Abstract
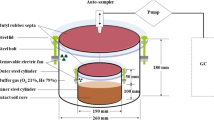
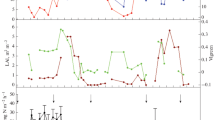
Despite many studies of the N2O emission, there is a lack of knowledge on the role of subsoil for N2O emission, particularly in sandy soils. To obtain insight into the entrapment, diffusion, convection and ebullition of N2O in the soil, the N2O concentration in the soil atmosphere was measured over a period of 1 year in 4 lysimeters (agricultural soil monoliths of 1 m2 × 2 m) at 30, 50, 80, 155, and 190 cm depth with altogether 86 gas probes. Additionally the N2O emission into the atmosphere was measured in 20 closed chambers at the soil surface. Concurrently the soil temperature and soil water content were recorded in order to quantify their effects on the fate of N2O in the soil. Results of the continuous measurements between January and December 2006 were: N2O concentrations were highest in the deeper soil; maximum concentration was found at a depth of 80 cm, where the water content was high and the gas transport reduced. The highest N2O concentration was recorded after ‘special events’ like snowmelt, heavy rain, fertilization, and grubbing. The combination of fertilization and heavy rain led to an increase of up to 2,700 ppb in the subsoil.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama, H., Tsuruta, H., & Watanabe, T. (2000). N2O and NO emissions from soils after the application of different chemical fertilizers. Chemosphere Global Change Science, 2, 313–320.
Ball, B. C., Parker, J. P., & Scott, A. (1999). Soil and residue management effects on cropping conditions and nitrous oxide fluxes under controlled traffic in Scotland; 2. Nitrous oxide, soil N status and weather. Soil and Tillage Research, 52, 191–201.
Brumme, R., Borken, W., & Finke, S. (1999). Hierarchical control on nitrous oxide emission in forest ecosystems. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 13, 1137–1148.
Butterbach-Bahl, K., Gasche, R., Willibald, G., & Papen, H. (2002). Exchange of N-gases at the Hoglwald Forest – A summary. Plant Soil, 240, 117–123.
Castle, K., Arah, J. R. M., & Vinten, A. J. A. (1998). Denitrification in intact subsoil cores. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 28, 12–18.
Chatskikh, D., Olesen, J. E., Berntsen, J., Regina, K., & Yamulki, S. (2005). Simulation of effects of soils, climate and management on N2O emission from grasslands. Biogeochemistry, 76, 395–419.
Clough, T. J., Stevens, R. J., Laughlin, R. J., Sherlock, R. R., & Cameron, K. C. (2001). Transformations of inorganic-N in soil leachate under differing storage conditions. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 33, 1473–1480.
Crutzen, P. J. (1981). Atmospheric chemical processes of the oxides of nitrogen, including nitrous oxide. In C. C. Delwiche (Ed.) Denitrification, nitrification and atmospheric nitrous oxide (pp. 17–45). New York: Wiley.
Flessa, H., Potthoff, M., & Loftfield, N. (2002). Greenhouse estimates of CO2 and N2O emissions following surface application of grass mulch: Importance of indigenous microflora of mulch. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 34, 875–879.
Flessa, H., Wild, U., Klemisch, M., & Pfadenhauer, J. (1998). Nitrous oxide and methane fluxes from organic soils under agriculture. European Journal of Soil Science, 49, 327–335.
Gebauer, G., Hahn, G., Rodenkirchen, H., & Zuleger, M. (1998). Effects of acid irrigation and liming on nitrate reduction and nitrate content of Picea abies (L.) Karst. and Oxalis acetosella L. Plant Soil, 199, 59–70.
Grandy, S. A., & Robertson, P. G. (2006). Initial cultivation of a temperate-region soil immediately accelerates aggregate turnover and CO2 and N2O fluxes. Global Change Biology, 12, 1507–1520.
Granli, T., & Bockman, O. C. (1994). Nitrous oxide from agriculture. Norwegian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 12, 7–127.
Griffiths, B. S. (1994). Microbial-feeding nematodes and protozoa in soil: Their effects on microbial activity and nitrogen mineralization in decomposition hotspots and the rhizosphere. Plant and Soil, 164, 25–33.
Guo, H., Li, G., Zhang, X., Yan, F., Zhang, D., & Lu, C. (2003). Spatial research of denitrification and nitrification potential of agricultural soils in relation to fertilization practice. Proceedings of the 2003 International Symposium on Water Resources and the Urban Environment (pp. 179–185).
Heincke, M., & Kaupenjohann, M. (1999). Effects of soil solution on the dynamics of N2O emissions: A review. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 55, 133–157.
Hesselsøe, M., Pedersen, A., Bundgaard, K., Brandt, K. K., & Sørensen, J. (2001). Development of nitrification hot-spots around degrading red clover (Trifolium pratense) leaves in soil. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 33, 238–245.
Hosen, Y., Tsuruta, H., & Minami, K. (2000). Effects of the depth of NO and N2O productions in soil on their emission rates to the atmosphere: Analysis by a simulation model. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 57, 83–98.
Huetsch, B. W., Wang, X., Feng, K., Yan, F., & Schubert, S. (1999). Nitrous oxide emission as affected by changes in soil water content and nitrogen fertilization. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 162, 607–613.
IPCC (1996). Climate change (1995). The science of climate change. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
IPCC (2001). Climate Change (2001). The scientific basis. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Kamp, T., Steindl, H., Hantschel, R. E., Beese, F., & Munch, J. C. (1998). Nitrous oxide emissions from a fallow and wheat field as affected by increased soil temperatures. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 27, 307–314.
Kühn, S. S. (2004). Bedeutung der leistung mikrobieller lebensgemeinschaften beim umsatz und abbau von isoproturon in böden und möglichkeiten zur steuerung des in-situ-pestizidabbaus. Institut für Bodenökologie, GSF-Forschungszentrum für Umwelt und Gesundheit, Technischen Universität München, 183 pp.
Loftfield, N., Flessa, H., Augustin, J., & Beese, F. (1997). Automated gas chromatographic system for rapid analysis of the atmospheric trace gases methane, carbon dioxide, and nitrous oxide. Journal of Environmental Quality, 26, 560–564.
Luo, J., Tillman, R. W., White, R. E., & Ball, P. R. (1998). Variation in denitrification activity with soil depth under pasture. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 30, 897–903.
Mergel, A., Kloos, K., & Bothe, H. (2001). Seasonal fluctuations in the population of denitrifying and N2-fixing bacteria in an acid soil of a Norway spruce forest. Plant and Soil, 230, 145–160.
Potter, C. S., & Klooster, S. A. (1998). Interannual variability in soil trace gas (CO2, N2O, NO) fluxes and analysis of controllers on regional to global scales. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 12, 621–635.
Reth, S., Hentschel, K., Drössler, M., & Falge, E. (2005). DenNit – Experimental analysis and modelling of soil N2O efflux in response on changes of soil water content, soil temperature, soil pH, nutrient availability and the time after rain event. Plant Soil, 272, 349–363.
Rudaz, A. O., Walti, E., Kyburz, G., Lehmann, P., & Fuhrer, J. (1999). Temporal variation in N2O and N2 fluxes from a permanent pasture in Switzerland in relation to management, soil water content and soil temperature. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 73, 83–91.
Ruser, R., Flessa, H., Russow, R., Schmidt, G., Buegger, F., & Munch, J. C. (2006). Emission of N2O, N2 and CO2 from soil fertilized with nitrate: Effect of compaction, soil moisture and rewetting. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 38, 263–274.
Ruser, R., Flessa, H., Schilling, R., Beese, F., & Munch, J. C. (2001). Effect of crop-specific field management and N fertilization on N2O emissions from a fine–loamy soil. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 59, 177–191.
Russow, R., Knappe, S., & Neue, H.-U. (2002). The N2O content of soil air at different depths as well as its related content in and transport by seepage in lysimeter soils. In Non-CO2 greenhouse gases: Scientific understanding, control options and policy aspects (pp. 151–152). Rotterdam, The Netherlands: Millpress.
Sanchez, L., Diez, J. A., Vallejo, A., & Cartagena, M. C. (2001). Denitrification losses from irrigated crops in central Spain. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 33, 1201–1209.
Schürmann, A., Mohn, J., & Bachofen, R. (2002). N2O emissions from snow-covered soils in the Swiss Alps. Tellus B, 54, 134–142.
Sharma, S., Szele, Z., Schilling, R., Munch, J. C., & Schloter, M. (2006). Influence of freeze-thaw stress on the structure and function of microbial communities and denitrifying populations in soil. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72, 2148–2154.
Silgram, M., Waring, R., Anthony, S., & Webb, J. (2001). Intercomparison of national & IPCC methods for estimating N loss from agricultural land. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 60, 189–195.
Šimek, M., Elhottova, D., Klimes, F., & Hopkins, D. W. (2004). Emissions of N2O and CO2, denitrification measurements and soil properties in red clover and ryegrass stands. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 36, 9–21.
Stevens, R. J., & Laughlin, R. J. (2001). Cattle slurry affects nitrous oxide and dinitrogen emissions from fertilizer nitrate. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 65, 1307–1314.
Stevens, R. J., & Laughlin, R. J. (2002). Cattle slurry applied before fertilizer nitrate lowers nitrous oxide and dinitrogen emissions. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 66, 647–652.
Teepe, R., Brumme, R., & Beese, F. (2000). Nitrous oxide emissions from frozen soils under agricultural, fallow and forest land. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 32, 1807–1810.
UNFCCC (1992). Kyoto protocol to the United Nations Framework Convention on climate change. Bonn: UNFCCC Sekretariat.
Van Groenigen, J. W., Georgius, P. J., Van Kessel, C., Hummelink, E. W. J., Velthof, G. L., & Zwart, K. B. (2005). Subsoil 15N-N2O concentrations in a sandy soil profile after application of 15N-fertilizer. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 72, 13–25.
Weier, K. L., Doran, J. W., Power, J. S., & Walters, D. T. (1993). Denitrification and the dinitrogen/nitrous oxide ration as effected by soil water, available carbon, and nitrate. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 57, 66–72.
Wrage, N., Lauf, J., del Prado, A., Pinto, M., Pietrzak, S., & Yamulki, S. (2004). Distinguishing sources of N2O in European grasslands by stable isotope analysis. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 18, 1201–1207.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reth, S., Graf, W., Gefke, O. et al. Whole-year-round Observation of N2O Profiles in Soil: A Lysimeter Study. Water Air Soil Pollut: Focus 8, 129–137 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11267-007-9165-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11267-007-9165-3