Abstract
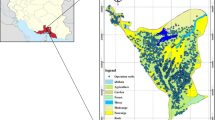
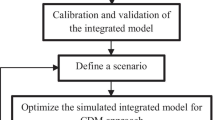
Groundwater is the unique source of fresh water in El-Farafra Oasis, western desert, Egypt. The increasing demand of groundwater in El-Farafra Oasis has resulted in an indiscriminate exploitation of this source causing environmental hazards such as decline of groundwater levels and well interference. In this paper, the study of these problems is conducted. The methodology introduced in this paper includes application of mathematical and Genetic Algorithm (GA) techniques. This situation has led to a growing realization that through good management, use of groundwater can be made more productive and sustainable. The proposed model of optimization is based on the combination of the MODFLOW with GA. The performance of the proposed model is tested on groundwater management problem (maximization of total pumping rate from an aquifer at steady-state). The results show that the GA solutions nearly agree with the solutions of other methods of previous works. Thus, it can be used to solve the management problems in groundwater. This model is used to develop the optimal pumping rate and number of wells in El-Farafra Oasis under different scenarios. The results show that under the current situation, the optimal pumping rate is 183023 m3/day. The second scenario assumes an increase of number of wells by 20%, the optimal rate reaches 220016 m3/day. The third scenario proposes pumping rate 254484 m3/day which equalizes an increase in the cultivated area by 4000 acres, the optimal rate reaches 258007 m3/day.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel Atti AA (2002) Hydrogeological studies on the Nubia Sandstone aquifer in Bahariya and Farafra depressions, Western Desert, Egypt, Ph. D. Thesis submitted to Geology Depart., Faculty of Science, Ain Shams University
Ali MT (2004) Evaluation of groundwater resources of El Sheikh Marzouq area at Farafra Oasis in the Desert of Egypt. PH. D. Thesis, Geol. Dep. Fac. of Sci. Menoufiya Univ., Egypt, 238 p
Ayvaz MT (2009) Application of harmony search algorithm to the solution of groundwater management models. Adv Water Resour 32:916–924
Bear J (1979) Hydraulics of groundwater. McGraw-Hill, New York, 569p
Desert Research Center (DRC) (2005) Evaluation of crop unit in El wadi El Gadid district, unpublished internal report submitted to MWRI—Desert Research center—112 p
Ebraheem AM, Riad S, Wycisk P, Seif El-Nasr AM (2002) Simulation of impact of present and future groundwater extraction from the non-replenished Nubian Sandstone aquifer in southeast Egypt. J Environ Geol 43:188–196
El Ramly IM (1964) The use of the fissured limestone in locating groundwater resources and its application to Farafra Oasis, Western Desert, U.A. R. Arab Society for Min. & Petrol. Assoc. Bull. V. XIX, 15 p
El Sabri MA, El Sheikh AE (2009) Groundwater sustainability of the post nubian sandstone aquifer in Farafra Oasis, Western Desert, Egypt. Journal of Science, Faculty of Science, Assut University 3:64–72
Hamad MH (2004) Subsurface geological, hydrogeological and hydrogeochemical studies on the inter-stratal water in Farafra oasis, western Desert, A. r. Egypt, M. Sc. Thesis submitted to Geology Depart., Faculty of Science, Cairo University
Guan J, Kentel E, Aral MM (2008) Genetic algorithm for constrained optimization models and its application in groundwater resources management. J Water Resour Plann Manag 134(1):64–72
Liu Q, Zou L, Li (2002) The application of genetic algorithms in groundwater management. World Geology 21(2):145–149
Mahinthakumar G, Sayeed M (2005) Hybrid genetic algorthim-local search methods for solving groundwater source indentification inverse problems. J Water Resour Plann Manag 131(1)
Mckinney DC, Lin M (1994) Genetic algorithm solution of groundwater management models. Water Resour Res 30(6):1897–1906
Singh RM, Datta B (2006) Identification of groundwater pollution sources using GA—based linked simulation optimization model. J Hydrolog Eng 11, No. 2(12)
Thorweihe U (1990) Das Groundwsser der Ostsahara. Die Geowissenschaten 8:211–219
Wang M, Zheng C (1998) Groundwater management optimization using genetic algorithms and simulated annealing: formulation and comparison. J Am Water Resour Assoc 34(3):519–530
Wu J, Zhu X (2006) Using the shuffled complex evolution global optimization method to solve groundwater management models. Lecture Note Comput Sci 3841:986–995
Wu J, Zhu X, Liu J (1999) Using genetic algorithm based simulated annealing penalty function to solve groundwater management model. Sci China Ser E: Technol Sci 42(5):521–529
Yan T, Wu J, Xue Y (2003) A comparison of genetic algorithm and trial-and-error approach in solving the hydrogeologic inverse problem. In: Proceedings of the international Symposium on Water Resources and the Urban Environment. China Environment Science Press, Beijing, pp 137–141
Yao L, Li J, Li Z (2003) Parameter identification of groundwater flow numerical modeling by means of improved genetic algorithm. J Hydraul Eng 34(12):40–46
Zaghloul EA (1983) Geology of Abu Minqar-Farafra-Ain Dalla strech, Western Desert, Egypt. Ph. D. Thesis, Geology Dep., Fac. of Sci., Cairo Univ., Egypt
Zhu X, Wu J, Ye S, Zhao J, Wu M (2003) Evaluation of groundwater resource in deep aquifers of the Yangtze Delta (south of the Yangtze Delta). In: Proceedings of the international Symposium on Water Resources and the Urban Environment. China Environment Science Press, Beijing, pp 467–473
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank to Dr. Emad Elbeltagi Associate Professor of Construction Management Dept. of Structural Eng., Mansoura University, Egypt, for his enormous help and fruitful advice in Genetic Algorithm part.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moharram, S.H., Gad, M.I., Saafan, T.A. et al. Optimal Groundwater Management Using Genetic Algorithm in El-Farafra Oasis, Western Desert, Egypt. Water Resour Manage 26, 927–948 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-011-9865-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-011-9865-3