Abstract
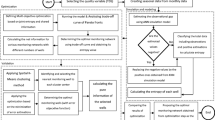
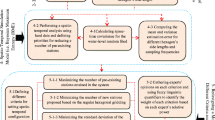
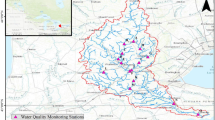
Selection of the number and location of groundwater quality monitoring wells may require the consideration of different aspects such as: monitoring objectives, temporal frequency of monitoring, and monitoring costs. These aspects were examined using observations of groundwater quality variables made twice a year in 124 wells in the northern part of the Gaza Strip, where groundwater is of the best quality. Considering these features the groundwater quality monitoring network was assessed and redesigned using entropy. The assessment procedure was based on expressing transinformation as a function of distance between wells. It was found that the number and location of groundwater quality monitoring wells varied if these aspects were embedded in the assessment and redesign procedure.
Article PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
References
Andricevic R (1990) Cost effective network design for groundwater flow monitoring. Stoch Hydrol Hydraul 4(1):27–41
ASCE (1990) Review of geostatistics in geohydrology, II: applications. J Hydraul Eng ASCE 116(5):633–658
Bueso MC, Angulo JM, Alonso FJ (1998) A state-space model approach to optimum spatial sampling design based on entropy. Environ Ecol Stat 5:29–44
Caselton WF, Zidek JV (1991) Quality data networks that minimize entropy. In: Walden AT, Guttorp P, Arlond E (eds) Statistics in the environmental and earth sciences. Wiley, Toronto, pp 11–38
Cox DD, Cox LH, Ensor KB (1997) Spatial sampling and the environment: some issues and directions. Environ Ecol Stat 4(3):219–233
Cressie NC (1990) Statistics for spatial data, revised edn. Wiley, New York, 900 pp
Gokhale D, Kullback S (1978) The information in contingency tables. Marcel Dekker, New York
Harmancioglu NB, Alpaslan N (1992) Water quality monitoring network design. Water Resour Bull 28(1):179–192
Loaiciga H (1989) An optimisation approach for groundwater quality monitoring network design. Water Resour Res 25(8):1771–1782
Loaiciga H, Charbeneau JR, Everett GL, Fogg EG, Hobbs FB, Rouhani S (1992) Review of groundwater quality monitoring network design. J Hydraul Eng ASCE 118(1):11–37
Mahar PS, Datta B (1997) Optimal monitoring and groundwater pollution source identification. J Water Resour Plan Manage ASCE 23(4):199–207
Metcalf & Eddy (2000) Costal aquifer management program, final report: modelling of Gaza Strip aquifer. The program is funded by US Agency for International Development (USAID) and owned by the Palestinian Water Authority (PWA), Gaza, Palestine
Meyer PD, Valcchoni AJ, Eheart JW (1994) Monitoring network design to provide initial detection of groundwater contamination. Water Resour Res 30(9):2647–2659
Mogheir Y (2003) Assessment and redesign of groundwater quality monitoring networks using the entropy theory – Gaza Strip case study. Ph.D. thesis, University of Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal, 319 pp
Mogheir Y, Singh VP (2002) Application of information theory to groundwater quality monitoring networks. Water Resour Manag 16(1):37–49
Mogheir Y, de Lima JLMP, Singh VP (2003a) Spatial structure assessment of groundwater quality variables based on the entropy theory. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 7(5):707–721
Mogheir Y, de Lima JLMP, Singh VP (2003b) Applying the entropy theory for describing the spatial structure of groundwater regionalized variables (EC and Chloride). In: Neves MV, Neves ACV (eds) Environment 2010: situation and perspectives for the European Union. University of Porto, Portugal, pp 1–6
Mogheir Y, Singh VP, de Lima JLMP (2003c) Redesigning the Gaza Strip groundwater quality monitoring network using entropy. In: Singh VP, Yadava RY (eds) Groundwater pollution. Allied, New Delhi, pp 315–331
Mogheir Y, de Lima JLMP, Singh VP (2004) Characterising the spatial variability of groundwater quality using the entropy theory: II. Case study from Gaza Strip. Hydrol Process 18(13):2579–2590
Motulsky HJ (1999) Analysing data with GraphPad Prism. GraphPad Software, San Diego. www.graphpad.com
Patrick R, Misker B, Valocchi AJ (2000) Cost-effective long-term groundwater monitoring design using a genetic algorithm and global interpolation. Water Resour Res 36(12):3731–3741
Quimpo RG, Yang JY (1970) Sampling consideration in stream discharge and temperature measurements. Water Resour Res 6:1771–1774
Radford PJ, West J (1986) Models to minimize monitoring. Water Resour 20:1059–1066
Rodriguez-Iturbe I, Mejia JM (1974) The design of rainfall networks in time and space. Water Resour Res 10:713–728
Rouhani S, Hall TJ (1988) Geostatistical schemes for groundwater sampling. J Hydrol 103:85–102
Sanders TG, Adrian DD (1978) Sampling frequency for river quality monitoring. Water Resour Res 14:569–576
Stein A, Van Groenigen JM, Jeger MJ, Hoosbeek MR (1998) Space-time statistics for environmental and agricultural related phenomena. Environ Ecol Stat 5(2):155–172
Yang Y, Burn D (1994) An entropy approach to data collection network design. J Hydrol 157:307–324
Zhou Y (1996) Sampling frequency for monitoring the actual state of groundwater systems. J Hydrol 180:301–318
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/2.0), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
About this article
Cite this article
Mogheir, Y., de Lima, J.L.M.P. & Singh, V.P. Entropy and Multi-Objective Based Approach for Groundwater Quality Monitoring Network Assessment and Redesign. Water Resour Manage 23, 1603–1620 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-008-9343-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-008-9343-8