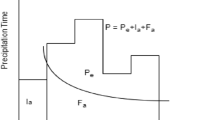
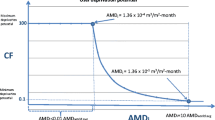
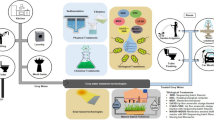
Abstract
Rainwater collected from residential roofs and greywater generated from domestic uses except toilets are viewed as possible substitutes for high grade water sources which supply nonpotable indoor uses and irrigation in Australia. This paper searches for alternatives by adopting roofwater and greywater in residential envelope as per Australian water standards. A water balance model Aquacycle was applied to determine storage capacities and to evaluate the percentage reduction in water supplying, stormwater run-off and wastewater disposal, as well as volume of rainwater use and greywater reuse. This study provides the results of greywater recycling, which contributes to the greater saving of mains water supply than rainwater use, and which reduces more than half of the wastewater to receiving waters in the rural township of Cranbrook, Western Australia. The results of this study provide greywater usage (maximum reduction 32.5%) more significantly reduces scheme water supply than rainwater harvesting (maximum reduction 25.1%). Use of greywater on individual residential lots has the dramatic effect for drainage system by reduction approximately 54.1% or 88.1 m3/lot/year. The results of rainwater use analysis show explicitly that rainwater tanks are much more effective in intercepting roof runoff, with the maximum stormwater reduction 48.1% or 68.3 m3/lot/year. This research endeavours to offer a typical paradigm for an integrated water system in the rural residential sectors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Jayyousi OR (2003) Greywater reuse: towards sustainable water management. Desalination 156(1–3):181–192. doi:10.1016/S0011-9164(03)00340-0
Brown R (2003) Institutionalisation of integrated urban water management: multiple-case analysis of local management reform across metropolitan Sydney. PhD thesis, University of New South Wales
Chang MB, Lin NH, Lee HM, Lo YC (1997) Rainwater contamination and sources in Taoyuan county, Taiwan. J Environ Sci Health Part A, Environ Sci Eng Toxic Hazard Substance Control 32(6):1641–1653
Christova-Boal D, Eden RE, McFarlane S (1996) As investigation into greywater reuse for urban residential properties. Desalination 106(1–3):391–397. doi:10.1016/0011-9164(96)00134-8
Coombes P (2003) Rainwatr tanks revisited: new opportunities for urban water cycle management. PhD thesis, University of Newcastle
Coombes P (2007) The effect of selection of time steps and average assumptions on the continuous simulation of rainwater harvesting strategies. Water Sci Technol 55(4):125–133. doi:10.2166/wst.2007.102
Dixon A (2000) Computer simulation of domestic water re-use systems: greywater and rainwater in combination. PhD thesis, University of London
Eriksson E, Auffarth K, Henze M, Ledin A (2002) Characteristics of grey wastewater. Urban Water 4(1):85–104. doi:10.1016/S1462-0758(01)00064-4
European Environment Agency (EEA) (2003) Indicator fact sheet. Water use in urban area (WQ02e). EEA, Copenhagen
Friedler E (2006) Economic feasibility of on-site greywater reuse in multi-storey buildings. Desalination 190(1–3):221–234. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2005.10.007
Ghisi E, Ferreira D (2007) Potential for potable water saving by using rainwater and greywater in a multi-storey residential building in southern Brazil. Build Environ 42(7):2512–2522. doi:10.1016/j.buildenv.2006.07.019
Grant A, Sharma A, Mitchell G, Grant T, Pamminger F (2006) Designing for sustainable water and nutrient outcomes in urban developments in Melbourne. Aust J Water Resour 10(3):251–260
Herrmann T (1999) Rainwater utilisation in Germany: efficiency, dimensioning, hydraulic and environmental aspects. Urban Water 1(4):307–316. doi:10.1016/S1462-0758(00)00024-8
Herrmann T, Hasse K (1997) Ways to get water: rainwater utilization or long-distance water supply? A holistic assessment. Water Sci Technol 36(8–9):313–318. doi:10.1016/S0273-1223(97)00580-5
Jeffrey SJ, Carter JO, Moodie KB, Beswick AR (2001) Using spatial interpolation to construct a comprehensive archive of Australian climate data. Environ Model Softw 16(4):309–330. doi:10.1016/S1364-8152(01)00008-1
Lazarova V, Hills S, Birks R (2003) Using recycled water for non-potable, urban uses: a review with particular reference to toilet flushing. Water Sci Technol 3(4):69–77
Loh M, Coghlan P (2003) Domestic water use study in Perth, Western Australia 1998–2001. Water Corporation, Perth
Madungwe E, Sakuringwa S (2007) Greywater reuse: a strategy for water demand management in Harare? Phys Chem Earth Parts ABC 32(15–18):1231–1236. doi:10.1016/j.pce.2007.07.015
Mitchell VG, Mein RG, McMahon TA (2001) Modelling the urban water cycle. Environ Model Softw 16(7):615–629. doi:10.1016/S1364-8152(01)00029-9
Nolde E (1999) Greywater reuse systems for toilet flushing in multi-storey buildings—over ten years experience in Berlin. Urban Water 1(4):275–284. doi:10.1016/S1462-0758(00)00023-6
Racoviceanu A (2005) In search of environmentally sustainable urban water supply systems. Ms thesis, University of Toronto
Wei H, Li JL, Liang TG (2005) Study on the estimation of precipitation resources for rainwater harvesting agriculture in semi-arid land of China. Agric Water Manage 71(1):33–45. doi:10.1016/j.agwat.2004.07.002
Winward GP, Avery LM, Williams RF, Pidou M, Jeffrey P (2007) A study of the microbial quality of grey water and an evaluation of treatment technoligies for reuse. Ecol Eng 32(2):187–197. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2007.11.001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Grant, A., Sharma, A. et al. Alternative Water Resources for Rural Residential Development in Western Australia. Water Resour Manage 24, 25–36 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-009-9435-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-009-9435-0