Abstract
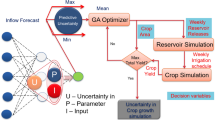
In this study, application of Genetic Algorithms (GA) is demonstrated to optimize reservoir release policies to meet irrigation demand and storage requirements. As it is commonly recognized that accuracy of inflow forecast and operating time horizon affects the optimal policies, a trial-and-error approach is suggested to identify the appropriate trade-off between forecast accuracy and operating horizon. The flexibility offered by GA to set up and evaluate objective functions is exploited towards this end. The results are also compared with Linear Programming (LP) model. It is concluded that forecasts models of high accuracy are desirable, particularly when the system is to be operated for periods of high demand. In such cases, the optimization with longer time horizon ensures achievement of the objective more uniformly over the period of operation. The performance of GA is found to be better than LP, when forecast model of higher accuracy and longer period of operating horizon are considered for optimization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen YM (1997) Management of water resources using improved genetic algorithms. J Comp Electro Agri 18:117–127
Gentry RW, Camp CV, Anderson JL (2001) Use of GA to determine areas of accretion tosemi confined aquifer. J Hyd Eng ASCE 127(9):738–746
Georgakakos AP (1989) The value of streamflow forecasting in reservoir operation.Water Res Bull 25(4):789–800
Huang C, Mayer AS (1997) Pump-and-treat optimization using well locations andpumping rates as decision variables. Water Resour Res 33(5):1001–1012
Kuo SF, Markley GP, Liu CW (2000) Decision support for irrigation project planningusing a genetic algorithms. Agri Water Mgt 45:243–266
Mohan S (1997) Parameter estimation of nonlinear Muskingum models using geneticalgorithm. J Hyd Eng ASCE 123(2):137–142
Morshed J, Kaluarachchi JJ (1998) Application of artificial neural network andgenetic algorithm in flow and transport simulations. Adv Water Resour 22(2):145–158
Oliviera R, Loucks DP (1997) Operating rules for multireservoir systems. WaterResour Res 33(4):839–852
Reddy SL (1996) Optimal land grading based on genetic algorithms. J Irrig Drain Eng ASCE 122:183–188
Reis LFR, Chaudhry FH (1997) Optimal location of control valves in pipe networks bygenetic algorithm. J Water Resour Mgt 123(6):317–320
Sharif M, Wardlaw R (2000) Multireservoir systems optimization using geneticalgorithms: case study. J Comp Civil Eng ASCE 14(4):255–263
Sivapragasam C, Vincent P, Vasudevan G (2006) GP model for forecast of short andnoisy data. J Hyd Proces (in press)
Srinivasa Raju K, Nagesh Kumar D (2004) Irrigation planning using geneticalgorithms. Water Res Mgt 18:163–176
Van Vuuren SJ (2002) Application of genetic algorithms — determination of theoptimal pipe diameters. Water SA 28(2):217–226
Wardlaw R, Sharif M (1999) Evaluation of genetic algorithms for optimal reservoirsystem operation. J Water Resour Plann Mgt ASCE 125(1):25–33
Wardlaw R, Bhaktikul K (2001) Application of a genetic algorithm for waterallocation in an irrigation system. Irrig Drain 50:159–170
Yagi S, Shiba S (1999) Application of genetic algorithms and fuzzy control to acombined sewer pumping station. Water Sci Technol 39(9):217–224
Yoon JH, Shoemaker CA (2001) An improved real-coded GA for groundwaterbioremediation. J Comp Civil Eng ASCE 15:224–231
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sivapragasam, C., Vasudevan, G. & Vincent, P. Effect of inflow forecast accuracy and operating time horizon in optimizing irrigation releases. Water Resour Manage 21, 933–945 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-006-9065-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-006-9065-8