Abstract
The serious lake eutrophication has drawn increasingly attention, requiring further and deeper knowledge to understand its restriction factors of pre-disturbance conditions or historical reference conditions. In the meanwhile, Lake Nutrient Reference Conditions (LNRCs) are important indicators of eutrophication but hardly determined in the presence of eutrophication. In this research, a novel extrapolation approach was raised to determine LNRCs and its impacts on eutrophication, with the integral model of Optimal Map Recognition (OMR) and Pattern Recognition Inverse Mapping (PRIM). Validated with public data and experimental simulation, the approach was suggested as a reliable extrapolation for LNRCs determination. Further case study on Dianshan Lake and Chenghai Lake applied the novel extrapolation model in real eutrophication estimation and prediction, the results of which were in good agreement with those deduced by other techniques.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn C-Y, Park M-H, Joung S-H, Kim H-S, Jang K-Y, Oh H-M (2003) Growth inhibition of cyanobacteria by ultrasonic radiation: laboratory and enclosure studies. Environ Sci Technol 37:3031–3037
Almeida VPS, Cogo K, Tsai SM, Moon DH (2006) Colorimetric test for the monitoring of microcystins in cyanobacterial culture and environmental samples from southeast—Brazil. Braz J Microbiol 37:192–198
Andersen JH, Conley DJ, Hedal S (2004) Palaeoecology, reference conditions and classification of ecological status: the EU Water Framework Directive in practice. Mar Pollut Bull 49:283–290
Bao XH, Lu WC, Liu L, Chen NY (2003) Hyper-polyhedron model applied to molecular screening of guanidines as Na/H exchange inhibitors. Acta Pharmacol Sin 24:472–476
Bennion H, Simpson G (2011) The use of diatom records to establish reference conditions for UK lakes subject to eutrophication. J Paleolimnol 45:469–488
Bennion H, Juggins S, Anderson NJ (1996) Predicting epilimnetic phosphorus concentrations using an improved diatom-based transfer function and its application to lake eutrophication management. Environ Sci Technol 30:2004–2007
Bennion H, Fluin J, Simpson GL (2004) Assessing eutrophication and reference conditions for Scottish freshwater lochs using subfossil diatoms. J Appl Ecol 41:124–138
Bennion H, Battarbee R, Sayer C, Simpson G, Davidson T (2011a) Defining reference conditions and restoration targets for lake ecosystems using palaeolimnology: a synthesis. J Paleolimnol 45:533–544
Bennion H, Simpson G, John Anderson N, Clarke G, Dong X, Hobæk A et al (2011b) Defining ecological and chemical reference conditions and restoration targets for nine European lakes. J Paleolimnol 45:415–431
Chen N, Qin P (2000) Methods of pattern recognition application in chemical industry. Science Press, Beijing
Chen N, Li C, Qin P (1997) Chemical pattern recognition applied to materials optimal design and industry optimization. Chin Sci Bull 42:793–799
Chen N, Lu W, Chen R, Li C, Qin P (1999) Chemometric methods applied to industrial optimization and materials optimal design. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 45:329–333
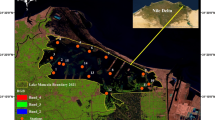
Cheng X, Li X (2008) 20-year variations of nutrients (N and P) and their impacts on algal growth in Lake Dianshan, China. J Lake Sci 20:409–419
Dodds WK, Oakes RM (2004) A technique for establishing reference nutrient concentrations across watersheds affected by humans. Limnol Oceanogr Methods 2:333–341
Dodds WK, Carney E, Angelo RT (2006) Determining ecoregional reference conditions for nutrients, Secchi depth and chlorophyll a in Kansas lakes and reservoirs. Lake Reserv Manag 22:151–159
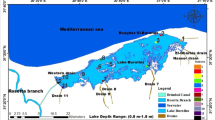
Dong Y, Jin Y, Hu J, Guan Z, He X (2010) Characteristics and origin and countermeasures of water bloom of Chenghai Lake in the winter. Environ Sci Surv 29:28–31
Du L-N, Li Y, Chen X-Y, Yang J-X (2011) Effect of eutrophication on molluscan community composition in the Lake Dianchi (China, Yunnan). Limnol Ecol Manag Inland Waters 41:213–219
Gibson G, Carlson R, Simpson J, Smeltzer E (2000) Nutrient criteria technical guidance manual: lakes and reservoirs (EPA-822-B-00-001). United States Environment Protection Agency, Washington DC
Golden RM (2001) Statistical pattern recognition. In: Neil JS, Paul BB (eds) International encyclopedia of the social & behavioral sciences. Pergamon, Oxford, pp 15040–15044
Ho G, Yun H, Pal J, Jaihie K (2006) Radial distortion refinement by inverse mapping-based extrapolation. Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition. 1, pp. 675–678
Huo SL, Zan FY, Chen Q, Xi BD, Su J, Ji DF, et al (2011) Determining reference conditions for nutrients, chlorophyll a and Secchi depth in Yungui Plateau ecoregion lakes, China. Water Environ J 26: Article first published online: 13 Nov 2011
Jin X, Tu Q (1990) Investigate specification of lake eutrophication. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing
Liu H-L (1999) A hybrid AI optimization method applied to industrial processes. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 45:101–104
Liu H, Chen Y, Chen N (1994) PCB method applied to material design—computer-aided synthesis of BiPbSrCaCuOF superconductor. J Chemom 8:439–443
Liu Y, Chen W, Li D, Huang Z, Shen Y, Liu Y (2011) Cyanobacteria-/cyanotoxin-contaminations and eutrophication status before Wuxi drinking water crisis in Lake Taihu, China. J Environ Sci 23:575–581
Paul MJ, Gerritsen J (2002) Nutrient criteria for florida lakes: a comparison of approaches. Tetra Teelmologies Inc, Tallahassee
Rodrigues LHR, Arenzon A, Raya-Rodriguez MT, Fontoura NF (2011) Algal density assessed by spectrophotometry: a calibration curve for the unicellular algae Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. J Environ Chem Ecotoxicol 3:225–228
Shi P, Ma X, Hou Y, Li Q, Zhang Z, Qu S, Chen C, Cai T, Fang X (2013) Effects of land-use and climate change on hydrological processes in the upstream of Huai River, China. Water Resour Manag 27(5):1263–1278
Singh S (2005) Pattern recognition and data mining: Third International Conference on advanced in pattern recognition, ICAPR 2005. Springer, Bath
Smith RA, Alexander RB, Schwarz GE (2003) Natural background concentrations of nutrients in streams and rivers of the conterminous United States. Environ Sci Technol 37:3039–3047
Solheim AL (2005) Reference conditions of European Lakes—indicators and methods for the water framework directive assessment of reference conditions draft version. 5
Suplee MW, Varghese A, Cleland J (2007) Developing nutrient criteria for streams: an evaluation of the frequency distribution method. J Am Water Resour Assoc 43:453–472
Vilán VJA, Fernández AJR, Nieto GPJ, Lasheras SF, Juez CFJ, Muñiz DC (2013) Support vector machines and multilayer perceptron networks used to evaluate the cyanotoxins presence from experimental cyanobacteria concentrations in the Trasona Reservoir (Northern Spain). Water Resour Manag 27(9):3457–3476
Wan GJ, Chen JA, Wu FC, Xu SQ, Bai ZG, Wan EY et al (2005) Coupling between 210Pbex and organic matter in sediments of a nutrient-enriched lake: an example from Lake Chenghai, China. Chem Geol 224:223–236
Wang M, Xu Q, Che Y, Yang K (2010) Watershed-based management of Lake Dianshan for source water protection. 2010 International Conference on Management and Service Science (MASS 2010)
Wen H, Li W, Wang J, Miao P (1998) Application of pattern inverse mapping to process parameter design of synthetic mullite. J Chin Ceram Soc 26(5):651–655
Xu J, Zhang Z, Wu Y (2004) Application of data mining method to improve the accuracy of springback prediction in sheet metal forming. J Shanghai Univ (Engl Ed) 8:348–353
Xu YF, Yang J, Ou MM, Wang YL, Jia JP (2007) Study of Microcystis aeruginosa inhibition by electrochemical method. Biochem Eng J 36:215–220
Zhao P, Tang X, Tang J, Wang C (2013) Assessing water quality of three gorges reservoir, China, over a five-year period from 2006 to 2011. Water Resour Manag 27(13):4545–4558
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thank the financial support from the Mega-projects of Science Research for National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21107067), Water Environment Improvement (No. 2009ZX07106-001), and Shanghai Leading Academic Discipline Project (No. S30109). We appreciate Chinese Research Academy of Environmental Sciences and Shanghai Research Academy of Environmental Sciences for technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Ma, C., Huo, S. et al. Establishing Reference Conditions for Lake Water Quality: A Novel Extrapolation Approach. Water Resour Manage 28, 2161–2178 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0604-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0604-4