Abstract
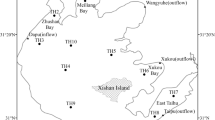
CH4 concentrations in both the surface and bottom waters of Jiaozhou Bay were determined during four surveys in 2003, which showed variability with both seasons and tidal cycles. Atmospheric fluxes of CH4 in Jiaozhou Bay showed obvious seasonal and spatial variations, with the highest values occurring in summer and the lowest in winter. The annual emission of CH4 from Jiaozhou Bay was estimated to be \( 7.98 \times 10^{6} - 18.0 \times 10^{6} \;{\text{mol}}/{\text{year}} \). CH4 in the water column of Jiaozhou Bay was found to come from several land-sources including riverine water input, sewage water input and groundwater input. The spatial and temporal variation in distributions and atmospheric fluxes of CH4 in Jiaozhou Bay was influenced mainly by the input of polluted river waters and the sewage effluents along the eastern coast, which highlights the effects of human impacts on CH4 emission rates.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bange, H. W., Bartell, U. H., Rapsomanikis, S., & Andrae, M. O. (1994). Methane in the Baltic and North Seas and a reassessment of the marine emissions of methane. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 8, 465–480.
Bates, T. S., Kelly, K. C., Johnson, J. E., & Gammon, R. H. (1996). A revaluation of the open ocean source of methane to the atmosphere. Journal of Geophysical Research, 101, 6953–6961.
Bungna, G. C., Chanton, J. P., Cable, J. E., Burnett, W. C., & Cable, P. H. (1996). The importance of groundwater discharge to the methane budgets of nearshore and continental shelf waters of the northeastern Gulf of Mexico. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 60(3), 4735–4746.
Crutzen, P. J. (1991). Methane’s sinks and sources. Nature, 350, 380–381.
De Angelis, M. A., & Lilley, M. D. (1987). Methane in surface waters of Oregon estuaries and rivers. Limnology and Oceanography, 32, 716–722.
De Angelis, M. A., & Scranton, M. I. (1993). Fate of methane in the Hudson River and Estuary. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 7, 509–523.
Houghton, J. T., Jenkins, G. J., & Ephraums, J. J. (1990). Climate change: The IPCC scientific assessment. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Huang, F. L., Zhang, X. H., Xia, X. H., Qiang, Z. J., Lin, C. G., & Zhang, Y. K. (1998). Distribution of methane and its homologues in the low atmosphere of the East China and the surface seawater. Chinese Science Bulletin, 43(16), 1767–1771.
IPCC. (2001). Climate Change 2001: The scientific basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. In J. T. Houghton, Y. Ding, D. J. Griggs, M. Noguer, P. J. van der Linden, X. Dai, K. Maskell, & C. A. Johnson (Eds.), (pp. 7–8 and pp. 248–250). United Kingdom and New York: Cambridge University Press.
Jiao, N. G. (2001). Ecological processes of embayments and sustainable development. Beijing: Science Press.
Karl, D. M., & Tilbrook, B. D. (1994). Production and transport of methane in oceanic particulate organic matter. Nature, 368, 732–734.
Kong, H. N., Kimochi, Y., Mizuochi, M., Inamori, R., & Inamori, Y. (2002). Study of the characteristics of CH4 and N2O emission and methods of controlling their emission in the soil-trench wastewater treatment process. The Science of the Total Environment, 290, 59–67.
Lelieveld, J., Crutzen, P. J., & Dentener, F. J. (1998). Changing concentration, lifetime and climate forcing of atmospheric methane. Tellus, 50B, 128–150.
Liss, P. S., & Merlivat, L. (1986). Air-sea gas exchange rates: Introduction and synthesis. In The role of air-sea exchange in geochemical cyclings. NATO ASI series, vol. 185 (pp. 113–127). New York: Reidel.
Liu, R. Y. (1992). Characteristics of physical environmental of Jiaozhou Bay. In R.Y. Liu (Eds), Ecology and Biological Resources of Jiaozhou Bay (pp. 2–3). Beijing: Science Press.
Liu, G. Q., Wang, S. Y., Zhu, X. J., Liu, S. M., & Zhang, J. (2006). Groundwater and nutrients discharge into the Jiaozhou Bay, North China. Water, Air and Soil Pollution: Focus, (in this volume).
Patra, P. K., Lal, S., Venkataramani, S., Gauns, M., & Sarma, V. V. S. S. (1998). Seasonal variability in distribution and fluxes of methane in the Arabian Sea. Journal of Geophysical Research, 103, 1167–1176.
Qingdao Environment Protection Bureau. (2003). Bulletin of Environment Status of Qingdao.
Shen, Z. L. (2001). Historical changes in nutrient structure and its influences on phytoplantkon composition in Jiaozhou Bay. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 52, 211–224.
Sun, Y. L., Sun, C. Q., Wang, X. C., Tian, H., & Chen, S. J. (1994). Forecast of impact of Qingdao Bay bridge on tide, tidal current and residual current of Jiaozhou Bay 1. Tidal current of Jiaozhou Bay and adjacent sea area. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, Special Issue, 105–119. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Sun, S., Zhang, Y. S., Wu, Y. L., Zhang, G. T., Zhang, F., & Pu, X. M. (2005). Annual variation of primary productivity in Jiaozhou Bay. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 36(6), 481–486 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Upstill-Goddard, R. C., Barnes, J., Frost, T., Punshon, S., & Owens, N. J. P. (2000). Methane in the southern North Sea: Low-salinity inputs, estuarine, and atmospheric flux. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 14, 1205–1216.
Wanninkhof, R. (1992). Relationship between wind speed and gas exchange over the ocean. Journal of Geophysical Research, 97(C5), 7373–7382.
Watanabe, S. (1994). Annual variation of methane in seawater of Funka Bay, Japan. Journal of Oceanography, 50, 415–421.
Wiesenburg, D. A., & Guinasso Jr., N. L. (1979). Equilibrium solubilities of methane, carbon monoxide and hydrogen in water and seawater. Journal of Chemical Engineering Data, 24(4), 356–360.
Yan, J., Bao, X. W., Wang, H., & Shi, L. (2001). Three dimensional simulation transportation and diffusion of pollutant COD in Jiaozhou Bay. Research of Environmental Sciences, 14(2), 14–17. (in Chinese).
Yang, S. S. (1998). Methane production in river and lakes sediments in Taiwan. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 20, 245–249.
Zang, J. Y., & Wang, X. Q. (1997). The dissolved methane in seawater of estuaries II concentration, sea air exchange flux. Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai & Bohai Seas, 15(3), 1–9. (in Chinese).
Zhang, G. L., Zhang, J., Kang, Y. B., & Liu, S. M. (2004). Distributions and fluxes of methane in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea in spring. Journal of Geophysical Research, 109(C7), C07011. doi:10.1029/2004JC002268.
Zhang, G. L. (2004). Studies on biogeochemistry of dissolved methane and nitrous oxide in coastal waters of China. Ph.D. thesis, Ocean University of China.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China through Grant nos. 40036010, 40506025 and 40490265. Dr. H. Wei is acknowledged for providing us with the hydrographic data. We are grateful to Drs. G.Q. Liu, F. Liu and J. Liu for their cooperation and help in groundwater and riverine water samplings. The authors are grateful to the two anonymous reviewers for their constructive suggestions, which greatly improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, G.L., Zhang, J., Xu, J. et al. Distributions, Land-source Input and Atmospheric Fluxes of Methane in Jiaozhou Bay. Water Air Soil Pollut: Focus 7, 645–654 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11267-007-9126-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11267-007-9126-x