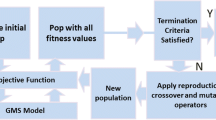
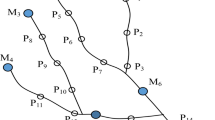
Abstract
Implementation of monitoring strategy for increasing the efficiency of groundwater pollutant source characterization is often necessary, especially when only inadequate and arbitrary concentration measurement data are initially available. Two main parameters that need to be estimated for efficient and accurate characterization of groundwater pollution sources are: location of the source and the time when the source became active. Complexities involved with the explicit estimation of the time of start and source activity have not been addressed so far in previous studies. The main complexity arises due to the fact that the spatial location and time of activity are inter-related. Therefore, specifying one and solving for the other simplifies the source characterization problem. Hence, in this study, both the source location and time of initiation are treated as unknowns. The developed methodology uses dynamic time warping distance in the linked simulation-optimization model to address some complex issues in designing a monitoring network to efficiently estimate source characteristics including the time of first activity of unknown groundwater source. Performance of the developed methodology is evaluated on illustrative contaminated aquifer. These evaluation results demonstrate the potential use of the developed methodology.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aral MM, Guan J, Maslia ML (2001) Identification of contaminant source location and release history in aquifers. J Hydrol Eng 6(3):225–234
Atmadja J, Bagtzoglou AC (2001) State of the art report on mathematical methods for groundwater pollution source identification. Environ Forensic 2(3):205–214
Bagtzoglou A, Atmadja J (2005) Mathematical methods for hydrologic inversion: The case of pollution source identification. In: Kassim T (ed) Water pollution, The handbook of environmental chemistry, vol 3. Springer, Berlin, pp 65–96. doi:10.1007/b11442
Bagtzoglou AC, Tompson AFB, Dougherty DE (1991) Probabilistic simulation for reliable solute source identification in heterogeneous porous media. In: Ganoulis J (ed) Water resources engineering risk assessment. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, pp 189–201
Bagtzoglou AC, Dougherty DE, Tompson AFB (1992) Application of particle methods to reliable identification of groundwater pollution sources. Water Resour Manag 6:15–23. doi:10.1007/BF00872184
Chadalavada S, Datta B (2008) Dynamic optimal monitoring network design for transient transport of pollutants in groundwater aquifers. Water Resour Manag 22(6):651–670
Chadalavada S, Datta B, Naidu R (2011a) Optimisation approach for pollution source identification in groundwater: An overview. Int J Environ Waste Manag 8(1):40–61
Chadalavada S, Datta B, Naidu R (2011b) Uncertainty based optimal monitoring network design for a chlorinated hydrocarbon contaminated site. Environ Monit Assess 173:929–940. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1435-2
Datta B (2002) Discussion of “identification of contaminant source location and release history in aquifers. In: Mustafa M, Aral Jiabao Guan, Morris L. Maslia (eds) Journal of hydrologic engineering, vol 7, pp 399–400
Datta B (1992) Optimal design of groundwater quality monitoring network incorporating uncertainties. In: Proceedings of the national symposium on environment, Bhabha atomic research center. Bombay, India, pp 129–131
Datta B, Chakrabarty D, Dhar A (2009a) Optimal dynamic monitoring network design and identification of unknown groundwater pollution sources. Water Resour Manag 23(10):2031–2049
Datta B, Chakrabarty D, Dhar A (2009b) Simultaneous identification of unknown groundwater pollution sources and estimation of aquifer parameters. J Hydrol 376(1–2):48–57
Datta B, Prakash O, Campbell S, Escalada G (2013) Efficient identification of unknown groundwater pollution sources using linked simulation-optimization incorporating monitoring location impact factor and frequency factor. Water Resour Manag 27(14):4959–4976
Datta BDC, Dhar A (2011) Identification of unknown groundwater pollution sources using classical optimization with linked simulation. J Hydro-Environ Res 1:25–36
Dhar A, Datta B (2010) Logic-based design of groundwater monitoring network for redundancy reduction. J Water Resour Plan Manag 13(1):88–94
Gorelick SM, Evans B, Remson I (1983) Identifying sources of groundwater pollution: an optimization approach. Water Resour Res 19(3):779–790
Jha M, Datta B (2013) Three-dimensional groundwater contamination source identification using adaptive simulated annealing. J Hydrol Eng 18(3):307–317. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000624
Kollat JB, Reed PM, Maxwel RM (2011) Many-objective groundwater monitoring network design using bias-aware ensemble Kalman filtering, evolutionary optimization, and visual analytics. Water Resour Res 47(W02529). doi:10.1029/2010WR009194
Loaiciga H, Charbeneau R, Everett L, Fogg G, Hobbs B, Rouhani S (1992) Review of groundwater quality monitoring network design. J Hydraul Eng - ASCE 118(1):11–37
Mahar PS, Datta B (1997) Optimal monitoring network and ground-water-pollution source identification. J Water Resour Plan Manag 123(4):199–207
Mahar PS, Datta B (2000) Identification of pollution sources in transient groundwater systems. Water Resour Manag 14(3):209–227
Mahar PS, Datta B (2001) Optimal identification of ground-water pollution sources and parameter estimation. J Water Resour Plan Manag 127(1):20–29
Mahinthakumar GK, Sayeed M (2005) Hybrid genetic algorithm – local search methods for solving groundwater source identification inverse problems. J Water Resour Plan Manag 131:45
Michalak AM, Kitanidis PK (2004) Estimation of historical groundwater contaminant distribution using the adjoint state method applied to geostatistical inverse modeling. Water Resour. Manag. 40(8):W08, 302
Minsker B (2003) Long-term groundwater monitoring-the state of the art. American Society of Civil Engineers stock (40678)
Pinder G, Ross J, Dokou Z (2009) Optimal search strategy for the definition of a DNAPL source. Tech rep. Strategic Environmental Research and Development Program (SERDP, US Department of Defence
Rabiner L, Juang BH (1993) Fundamentals of speech recognition, vol 103. Prentice Hall
Singh RM, Datta B (2004) Groundwater pollution source identification and simultaneous parameter estimation using pattern matching by artificial neural network. Environ Forensic 5(3):143–153
Singh RM, Datta B (2006) Identification of groundwater pollution sources using GA-based linked simulation optimization model. J Hydrol Eng 11:101
Singh RM, Datta B (2007) Artificial neural network modeling for identification of unknown pollution sources in groundwater with partially missing concentration observation data. Water Resour Manag 21:557–572. doi:10.1007/s11269-006-9029-z
Singh RM, Datta B, Jain A (2004) Identification of unknown groundwater pollution sources using artificial neural networks. J Water Resour Plan Manag 130:506
Sun AY, Painter SL, Wittmeyer GW (2006a) A constrained robust least squares approach for contaminant release history identification. Water Resour Res 42(4)(W04):414
Sun AY, Painter SL, Wittmeyer GW (2006b) A robust approach for iterative contaminant source location and release history recovery. J Contam Hydrol 88(3-4):181–196
Sun NZ (1994) Inverse problems in groundwater modeling, pp 12–37
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jha, M.K., Datta, B. Linked Simulation-Optimization based Dedicated Monitoring Network Design for Unknown Pollutant Source Identification using Dynamic Time Warping Distance. Water Resour Manage 28, 4161–4182 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0737-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0737-5