Abstract
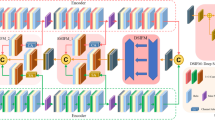
In recent years, although significant progress has been made in infrared and visible image fusion, existing methods typically assume that the source images have been rigorously registered or aligned prior to image fusion. However, the difference in modalities of infrared and visible images poses a great challenge to achieve strict alignment automatically, affecting the quality of the subsequent fusion procedure. To address this problem, this paper proposes a deep learning framework for misaligned infrared and visible image fusion, aiming to free the fusion algorithm from strict registration. Technically, we design a convolutional neural network (CNN)-Transformer Hierarchical Interactive Embedding (CTHIE) module, which can combine the respective advantages of CNN and Transformer, to extract features from the source images. In addition, by characterizing the correlation between the features extracted from misaligned source images, a Dynamic Re-aggregation Feature Representation (DRFR) module is devised to align the features with a self-attention-based feature re-aggregation scheme. Finally, to effectively utilize the features at different levels of the network, a Fully Perceptual Forward Fusion (FPFF) module via interactive transmission of multi-modal features is introduced for feature fusion to reconstruct the fused image. Experimental results on both synthetic and real-world data demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, verifying the feasibility of directly fusing infrared and visible images without strict registration.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availibility
The datasets for this study can be found in the VOT2020-RGBT dataset https://www.votchallenge.net/vot2020/dataset.html, the KAIST dataset https://github.com/SoonminHwang/rgbt-ped-detection/blob/master/data/README.md and the CVC_14 dataset http://adas.cvc.uab.es/elektra/enigma-portfolio/cvc-14-visible-fir-day-night-pedestrian-sequence-dataset/.
References
Bulanon, D., Burks, T., & Alchanatis, V. (2009). Image fusion of visible and thermal images for fruit detection. Biosystems Engineering, 103(1), 12–22.
Carion, N., Massa, F., Synnaeve, G., et al. (2020). End-to-end object detection with transformers. In European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) (pp. 213–229). Cham: Springer.
Chen, C.F., Panda, R., & Fan, Q. (2022). Regionvit: Regional-to-local attention for vision transformers. In Proceedings of the international conference on learning representations (ICLR).
Chen, H., & Varshney, P. K. (2007). A human perception inspired quality metric for image fusion based on regional information. Information Fusion, 8(2), 193–207.
Chen, H., Wang, Y., Guo, T., et al. (2021). Pre-trained image processing transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp 12,299–12,310).
Chen, Y., & Blum, R. S. (2009). A new automated quality assessment algorithm for image fusion. Image and Vision Computing, 27(10), 1421–1432.
Dosovitskiy, A., Beyer, L., & Kolesnikov, A. (2021). An image is worth 16\(\times \)16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. In Proceedings of the international conference on learning representations (ICLR).
González, A., Fang, Z., Socarras, Y., et al. (2016). Pedestrian detection at day/night time with visible and fir cameras: A comparison. Sensors, 16(6), 820.
Gu, J., Lu, H., Zuo, W. et al. (2019). Blind super-resolution with iterative kernel correction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp 1604–1613)
Han, J., & Bhanu, B. (2007). Fusion of color and infrared video for moving human detection. Pattern Recognition, 40(6), 1771–1784.
Han, K., Xiao, A., Wu, E., et al. (2021). Transformer in transformer. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 34, 15908–15919.
Hwang, S., Park, J., Kim, N., et al. (2015). Multispectral pedestrian detection: Benchmark dataset and baseline. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp 1037–1045).
Kingma, D.P., & Ba, J. (2015). Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In International conference on learning representations (ICLR).
Kristan, M., Leonardis, A., Matas, J., et al. (2020). The eighth visual object tracking vot2020 challenge results. In European conference on computer vision (ECCV) (pp 547–601). Springer.
Kumar, P., Mittal, A., & Kumar, P. (2006). Fusion of thermal infrared and visible spectrum video for robust surveillance. In Computer vision, graphics and image processing (pp. 528–539). Springer.
Li, H., & Wu, X. (2018). Densefuse: A fusion approach to infrared and visible images. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 28(5), 2614–2623.
Li, H., Qiu, H., Yu, Z., et al. (2016). Infrared and visible image fusion scheme based on NSCT and low-level visual features. Infrared Physics & Technology, 76, 174–184.
Li, H., Wang, Y., Yang, Z., et al. (2020). Discriminative dictionary learning-based multiple component decomposition for detail-preserving noisy image fusion. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 69(4), 1082–1102.
Li, H., Wu, X. J., & Durrani, T. (2020). Nestfuse: An infrared and visible image fusion architecture based on nest connection and spatial/channel attention models. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 69(12), 9645–9656.
Li, H., Cen, Y., Liu, Y., et al. (2021). Different input resolutions and arbitrary output resolution: A meta learning-based deep framework for infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 30, 4070–4083.
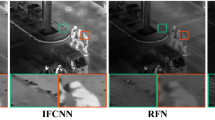
Li, H., Wu, J., & Kittler, J. (2021). Rfn-nest: An end-to-end residual fusion network for infrared and visible images. Information Fusion, 73, 72–86.
Li, H., Xu, T., Wu, X., et al. (2023). Lrrnet: A novel representation learning guided fusion network for infrared and visible images. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 45(9), 11040–11052.
Liu, Y., Chen, X., Ward, R. K., et al. (2015). Simultaneous image fusion and denoising with adaptive sparse representation. IET Image Processing, 9(5), 347–357.
Liu, Y., Liu, S., & Wang, Z. (2015). A general framework for image fusion based on multi-scale transform and sparse representation. Information Fusion, 24, 174–164.
Liu, Y., Chen, X., Ward, R. K., et al. (2016). Image fusion with convolutional sparse representation. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 23(12), 1882–1886.
Liu, Y., Chen, X., Peng, H., et al. (2017). Multi-focus image fusion with a deep convolutional neural network. Information Fusion, 36, 191–207.
Liu, Z., Lin, Y., Cao, Y., et al. (2021). Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision (ICCV) (pp. 10012–10022).
Ma, J., Ma, Y., & Li, C. (2019). Infrared and visible image fusion methods and applications: A survey. Information Fusion, 45, 153–178.
Ma, J., Yu, W., Liang, P., et al. (2019). Fusiongan: A generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion. Information Fusion, 48, 11–26.
Ma, J., Xu, H., Jiang, J., et al. (2020). Ddcgan: A dual-discriminator conditional generative adversarial network for multi-resolution image fusion. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 29, 4980–4995.
Ma, J., Tang, L., Fan, F., et al. (2022). Swinfusion: Cross-domain long-range learning for general image fusion via swin transformer. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 9(7), 1200–1217.
Van der Maaten, L., & Hinton, G. (2008). Visualizing data using t-sne. Journal of machine learning research, 9(11), 2579–2605.
Meinhardt, T., Kirillov, A., Leal-Taixé, L., et al. (2021). Trackformer: Multi-object tracking with transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 8844–8854).
Paszke, A., Gross, S., Massa, F., et al. (2019). Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. (pp. 8026–8037).
Ram Prabhakar, K., Sai Srikar, V., & Venkatesh Babu, R. (2017). Deepfuse: A deep unsupervised approach for exposure fusion with extreme exposure image pairs. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV) (pp. 4714–4722).
Roberts, J. W., Van Aardt, J. A., & Ahmed, F. B. (2008). Assessment of image fusion procedures using entropy, image quality, and multispectral classification. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2(1), 023522.
Simonyan, K., & Zisserman, A. (2015). Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In International conference on learning representations (ICLR).
Singh, R., Vatsa, M., & Noore, A. (2008). Integrated multilevel image fusion and match score fusion of visible and infrared face images for robust face recognition. Pattern Recognition, 41(3), 880–893.
Srinivas, A., Lin, T.Y., Parmar, N., et al. (2021). Bottleneck transformers for visual recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 16,519–16,529)
Tang, H., Li, Z., Peng, Z., et al. (2020). Blockmix: Meta regularization and self-calibrated inference for metric-based meta-learning. In ACM Multimedia (pp. 610–618).
Tang, H., Yuan, C., Li, Z., et al. (2022). Learning attention-guided pyramidal features for few-shot fine-grained recognition. Pattern Recognition, 130(108), 792.
Tang, L., Deng, Y., Ma, Y., et al. (2022). Superfusion: A versatile image registration and fusion network with semantic awareness. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 9(12), 2121–2137.
Tang, L., Yuan, J., & Ma, J. (2022). Image fusion in the loop of high-level vision tasks: A semantic-aware real-time infrared and visible image fusion network. Information Fusion, 82, 28–42.
Tang, W., He, F., Liu, Y., et al. (2023). Datfuse: Infrared and visible image fusion via dual attention transformer. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 33(7), 3159–3172.
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., et al. (2017). Attention is all you need. In Advances in neural information processing systems.
Vs, V., Valanarasu, J.M.J., Oza, P., et al. (2022). Image fusion transformer. In 2022 IEEE International conference on image processing (ICIP) (pp. 3566–3570).
Wang, D., Liu, J., Fan, X., et al. (2022). Unsupervised misaligned infrared and visible image fusion via cross-modality image generation and registration. In Proceedings of the thirty-first international joint conference on artificial intelligence (IJCAI) (pp. 3508–3515).
Wang, X., Yu, K., Dong, C., et al. (2018). Recovering realistic texture in image super-resolution by deep spatial feature transform. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 606–615).
Wang, Z., Bovik, A. C., Sheikh, H. R., et al. (2004). Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 13(4), 600–612.
Wu, H., Xiao, B., & Codella, N. (2021). Cvt: Introducing convolutions to vision transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision (ICCV) (pp. 22–31).
Xiao, W., Zhang, Y., Wang, H., et al. (2022). Heterogeneous knowledge distillation for simultaneous infrared-visible image fusion and super-resolution. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 71, 1–15.
Xu, H., Ma, J., Jiang, J., et al. (2022). U2fusion: A unified unsupervised image fusion network. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 44(1), 502–518.
Xu, H., Ma, J., Yuan, J., et al. (2022b). Rfnet: Unsupervised network for mutually reinforcing multi-modal image registration and fusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 19,679–19,688).
Xu, H., Yuan, J., & Ma, J. (2023). Murf: Mutually reinforcing multi-modal image registration and fusion. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 45(10), 12148–12166.
Xydeas, C. S., Petrovic, V., et al. (2000). Objective image fusion performance measure. Electronics Letters, 36(4), 308–309.
Yao, Y., Zhang, Y., Wan, Y., et al. (2021). Heterologous images matching considering anisotropic weighted moment and absolute phase orientation. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 46(11), 1727–1736.
Yi, P., Wang, Z., & Jiang, K. (2021). Omniscient video super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision (CVPR) (pp. 4429–4438).
Yu, C., Gao, C., Wang, J., et al. (2021). Bisenet v2: Bilateral network with guided aggregation for real-time semantic segmentation. International Journal of Computer Vision, 129, 3051–3068.
Yuan, K., Guo, S., Liu, Z., et al. (2021). Incorporating convolution designs into visual transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision (ICCV) (pp. 579–588)
Zhang, G., Zhang, P., Qi, J., et al. (2021). Hat: Hierarchical aggregation transformers for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM international conference on multimedia (ACMMM). (pp. 516–525).
Zhang, H., & Ma, J. (2021). Sdnet: A versatile squeeze-and-decomposition network for real-time image fusion. International Journal of Computer Vision, 129(10), 2761–2785.
Zhang, H., Xu, H., Xiao, Y., et al. (2020a). Rethinking the image fusion: A fast unified image fusion network based on proportional maintenance of gradient and intensity. In Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence (pp. 12,797–12,804).
Zhang, Y., Liu, Y., Sun, P., et al. (2020). IFCNN: A general image fusion framework based on convolutional neural network. Information Fusion, 54, 99–118.
Zhao, Z., Xu, S., Zhang, J., et al. (2022). Efficient and model-based infrared and visible image fusion via algorithm unrolling. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 32(3), 1186–1196.
Zheng, S., Lu, J., & Zhao, H. (2021). Rethinking semantic segmentation from a sequence-to-sequence perspective with transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 6881–6890).
Zhu, X., Su, W., & Lu, L. et al. (2021). Deformable detr: Deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection. In International conference on learning representations (ICLR).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62161015, 62176081 and U23A20294), and Yunnan Fundamental Research Projects (No. 202301AV070004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Communicated by Ondra Chum.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Liu, J., Zhang, Y. et al. A Deep Learning Framework for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Without Strict Registration. Int J Comput Vis 132, 1625–1644 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-023-01948-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-023-01948-x