Abstract
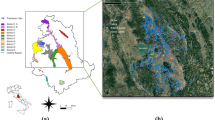
Small reservoirs play an important role in supporting the local economy in the savannah areas of Brazil and are primarily used for the provision of water for irrigation and watering livestock. Hundreds of small reservoirs have been built in the last few decades in the Preto River Basin, but efficient water management and sound planning are hindered by inadequate knowledge of the number, storage capacity and spatial distribution of reservoirs in the basin. The main reason for the lack of this information is that current methodologies for quantifying the physical parameters of reservoirs are laborious, time consuming and costly. To address this lack of data, a simple method to estimate reservoir storage volumes based on remotely sensed reservoir surface area measured with LANDSAT was developed. The method was validated with a subset of reservoirs in the Preto River Basin for which surface areas, shapes and depths were determined with ground-based survey measurements. The agreement between measured and the remotely sensed reservoir volumes was satisfactory, indicating that remotely-sensed images can be used for improved management of water in the Brazilian Savannah region. With the newly developed methods we found that the Preto River Basin’s 147 small reservoirs can store 19 × 106 m3 of water at full capacity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carvalho MSBS, Martins SPRM, Soares AMM et al. (2009) Levantamento dos espelhos d’água acima de 20 ha em todo o território brasileiro através de sensoriamento remoto, Proceedings of the remote sensing symposium held in Natal, Brazil, p.1967–1974
Frazier PS, Page KJ (2000) Water body detection and delineation with Landsat TM data. ISPRS J Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 66(12):1461–1467
Hui FM, Xu B, Huang HB, Yu Q, Gong P (2008) Modelling spatial-temporal change of Poyang Lake using multitemporal Landsat imagery. Int J Remote Sens 29:5767–5784
Kääb A, Huggel C, Fischer L, Guex S, Paul F, Roer I, Salzmann N, Schlaefli S, Schmutz K, Schneider TS, Weidmann Y (2005) Remote sensing of glacier- and permafrost-related hazards in high mountains: an overview. Nat Hazard Earth Syst Sci 5:527–554
Kuleli T (2010) Quantitative analysis of shoreline changes at the Mediterranean Coast in Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 167:387–397
Liebe J (2002) Estimation of water storage capacity and evaporation losses of small reservoirs in the Upper East Region of Ghana. Department of Geography, University of Bonn, Bonn, Diploma thesis
Liebe J, van de Giesen N, Andreini M (2005) Estimation of small reservoir storage capacities in a semi-arid environment: a case study in the Upper East region of Ghana. Phys Chem Earth 30:448–454
Liebe JR, van de Giesen N, Andreini M, Walter MT, Steenhuis TS (2009) Determining watershed response in data poor environments with remotely sensed small reservoirs as runoff gauges. Water Resour Res 45:W07410. doi:10.1029/2008WR007369
Magome J, Ishidaira H, Taheuchi K (2003) Method for satellite monitoring of water storage in reservoirs for efficient regional water management. Water Resources Systems— Hydrological Risk, Management and Development (Proceedings of symposium. HS02b held during IUOG 2003 at Sapporo, July 2003). IAHS Publ. no. 281
Meigh J (1995) The impact of small farm reservoirs on urban water supplies in Botswana. Nat Resour Forum 19(1):71–83
Mendonça AF, Pires ACB, Barros JGC (1994) Pseudosinkhole occurrences in Brasilia, Brazil. Environ Geol 23:36–40
Mialhe F, Gunnell Y, Mering C (2008) Synoptic assessment of water resource variability in reservoirs by remote sensing: general approach and application to the runoff harvesting systems of south India. Water Resour Res 44:W05411
Nash JE, Suttcliffe JV (1970) River flow forecasting through conceptual models. 1. A discussion of principles. J Hydrol 10:282–290
Reis S, Yilmaz HM (2008) Temporal monitoring of water level changes in Seyfe Lake using remote sensing. Hydrol Process 22:4448–4454
Rodrigues LN, Sano EE, Azevedo JA, Silva EM (2007) Distribuição espacial e área máxima do espelho d’água de pequenas barragens de terra na Bacia do Rio Preto. Espaço e Geografia (UnB) 10:101–122
Sawunyama T, Senzanje A, Mhizha A (2006) Estimation of small reservoir storage capacities in Limpopo River Basin using geographical information systems (GIS) and remotely sensed surface areas: case of Mzingwane catchment. Phys Chem Earth 31:935–943
Acknowledgments
The presented research was carried out as part of the Small Reservoir Project. We gratefully acknowledge financial support of Advisory Service on Agricultural Research for Development (BEAF) through the Challenge Program on Water and Food.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodrigues, L.N., Sano, E.E., Steenhuis, T.S. et al. Estimation of Small Reservoir Storage Capacities with Remote Sensing in the Brazilian Savannah Region. Water Resour Manage 26, 873–882 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-011-9941-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-011-9941-8