Abstract
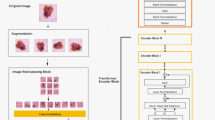
Skin cancer is a complex public health problem and one of the most common types of cancer worldwide. A biopsy of the skin lesion gives the definitive diagnosis of skin cancer. However, before the definitive diagnosis, specialists observe some symptoms that justify the request for a biopsy and consider a early diagnosis. Early diagnosis of skin cancer is subject to errors due to the lack of experience of specialists and similar characteristics with other diseases. This work proposes a CNN architecture, called EfficientAttentionNet, to provide early diagnosis of melanoma and non-melanoma skin lesions. The methodology represents the stages of development of the proposed classification model and the benefits of each stage. In the first step, the set of images from the International Society for Digital Skin Imaging (ISDIS) is pre-processed to eliminate the hair around the skin lesion. Then, a Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) model generates synthetic images to balance the number of samples per class in the training set. In addition, a U-net model creates masks for regions of interest in the images. Finally, EfficientAttentionNet training with the mask-based attention mechanism to classify skin lesions. The proposed model achieved high performance, being a reference for future research in the classification of skin lesions.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sung, H., Ferlay, J., Siegel, R. L., Laversanne, M., Soerjomataram, I., Jemal, A., & Bray, F. (2021). Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 71(3):209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Jones, O. T., Ranmuthu, C. K. I., Hall, P. N., Funston, G., & Walter, F. M. (2019). Recognising skin cancer in primary care. Advances in Therapy, 37(1), 603–616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-019-01130-1
Dorrell, D. N., & Strowd, L. C. (2019). Skin cancer detection technology. Dermatologic Clinics, 37(4), 527–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.det.2019.05.010
Massone, C., Stefani, A. D., & Soyer, H. P. (2005). Dermoscopy for skin cancer detection. Current Opinion in Oncology, 17(2), 147–153. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.cco.0000152627.36243.26
Stefani, A. D., & Cornacchia, L. (2020). Dermoscopy for melanoma. In: Technology in Practical Dermatology, Springer International Publishing, pp 37–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-45351-0_3
Fee, J. A., McGrady, F. P., Rosendahl, C., & Hart, N. D. (2019). Training primary care physicians in dermoscopy for skin cancer detection: a scoping review. Journal of Cancer Education, 35(4), 643–650. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13187-019-01647-7
Kittler, H., Pehamberger, H., Wolff, K., & Binder, M. (2002). Diagnostic accuracy of dermoscopy. The Lancet Oncology, 3(3), 159–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(02)00679-4
Affonso, E. T., Rodríguez, D. Z., Rosa, R. L., Andrade, T., & Bressan, G. (2016). Voice quality assessment in mobile devices considering different fading models. In: 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Consumer Electronics (ISCE), pp 21–22. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISCE.2016.7797329
Basit, A., Ali Khan, S., Tariq Toor, W., Maroof, N., Saadi, M., & Ali Khan, A. (2019). A novel dissimilarity of activity biomarker and functional connectivity analysis for the epilepsy diagnosis. Symmetry, 11(8), 979.
Silva, D. H., Maziero, E. G., Saadi, M., Rosa, R. L., Silva, J. C., Rodriguez, D. Z., & Igorevich, K. K. (2022). Big data analytics for critical information classification in online social networks using classifier chains. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications pp 1–16.
Rosa, R. L., De Silva, M. J., Silva, D. H., Ayub, M. S., Carrillo, D., Nardelli, P. H. J., & Rodríguez, D. Z. (2020). Event detection system based on user behavior changes in online social networks: Case of the covid-19 pandemic. IEEE Access, 8, 158806–158825. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3020391
Teodoro, A. A., Silva, D. H., Saadi, M., Okey, O. D., Rosa, R. L., Otaibi, S. A., & Rodríguez, D. Z. (2021). An analysis of image features extracted by cnns to design classification models for covid-19 and non-covid-19. Journal of Signal Processing Systems, pp 1–13
Zhou, Z., Chen, X., Zhang, Y., & Mumtaz, S. (2020). Blockchain-empowered secure spectrum sharing for 5g heterogeneous networks. IEEE Network, 34(1), 24–31.
Deepak, S., & Ameer, P. (2019). Brain tumor classification using deep CNN features via transfer learning. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 111:103345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2019.103345
Jeyaraj, P. R., & Nadar, E. R. S. (2019). Computer-assisted medical image classification for early diagnosis of oral cancer employing deep learning algorithm. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology, 145(4), 829–837. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-018-02834-7.
Yang, H., Kim, J. Y., Kim, H., & Adhikari, S. P. (2020). Guided soft attention network for classification of breast cancer histopathology images. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 39(5), 1306–1315. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmi.2019.2948026
Zheng, J., Lin, D., Gao, Z., Wang, S., He, M., & Fan, J. (2020). Deep learning assisted efficient AdaBoost algorithm for breast cancer detection and early diagnosis. IEEE Access, 8, 96946–96954. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.2993536
Sallam, A., Alawi, A. E. B., & Saeed, A. Y. A. (2021). A CNN-based model for early melanoma detection. In: Lecture Notes on Data Engineering and Communications Technologies, Springer International Publishing, pp 41–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-70713-2_5
Acosta, M. F. J., Tovar, L. Y. C., Garcia-Zapirain, M. B., & Percybrooks, W. S. (2021). Melanoma diagnosis using deep learning techniques on dermatoscopic images. BMC Medical Imaging, 21(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12880-020-00534-8
Kondaveeti, H. K., & Edupuganti, P. (2020). Skin cancer classification using transfer learning. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Advent Trends in Multidisciplinary Research and Innovation (ICATMRI), IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/icatmri51801.2020.9398388
Aburaed, N., Panthakkan, A., Al-Saad, M., Amin, S. A., & Mansoor, W. (2020). Deep convolutional neural network (DCNN) for skin cancer classification. In: 2020 27th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (ICECS), IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/icecs49266.2020.9294814
Jusman, Y., Firdiantika, I. M., Dharmawan, D. A., & Purwanto, K. (2021). Performance of multi layer perceptron and deep neural networks in skin cancer classification. In: 2021 IEEE 3rd Global Conference on Life Sciences and Technologies (LifeTech), IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/lifetech52111.2021.9391876
Saini, S., Jeon, Y.S., & Feng, M. (2021). B-SegNet. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Health, Inference, and Learning, ACM. https://doi.org/10.1145/3450439.3451873
Qamar, S., Ahmad, P., & Shen, L. (2021). Dense encoder-decoder–based architecture for skin lesion segmentation. Cognitive Computation, 13(2), 583–594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-020-09805-6
Kaur, R., GholamHosseini, H., & Sinha, R. (2021). Deep learning in medical applications: Lesion segmentation in skin cancer images using modified and improved encoder-decoder architecture. In: Nguyen M, Yan WQ, Ho H (eds) Geometry and Visionfirst International Symposium, ISGV 2021, Auckland, New Zealand, January 28-29, 2021, Revised Selected Papers, Springer International Publishing, Cham, vol 1386, pp 39–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72073-5_4
Goudarzi, S., Kama, N., Anisi, M. H., Zeadally, S., & Mumtaz, S. (2019). Data collection using unmanned aerial vehicles for internet of things platforms. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 75, 1–15.
Penpinun, C., Woradit, K., Tangwongchai, S., Tunvirachaisakul, C., Sasithong, P., Noisri, S., et al. (2021). An online cognitive intervention tool for the patients with mild cognitive impairment using virtual reality. 2021 36th International Technical Conference on Circuits/Systems (pp. 1–4). IEEE: Computers and Communications (ITC-CSCC).
Zhou, Z., Zhang, C., Wang, J., Gu, B., Mumtaz, S., Rodriguez, J., & Zhao, X. (2019). Energy-efficient resource allocation for energy harvesting-based cognitive machine-to-machine communications. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 5(3), 595–607.
Goodfellow, I. J., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B., Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., et al. (2020). Generative adversarial networks. Communication ACM, 63(11), 139–144. https://doi.org/10.1145/3422622
Xu, Z., Sheykhahmad, F. R., Ghadimi, N., & Razmjooy, N. (2020). Computer-aided diagnosis of skin cancer based on soft computing techniques. Open Medicine, 15(1), 860–871. https://doi.org/10.1515/med-2020-0131
Razmjooy, N., Ashourian, M., Karimifard, M., Estrela, V. V., Loschi, H. J., do Nascimento, D., et al. (2020). Computer-aided diagnosis of skin cancer: A review. Current Medical Imaging, 16(7), 781–793.
Lisboa, I. N. D., Azevedo Macena, M. S. D., Conceicao Dias, M. I. F. D., Almeida Medeiros, A. B. D., Lima, C. F. D., & Carvalho Lira, A. L. B. D. (2016). Prevalent signs and symptoms in patients with skin cancer and nursing diagnoses. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, 17(7), 3207–3211.
Zhang, L., Gao, H. J., Zhang, J., & Badami, B. (2020). Optimization of the convolutional neural networks for automatic detection of skin cancer. Open medicine (Warsaw, Poland), 15, 27–37. https://doi.org/10.1515/med-2020-0006
Vasilev, I. (2019). Python deep learning : exploring deep learning techniques and neural network architectures with PyTorch, Keras, and TensorFlow. Birmingham, UK: Packt Publishing.
Bissoto, A., Perez, F., Valle, E., Avila, S. (2018). Skin lesion synthesis with generative adversarial networks. In: OR 2.0 Context-Aware Operating Theaters, Computer Assisted Robotic Endoscopy, Clinical Image-Based Procedures, and Skin Image Analysis, Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 294–302.
Oliveira, D. A. B. (2020). Controllable skin lesion synthesis using texture patches, bézier curves and conditional gans. In: 17th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, ISBI 2020, Iowa City, IA, USA, April 3-7, 2020, IEEE, pp 1798–1802. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISBI45749.2020.9098676
Qin, Z., Liu, Z., Zhu, P., & Xue, Y. (2020). A gan-based image synthesis method for skin lesion classification. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 195:105568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105568
Wang, T., Liu, M., Zhu, J., Tao, A., Kautz, J., & Catanzaro, B. (2018). High-resolution image synthesis and semantic manipulation with conditional gans. In: 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2018, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, June 18-22, 2018, IEEE Computer Society, pp 8798–8807. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00917
Mirza, M., & Osindero, S. (2014). Conditional generative adversarial nets. CoRR abs/1411.1784. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2021.3081694
Karras, T., Laine, S., & Aila, T. (2021). A style-based generator architecture for generative adversarial networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 43(12), 4217–4228. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2020.2970919
Fetty, L., Bylund, M., Kuess, P., Heilemann, G., Nyholm, T., Georg, D., & Löfstedt, T. (2020). Latent space manipulation for high-resolution medical image synthesis via the stylegan. Zeitschrift für Medizinische Physik, 30(4):305–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.zemedi.2020.05.001
Saini, S., & Arora, K. (2014). A study analysis on the different image segmentation techniques. International Journal of Information & Computation Technology, 4(14), 1445–1452.
Masood, S., Sharif, M., Masood, A., Yasmin, M., & Raza, M. (2015). A survey on medical image segmentation. Current Medical Imaging, 11(1), 3–14. https://doi.org/10.2174/157340561101150423103441
Barbosa, R. C., Ayub, M. S., Rosa, R. L., Rodríguez, D. Z., & Wuttisittikulkij, L. (2020). Lightweight pvidnet: a priority vehicles detection network model based on deep learning for intelligent traffic lights. Sensors, 20(21), 6218.
Liu, L., Mou, L., Zhu, X. X., & Mandal, M. (2019). Skin lesion segmentation based on improved u-net. In: 2019 IEEE Canadian Conference of Electrical and Computer Engineering, CCECE 2019, Edmonton, AB, Canada, May 5-8, 2019, IEEE, pp 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/CCECE.2019.8861848
Silva, J. C., Saadi, M., Wuttisittikulkij, L., Militani, D. R., Rosa, R. L., Rodríguez, D. Z., & Otaibi, S. A. (2021). Light-field imaging reconstruction using deep learning enabling intelligent autonomous transportation system. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems pp 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2021.3079644
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., & Brox, T. (2015). U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: International Conference on Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, Springer, pp 234–241.
Long, J., Shelhamer, E., & Darrell, T. (2017). Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 39(4), 640–651. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2572683
Iglovikov, V., Mushinskiy, S., & Osin, V. (2017). Satellite imagery feature detection using deep convolutional neural network: A kaggle competition. CoRR abs/1706.06169.
Chen, J., Xing, H., Xiao, Z., Xu, L., & Tao, T. (2021). A drl agent for jointly optimizing computation offloading and resource allocation in mec. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 8(24), 17508–17524. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2021.3081694
Xiao, Z., Xu, X., Xing, H., Luo, S., Dai, P., & Zhan, D. (2021). Rtfn: A robust temporal feature network for time series classification. Information Scientist, 571, 65–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2021.04.053
Giri, R., Isik, U., & Krishnaswamy, A. (2019). Attention wave-u-net for speech enhancement. In: 2019 IEEE Workshop on Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics, WASPAA 2019, New Paltz, NY, USA, October 20-23, 2019, IEEE, pp 249–253. https://doi.org/10.1109/WASPAA.2019.8937186
Zhou, T., Canu, S., & Ruan, S. (2021). Automatic COVID-19 CT segmentation using u-net integrated spatial and channel attention mechanism. International Journal of Imaging Systems and Technology, 31(1), 16–27. https://doi.org/10.1002/ima.22527
Jing, B., Xie, P., & Xing, E. P. (2018). On the automatic generation of medical imaging reports. In: Gurevych I, Miyao Y (eds) Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, ACL 2018, Melbourne, Australia, July 15-20, 2018, Volume 1: Long Papers, Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 2577–2586. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/P18-1240
Valanarasu, J. M. J., Oza, P., Hacihaliloglu, I., & Patel, V. M. (2021). Medical transformer: Gated axial-attention for medical image segmentation. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention - MICCAI 2021 - 24th International Conference, Strasbourg, France, September 27 - October 1, 2021, Proceedings, Part I, Springer, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 12901, pp 36–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87193-2_4
Jain, R., Jain, N., Aggarwal, A., & Hemanth, D. J. (2019). Convolutional neural network based alzheimer’s disease classification from magnetic resonance brain images. Cognitive Systems Research, 57, 147–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsys.2018.12.015
Rosa, R. L., Rodriguez, D. Z., & Bressan, G. (2013). Sentimeter-br: A new social web analysis metric to discover consumers’ sentiment. In: 2013 IEEE International Symposium on Consumer Electronics (ISCE), IEEE, pp 153–154.
Singh, L., Janghel, R. R., & Sahu, S. P. (2020). Trcsvm: a novel approach for the classification of melanoma skin cancer using transfer learning. Data Technologies and Applications.
Baeza-Yates, R., & Ribeiro-Neto, B. (2011). Modern Information Retrieval: The concepts and technology behind search (2nd ed.). Boston, MA: Addison-Wesley Publishing Company.
Guimarães, R., Rodríguez, D. Z., Rosa, R. L., & Bressan, G. (2016). Recommendation system using sentiment analysis considering the polarity of the adverb. In: 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Consumer Electronics (ISCE), IEEE, pp 71–72.
O’keefe, W., Ide, B., Al-Khassaweneh, M., Abuomar, O., & Szczurek, P. (2021). A cnn approach for skin cancer classification. In: 2021 International Conference on Information Technology (ICIT), IEEE, pp 472–475.
Pang, S., Meng, F., Wang, X., Wang, J., Song, T., Wang, X., & Cheng, X. (2020). Vgg16-t: A novel deep convolutional neural network with boosting to identify pathological type of lung cancer in early stage by ct images. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems, 13(1), 771–780.
Tan, M., & Le, Q. V. (2019). Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In: Chaudhuri K, Salakhutdinov R (eds) Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2019, 9-15 June 2019, Long Beach, California, USA, PMLR, Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, vol 97, pp 6105–6114.
Papadopoulos, A., Korus, P., & Memon, N. (2021). Hard-attention for scalable image classification. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 34.
Rotemberg, V., Kurtansky, N., Betz-Stablein, B., & Soyer, H. P. (2021). A patient-centric dataset of images and metadata for identifying melanomas using clinical context. Scientific Data, 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-021-00815-z
Tschandl, P., Rosendahl, C., & Kittler, H. (2018). The HAM10000 dataset, a large collection of multi-source dermatoscopic images of common pigmented skin lesions. Scientific Data, 5(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2018.161
Combalia, M., Codella, N. C. F., Rotemberg, V., Helba, B., Vilaplana, V., Reiter, O., Halpern, A. C., Puig, S., & Malvehy, J. (2019). BCN20000: dermoscopic lesions in the wild. CoRR abs/1908.02288.
Codella, N. C. F., Gutman, D. A., Celebi, M. E., Helba, B., Marchetti, M. A., Dusza, S. W., Kalloo, A., Liopyris, K., Mishra, N. K., Kittler, H., & Halpern, A. (2018). Skin lesion analysis toward melanoma detection: A challenge at the 2017 international symposium on biomedical imaging (isbi), hosted by the international skin imaging collaboration (ISIC). In: 15th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, ISBI 2018, Washington, DC, USA, April 4-7, 2018, IEEE, pp 168–172. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISBI.2018.8363547
Bibiloni, P., Hidalgo, M. G., & Massanet, S. (2017). Skin hair removal in dermoscopic images using soft color morphology. In: ten Teije A, Popow C, Holmes JH, Sacchi L (eds) Artificial Intelligence in Medicine - 16th Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, AIME 2017, Vienna, Austria, June 21-24, 2017, Proceedings, Springer, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 10259, pp 322–326. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59758-4_37
González-Hidalgo, M., Massanet, S., Mir, A., & Ruiz-Aguilera, D. (2013). A fuzzy filter for high-density salt and pepper noise removal. In C. Bielza, A. Salmerón, A. Alonso-Betanzos, J. I. Hidalgo, L. Martínez, A. Troncoso, et al. (Eds.), Advances in Artificial Intelligence (pp. 70–79). Heidelberg: Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin.
Zhao, S., Liu, Z., Lin, J., Zhu, J., & Han, S. (2020). Differentiable augmentation for data-efficient GAN training. In: Larochelle H, Ranzato M, Hadsell R, Balcan M, Lin H (eds) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 33: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2020, NeurIPS 2020, December 6-12, 2020, virtual.
Kingma, D. P., & Ba, J. (2015). Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In: Bengio Y, LeCun Y (eds) 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2015, San Diego, CA, USA, May 7-9, 2015, Conference Track Proceedings.
Zhang, X., Zou, Y., & Shi, W. (2017). Dilated convolution neural network with leakyrelu for environmental sound classification. In: 22nd International Conference on Digital Signal Processing (DSP), pp 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDSP.2017.8096153
Karras, T., Laine, S., Aittala, M., Hellsten, J., Lehtinen, J., & Aila, T. (2020). Analyzing and improving the image quality of stylegan. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 8110–8119.
Loshchilov, I., & Hutter, F. (2019). Decoupled weight decay regularization. In: 7th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2019, New Orleans, LA, USA, May 6-9, 2019, OpenReview.net.
Smith, L. N. (2018). A disciplined approach to neural network hyper-parameters: Part 1 - learning rate, batch size, momentum, and weight decay. CoRR abs/1803.09820.
Heusel, M., Ramsauer, H., Unterthiner, T., Nessler, B., Hochreiter, S., & (2017) Gans trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local nash equilibrium. In: Guyon I, von Luxburg U, Bengio S, Wallach HM, Fergus R, Vishwanathan SVN, Garnett R (eds) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2017(December), pp. 4–9,. (2017). Long Beach (pp. 6626–6637). USA: CA.
Aldwgeri, A., & Abubacker, N. F. (2019). Ensemble of deep convolutional neural network for skin lesion classification in dermoscopy images. In: Zaman HB, Smeaton AF, Shih TK, Velastin SA, Terutoshi T, Ali NM, Ahmad MN (eds) Advances in Visual Informatics - 6th International Visual Informatics Conference, IVIC 2019, Bangi, Malaysia, November 19-21, 2019, Proceedings, Springer, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 11870, pp 214–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-34032-2_20
Mahbod, A., Schaefer, G., Wang, C., Dorffner, G., Ecker, R., & Ellinger, I. (2020). Transfer learning using a multi-scale and multi-network ensemble for skin lesion classification. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 193:105475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105475
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teodoro, A.A.M., Silva, D.H., Rosa, R.L. et al. A Skin Cancer Classification Approach using GAN and RoI-Based Attention Mechanism. J Sign Process Syst 95, 211–224 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-022-01757-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-022-01757-4