Abstract
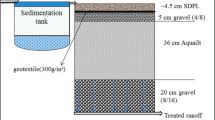
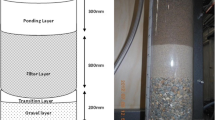
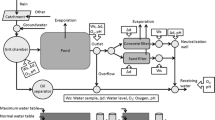
Stormwater filters are widely used in stormwater management, sometimes as standalone structures (e.g. stormwater filter beds), or as part of porous pavements, soak ways, infiltration basins and trenches. Due to the high levels of sediment present in stormwater, clogging is the main operational issue for these systems. A laboratory-based study was conducted to investigate the effect of filter bed design variables on the clogging phenomenon in non-vegetated stormwater filters with high infiltration rates. Design parameters studied include: filter media particle sizes (0.5 mm, 2 mm, 5 mm); depth of the filter bed (100 mm, 300 mm and 500 mm); and filter media packing configurations (layered or mixed). The size of filter media particles significantly impact the clogging process, as well as the overall sediment removal performance of the filters; filters with smaller particles had better sediment removal efficiency, but subsequently shorter lifespan. Deeper systems had longer lifespan compared with shallower ones, notwithstanding deeper systems removed more sediment over their life span. Having two layers of distinct sized media in the filter bed improved performance (e.g. volume of water treated; sediment removed) over the single-layered systems. However, the three-layered systems behaved similarly to two-layered systems. Mixed systems also showed improved performance, as compared with single-layered systems, and were similar to the three-layered systems. This study therefore suggests that simple modifications to a stormwater filtration system can help improve sediment removal performance and/or reduce maintenance intervals significantly, while only slightly affecting sediment removal performance.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASTM D2434-68 (2006) Standard test method for permeability of granular soils (constant head). ASTM International, West Conshohocken
ASTM D5907-09 Standard Test Method for Filterable and Non-filterable Matter in Water. American Society for Testing and Materials, West Conshohocken, PA
Bardin JP, Gautier A, Barraud S, Chocat B (2001) The purification performance of infiltration basins fitted with pre-treatment facilities: a case study. J Water Sci Technol 43(5):119–128
Barraud S, Gautier A, Bardin JP, Riou V (1999) The impact of intentional stormwater infiltration on soil and groundwater. J Water Sci Technol 39(2):185–192
Booker NA, Cooney EL, Priestley AJ (1996) Ammonia removal from sewage using natural Australian zeolite. J Water Sci Technol 34:17–24
Bouwer H (2002) Artificial recharge of groundwater: hydrogeology and engineering. J Hydrogeol 10(1):121–142
Bratieres K, Fletcher TD, Deletic A, Zinger Y (2008) Nutrient and sediment removal by stormwater biofilters: a large-scale design optimisation study. Water Res 42(14):3930–3940
Bratieres K, Schang C, Deletic A, McCarthy DT (2012) Performance of enviss™ stormwater filters: results of a laboratory trial. J Water Sci Technol 66(4):719–727
Brown R, Farrelly M (2007) Advancing urban stormwater quality management in Australia: Survey results of stakeholder perceptions of institutional drivers and barriers. Report No. 07/05, National Urban Water Governance Program, Monash University
Bureau of Meteorology (BoM), Climate Data. www.bom.gov.au
Clark S, Pitt R (1999) Evaluation of filtration media for stormwater treatment. U.S. EPA, Water Supply and Water Resources Division, National Risk Management Research Laboratory. EPA/600/R-00/016, Cincinnati, Ohio. 442 pgs
Duncan HP (1999) Urban stormwater quality: a statistical overview. Co-operative Research Centre for Catchment Hydrology. Report 99/3, Melbourne, Australia
Farizoglu B, Nuhoglu A, Yildiz E, Keskinler B (2003) The performance of pumice as a filter bed material under rapid filtration conditions. Filtr Sep 40(3):41–47
Fletcher TD, Mitchell VG, Deletic A, Ladson A (2007) Is stormwater harvesting beneficial to urban waterway flow? J Water Sci Technol 55(4):265–272
Francey M, Fletcher TD, Deletic A, Duncan HP (2010) New insights into water quality of urban stormwater in South Eastern Australia. J Environ Eng 136(4):381–390
Grant SB, Saphores JD, Feldman DL, Hamilton AJ, Fletcher TD, Cook PL, Stewardson M, Sanders BF, Levin LA, Ambrose RF, Deletic A, Brown RR, Jiang SC, Rosso D, Cooper WJ, Marusic I (2012) Taking the “waste” out of “wastewater” for human security and ecosystem sustainability. Science 337(6095):681–686
Haselbach ML (2010) Potential for clay clogging of pervious concrete under extreme conditions. J Hydrol Eng 15(1):67–69
Hatt BE, Deletic A, Fletcher TD (2008) Hydraulic and pollutant removal performance of fine media stormwater filtration systems. Environ Sci Technol 42:2535–2541
Herzig JP, Leclerc DM, Le Goff P (1970) Flow of suspensions through porous media, application to deep filtration. J Ind Eng Chem 62(5):8–35
Hillel D (1998) Environmental soil physics. Academic, San Diego, 771
Kandra HS, McCarthy D, Fletcher TD and Deletic A (2014) Assessment of clogging phenomenon in granular filter media used for stormwater treatment. J Hydrol (in press)
Knowles P, Dotro G, Nivala J, Garcia J (2011) Clogging in subsurface-flow treatment wetlands: occurrence and contributing factors. Ecol Eng 37:99–112
Lang JS, Giron JJ, Hansen AT, Trussell R, Hodges WE Jr (1993) Investigating filter performance as a function of the ratio is filter size to media size. Am Water Works Assoc 85(10):122–130
Le Coustumer S, Barraud S (2007) Long-term hydraulic and pollution retention performance of infiltration systems. J Water Sci Technol 55(4):235–243
Le Coustumer S, Fletcher TD, Deletic A, Barraud S, Poelsma P (2012) The influence of design parameters on clogging of stormwater biofilters: a large-scale column study. Water Res 46(20):6743–6752
Li H, Davis A (2008) Urban particle capture in bioretention media. I: Laboratory and field studies. J Environ Eng 134(6):409–418
Lindsey G, Roberts L, Page W (1992) Inspection and maintenance of infiltration facilities. J Soil Water Conserv 47(6):481–486
Lloyd SD, Wong THF, Iliebig T, Becker M (1998) Sediment characteristics in stormwater pollution control ponds. Proceedings of the R-12 HydraStorm ’98, 3rd International Symposium on Stormwater Management, Adelaide, Australia: 209-214
Mays CM, Hunt JR (2005) Hydrodynamic aspects of particle clogging in porous media. Environ Sci Technol 39:577–584
Mays DC (2010) Contrasting clogging in granular media filters, soils, and dead-end membranes. J Environ Eng 136(5):475–480
McIsaac R, Rowe RK (2007) Clogging of gravel drainage layers permeated with landfill leachate. ASCE J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 133(8):1026–1039
Mitchell VG, Mein RG, McMahon TA (2002) Utilising stormwater and wastewater resources in urban areas. Aust J Water Resour 1:31–43
Perez-Paricio A (2001) Integrated modelling of clogging processes in artificial groundwater recharge. Technical University of Catalonia, Barcelona
Raimbault G, Nadji D, Gauthier C (1999) Stormwater infiltration and porous material clogging. Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Urban Storm Drainage, Sydney, Australia: 1016–1024
Rodgers M, Walsh G, Healy MG (2011) Different depth sand filters for laboratory treatment of synthetic wastewater with concentrations close to measured septic tank effluent. J Environ Sci Health Part A Toxic/Hazard Subst Environ Eng 46(1):80–85
Schubert J (2002) Hydraulic aspects of riverbank filtration- field studies. J Hydrol 266:145–161
Siriwardene N, Deletic A, Fletcher TD (2007) Clogging of stormwater gravel infiltration systems and filters: insights from a laboratory study. Water Res 41:1433–1440
Tan SA, Fwa TF, Han CT (2003) Clogging evaluation of permeable bases. J Transp Eng 129(3):309–315
US Patent 4,011,067: Carey PH Jr (1977) Filter medium layered between supporting layers
US Patent 5,427,597: Osendorf RJ (1995) Layered air filter medium having improved efficiency and pleatability
Wanga S, Peng Y (2010) Natural zeolites as effective adsorbents in water and wastewater treatment. Chem Eng J 156(1):11–24
Warnaars E, Larsen AV, Jacobsen P, Mikkelsen PS (1999) Hydrologic behaviour of stormwater infiltration trenches in a central urban area during 23/4 years of operation. J Water Sci Technol 39(2):217–224
Yong CF, McCarthy DT, Deletic A (2013) Predicting physical clogging of porous and permeable pavements. J Hydrol 481:48–55
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank eWater, Monash Research Graduate School and Monash Water for Liveability for the financial support provided to undertake this research. . The authors are also thankful to the reviewers for their valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Figure I
(DOC 2756 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kandra, H.S., Deletic, A. & McCarthy, D. Assessment of Impact of Filter Design Variables on Clogging in Stormwater Filters. Water Resour Manage 28, 1873–1885 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0573-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0573-7