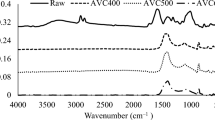
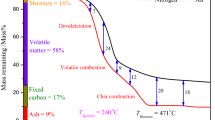
Abstract
Two different waste-derived by-products were examined and compared. Based on the thermogravimetric tests performed, it was proved that their decomposition occurs in two weight loss steps represented by two shoulders in the derivative thermogravimetric curves. The first shoulder is attributed to the devolatilisation of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin and the second one to the plastic fraction of the waste. Similarities in the degradation behaviour were observed for both wastes, despite of their different origin. Increased plastic fractions resulted in slightly higher conversions and lower pyrolysis rates. Enhanced lignocellulosic fractions led to higher rates during combustion. The lignocellulosic fraction was increased proportionally to the inorganic residue that remained after combustion. A wide variation of weight losses was attained even in refuse-derived fuel (RDF) samples of the same origin, whilst stronger deviations were observed in the decomposition of the plastic fraction. The independent parallel, first-order, reactions model was elaborated for the kinetic analysis of the pyrolysis results. The thermal degradation of the RDF samples was modelled assuming four parallel reactions corresponding to the devolatilisation of cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin and plastics. Increased activation energies were calculated for the plastics fraction, whilst lignin presented the lowest contribution in the pyrolysis of the samples. Generally, both RDF samples presented similar kinetic constants despite their heterogeneity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caballero, J. A., Font, R., & Esperanza, M. M. (1998). Kinetics of thermal decomposition of tannery waste. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 47, 165–181.
Cozzani, V., Petarca, L., & Tognotti, L. (1995a). Devolatilisation and pyrolysis of refuse derived fuels: characterization and kinetic modelling by a thermogravimetric and calorimetric approach. Fuel, 74(6), 903–912.
Cozzani, V., Nicollela, C., Petarca, L., Rovatti, M., & Tognotti, L. (1995b). A fundamental study on conventional pyrolysis of a refuse-derived fuel. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 34, 2006–2020.
Cozzani, V., Nicollela, C., Rovatti, M., & Tognotti, L. (1996). Modeling and experimental verification of physical and chemical processes during pyrolysis of a refuse-derived fuel. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 35, 90–98.
David, C., Salvador, S., Dirion, J. L., & Quintard, M. (2003). Determination of a reaction scheme for cardboard thermal degradation using thermal gravimetric analysis. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 67, 307–323.
European Commission Directorate General for Environment. (2003). Refusal derived fuels current situation and perspectives. (B4-3040/2000/306517/MAR/E3), Final report.
Heikkinen, J. M., Hordijk, J. C., de Jong, W., & Spliethoff, H. (2004). Thermogravimetry as a tool to classify waste components to be used for energy generation. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 71, 883–900.
Kathiravale, S., Yunus, M. N. M., Sopian, K., Samsuddin, A. H., & Rahman, R. A. (2003). Modeling the heating value of municipal solid waste. Fuel, 82, 1119–1125.
Lin, K.-S., Wang, H. P., Liu, S.-H., Chang, N.-B., Huang, Y.-J., & Wang, H.-C. (1999). Pyrolysis kinetics of refuse-derived fuel. Fuel Processing Technology, 60, 103–110.
Ohman, M., Nordin, A., Lundholm, K., & Bostrom, D. (2003). Ash transformations during combustion of meat-, bonemeal, and RDF in a (bench-scale) fluidized bed combustor. Energy Fuels, 17, 1153–1159.
Skodras, G., Grammelis, P., Basinas, P., Kakaras, E., & Sakellaropoulos, G. (2006). Pyrolysis and combustion characteristics of biomass and waste-derived feedstock. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 45, 3791–3799.
Skodras, G., Grammelis, P., & Basinas, P. (2007). Pyrolysis and combustion behaviour of coal-MBM blends. Bioresource Technology, 98, 1–8.
Sorum, L., Gronli, M. G., & Hustad, J. E. (2001). Pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of municipal solid wastes. Fuel, 80, 1217–1227.
Unapumnuk, K., Keener, C. T., Khang, S.-J., & Lu, M. (2006). Pyrolysis behaviour of tire derived fuels at different temperatures and heating rates. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 56(5), 618–627.
Williams, P.-T., & Besler, S. (1993) The pyrolysis of rice husks in a thermogravimetric analyser and static bath reactor. Fuel, 72, 151–159.
Wu, C.-H., Chang, C.-Y., & Lin, J.-P. (1997a). Pyrolysis kinetics of paper mixtures in municipal solid waste. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 68, 65–74.
Wu, C.-H., Chang, C.-Y., Lin, J.-P., & Hwang, J.-Y. (1997b). Thermal treatment of coated printing and writing paper is MSW: pyrolysis kinetics. Fuel, 76(12), 1151–1157.
Zheng, G., & Kozinski, J. A. (2000). Thermal events occurring during the combustion of biomass residue. Fuel, 79, 181–192.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skodras, G., Grammelis, P., Basinas, P. et al. A Thermochemical Conversion Study on the Combustion of Residue-Derived Fuels. Water Air Soil Pollut: Focus 9, 151–157 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11267-008-9197-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11267-008-9197-3