Abstract
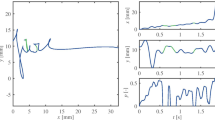
Handwriting dynamics which reflect fine motor skills of writers can be recorded with pen based writing systems. They are generally equipped with a diversity of sensors, such as pen tip pressure and tilt-acceleration sensors mounted inside the pen or pen tip x-y position sensors integrated on a specific graphic tablet. Such writing systems are essentially applied for biometric personal identification or handwriting recognition. In this paper, an advanced biometric pen based system for capturing and analyzing handwriting dynamics of a person is presented. Features of the device as well as evaluation of its sensor data are discussed. The system actually comprises a standard WACOM graphic tablet where its input pen is equipped additionally with a sensor to measure the grip pressure of fingers holding the pen. By combining x-y position data of the tablet and grip pressure data of the pen an improvement of performance in handwriting and person recognition is achieved. The experimental results have shown that among the single sensors, the grip sensor data gives best recognition accuracy and improves the recognition rates of handwritten PINs or persons by about 1%, when fused with x-y position data. It shows excellent accuracy in handwriting recognition and depicts detailed information about fine motor skill which is primarily because of data sampled by the finger grip pressure sensor. The enhanced input device has great promise not only for biometrics but also for biomedical applications.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Christian, G., & Bernhard, S. (2007). A Comparison of Biometric Writing Systems for Analysis of Human Fine Motor Skills. In Proc. Of SMCia/07 Three-Rivers Workshop on Soft Computing in Industrial Applications, University of Passau, Germany.
Bashir, M., & Kempf, J. (2009). Person Authentication with RDTW using Handwritten PIN and signature with a Novel Biometric Smart Pen Device. In SSCI Computational Intelligence in Biometrics, IEEE, Nashville.
Takita, T., Hangai, S., Kempf, J, Hook, C., & Scharfenberg, G. (2007). An Identification of Japanese Numerical Characters on a Biometrical Smart Pen System. In Automatic Identification Advanced Technologies, 2007 IEEE Workshop.
Gruber, C., Hook, C., Kempf, J., Scharfenberg, G., & Sick, B. (2006). A Flexible Architecture for Online Signature Verification Based on a Novel Biometric Pen. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Mountain Workshop on Adaptive and Learning Systems (SMCals/06), pp. 110–115; Logan.
Hook, C., Kempf, J., & Scharfenberg, G., (2004). A novel digitizing pen for the analysis of pen pressure and inclination in handwriting biometrics. Biometric Authentication Workshop, Prague 2004, LNCS Springer.
Dose, M., Gruber, C., Grunz, A., Hook, C., Kempf, J., Scharfenberg, G., & Sick, B. (2007). Towards an Automated Analysis of Neuroleptics’ Impact on Human Hand Motor Skills. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology (CIBCB 2007), pp. 494–501, Honolulu.
Ünlü, A., Brause, R., & Krakow, K. (2006). Handwriting Analysis for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Parkinson’s Disease. Proc. Int. Symp. Biological and Medical Data analysis, LNCS Vol. 4345, Springer Heidelberg, pp. 441–450.
Leis, B. C., Rand, M. K., et al. (2005). Movement precues in planning and execution of aiming movements in Parkinson’s disease. In J. Experimental Neurology, Elsevier, 194, 393–409.
Teulings, H.-L., Contreras-Vidal, J. L., Stelmach, G. E., & Adler, C. H. (2002). Adaptation of handwriting size under distorted visual feedback in patients with Parkinson’s disease and elderly and young controls. In Jnnp, 72(3): 315–324.
Eamonn Keogh, Chotirat Ann Ratanamahatana (2004). Exact indexing of dynamic time warping. In Knowledge and Information Systems 358–386, Springer London.
Rath, T. M., & Manmatha, R. (2003). Lower-bounding of dynamic time warping distances for multivariate time series. CIIR Technical Report MM-40.
Bashir, M., & Kempf, J. (2010). DTW Based Classification of Diverse Pre-processed Time Series Obtained from Handwritten PIN words and Signatures. In Journal of Signal Processing Systems, Springer, doi:10.1007/s11265-010-0501-x.
Acknowledgment
The support given by J. Kempf of the University of Applied Sciences Regensburg is highly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bashir, M., Kempf, F. Advanced Biometric Pen System for Recording and Analyzing Handwriting. J Sign Process Syst 68, 75–81 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-011-0576-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-011-0576-z