–172
Chen H, Guo S, CY X, Singh VP (2007) Historical temporal trends of hydro-climatic variables and runoff response to climate variability and their relevance in water resource management in the Hanjiang basin. J Hydrol 344(3):171–184
Feng X, Zhang G, Yin X (2011) Hydrological responses to climate change in Nenjiang river basin, northeastern China. Water Resour Manag 25(2):677–689
Gocic M, Trajkovic S (2014) Spatiotemporal characteristics of drought in Serbia. J Hydrol 510:110–123
Guo L, Ma KM, Zhang Y (2009) Denitrification potential of different land-use types in Jiansanjiang District. Journal of agro-environment Science 5: 015 (In Chinese)
IPCC (2007) Summary for policymakers of climate change 2007: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, New York, USA
IPCC (2013) Summary for Policymakers. In: TF S, Qin D (eds) . Plattner, GK
Kendall MG (1975) Rank Correlation Methods. Griffin, London
Khaliq MN, Ouarda TBMJ (2007) Short communication on the critical values of the standard normal homogeneity test (SNHT. Int J Climatol 27(5):681–687
Lehmann EL, D’Abrera HJ (2006) Nonparametric: statistical methods based on ranks. New York, Springer, pp. 464
Li B, Liang Z, Yu Z, Acharya K (2014) Evaluation of drought and wetness episodes in a cold region (Northeast China) since 1898 with different drought indices. Nat Hazards 71(3):2063–2085
Liu D, Luo M, Fu Q, Zhang Y, Imran KM, Zhao D, Li T, Abrar FM (2016) Precipitation complexity measurement using Multifractal spectra empirical mode decomposition Detrended fluctuation analysis. Water Resour Manag 30(2):505–522
Mann HB (1945) Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica: J Econometric Soc:245–259
McKee TB, Doesken NJ, Kleist J (1993) The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In proceedings of the 8th conference on applied climatology, Boston, MA, USA. Am Meteorol Soc 17(22):179–183
Nyeko-Ogiramoi P, Willems P, Ngirane-Katashaya G (2013) Trend and variability in observed hydro meteorological extremes in the Lake Victoria basin. J Hydrol 489:56–73
Qian W, Zhu Y (2001) Climate change in China from 1880 to 1998 and its impact on the environmental condition. Clim Chang 50(4):419–444
Sen PK (1968) Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J Am Stat Assoc 63(324):1379–1389
Shadmani M, Marofi S, Roknian M (2012) Trend analysis in reference evapotranspiration using Mann-Kendall and Spearman’s rho tests in arid regions of Iran. Water Resour Manag 26(1):211–224
Skansi M, Brunet M, Sigró J, Aguilar E, Arevalo Groening JA, Bentancur OJ, Castellón Geier YR, Correa Amaya RL, Jácome H, Malheiros Ramos A, Oria Rojas C, Pasten AM, Sallons Mitro S, Villaroel Jiménez C, Martínez R, Alexander LV, Jones PD (2013) Warming and wetting signals emerging from analysis of changes in climate extreme indices over South America. Glob Planet Chang 100:295–307
Song L, Cannon AJ, Whitfield PH (2007) Changes in seasonal patterns of temperature and precipitation in China during 1971–2000. Adv Atmos Sci 24(3):459–473
Song X, Song S, Sun W, Mu X, Wang S, Li J, Li Y (2015) Recent changes in extreme precipitation and drought over the Songhua River basin, China, during 1960–2013. Atmos Res 157:137–152
Stocker TF (2013) Climate change 2013: Thomas F (ed) The physical science basis: Working Group I contribution to the Fifth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Tsakiris G, Pangalou D, Vangelis H (2007) Regional drought assessment based on the reconnaissance drought index (RDI. Water Resour Manag 21(5):821–833
Wang S, Zhang Z (2011) Effects of climate change on water resources in China. Clim Res 47(1):77
Wang X, Shen H, Zhang W, Cao J, Qi Y, Chen G, Li X (2015) Spatial and temporal characteristics of droughts in the Northeast China transect. Nat Hazards 76(1):601–614
Weiliang CLZXL, Yunfeng L, Wenqin Z (2004) Characteristics of the climate change and its formation mechanism in China in last 80 years. Acta Metall Sin 5:010
Xu CY, Singh VP (2004) Review on regional water resources assessment models under stationary and changing climate. Water Resour Manag 18:291–612
Yan MH, Deng W, Chen PQ (2003) Recent trends of temperature and precipitation disturbed by large-scale reclamation in the Sangjiang plain of China. Chin Geogr Sci 13(4):317–321
Yaning C, Changchun X, Xingming H, Weihong L, Yapeng C, Chenggang Z, Zhaoxia Y (2009) Fifty-year climate change and its effect on annual runoff in the Tarim River basin, China. Quat Int 208(1):53–61
Yue S, Pilon P, Phinney B, Cavadias G (2002) The influence of autocorrelation on the ability to detect trend in hydrological series. Hydrol Process 16(9):1807–1829
Zhang Q, CY X, Yang T (2009) Variability of water resource in the Yellow River basin of past 50 years, China. Water Resour Manag 23:1157–1170
Zhang Q, Sun P, Singh VP, Chen X (2012) Spatial-temporal precipitation changes (1956–2000) and their implications for agriculture in China. Glob Planet Chang 82:86–95
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.41071053, No.51479032), Sub-Task of National Science and Technology Support Program for Rural Development in the 12th Five-Year Plan of China (No.2013BAD20B04-S3), Specialized Research Fund for the Public Welfare Industry of the Ministry of Water Resources (No.201301096), Specialized Research Fund for Innovative Talents of Harbin (Excellent Academic Leader) (No.2013RFXXJ001), Science and Technology Research Program of Education Department of Heilongjiang Province (No.12531012),Science and Technology Program of Water Conservancy of Heilongjiang Province (No.201319), Northeast Agricultural University Innovation Foundation For Postgraduate (No.yjscx14069).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
No conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, M., Liu, D., Fu, Q. et al. Recent Climate Trends and Drought Behavioral Assessment Based on Precipitation and Temperature Data Series in the Songhua River Basin of China. Water Resour Manage 30, 4839–4859 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1456-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1456-x