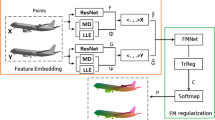
Abstract
The neural radiance field (NeRF) has shown promising results in preserving the fine details of objects and scenes. However, unlike explicit shape representations e.g., mesh, it remains an open problem to build dense correspondences across different NeRFs of the same category, which is essential in many downstream tasks. The main difficulties of this problem lie in the implicit nature of NeRF and the lack of ground-truth correspondence annotations. In this paper, we show it is possible to bypass these challenges by leveraging the rich semantics and structural priors encapsulated in a pre-trained NeRF-based GAN. Specifically, we exploit such priors from three aspects, namely (1) a dual deformation field that takes latent codes as global structural indicators, (2) a learning objective that regards generator features as geometric-aware local descriptors, and (3) a source of infinite object-specific NeRF samples. Our experiments demonstrate that such priors lead to 3D dense correspondence that is accurate, smooth, and robust. We also show that established dense correspondence across NeRFs can effectively enable many NeRF-based downstream applications such as texture transfer.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets that support the findings of this study are all publicly available for the research purpose.
References
Bau, D., Zhu, J. Y., Strobelt, H., Lapedriza, A., Zhou, B., & Torralba, A. (2020). Understanding the role of individual units in a deep neural network. PNAS https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1907375117, https://www.pnas.org/content/early/2020/08/31/1907375117.
Blanz, V., & Vetter, T. (1999). A morphable model for the synthesis of 3d faces. In SIGGRAPH.
Brock, A., Donahue, J., & Simonyan, K. (2019a). Large scale GAN training for high fidelity natural image synthesis. In ICLR.
Brock, A., Donahue, J., & Simonyan, K. (2019b). Large scale GAN training for high fidelity natural image synthesis. In ICLR, OpenReview.net, https://openreview.net/forum?id=B1xsqj09Fm.
Chan, E., Monteiro, M., Kellnhofer, P., Wu, J., & Wetzstein, G. (2021a). pi-gan: Periodic implicit generative adversarial networks for 3d-aware image synthesis. In CVPR.
Chan, E. R., Lin, C. Z., Chan, M. A., Nagano, K., Pan, B., Mello, S. D., Gallo, O., Guibas, L., Tremblay, J., Khamis, S., Karras, T., & Wetzstein, G. (2021b). Efficient geometry-aware 3D generative adversarial networks. In arXiv.
Chan, E. R., Monteiro, M., Kellnhofer, P., Wu, J., & Wetzstein, G. (2021c). pi-GAN: Periodic implicit generative adversarial networks for 3D-aware image synthesis. In CVPR.
Chan, E. R., Lin, C. Z., Chan, M. A., Nagano, K., Pan, B., Mello, S. D., Gallo, O., Guibas, L., Tremblay, J., Khamis, S., Karras, T., & Wetzstein, G. (2022a). Efficient geometry-aware 3D generative adversarial networks. In CVPR.
Chan, E. R., Lin, C. Z., Chan, M. A., Nagano, K., Pan, B., Mello, S. D., Gallo, O., Guibas, L., Tremblay, J., Khamis, S., Karras, T., & Wetzstein, G. (2022b). Efficient geometry-aware 3D generative adversarial networks. In CVPR.
Chang, A. X., Funkhouser, T., Guibas, L., Hanrahan, P., Huang, Q., Li, Z., Savarese, S., Savva, M., Song, S., Su, H., Xiao, J., Yi, L., & Yu, F. (2015). ShapeNet: An Information-Rich 3D Model Repository. Tech. Rep. arXiv:1512.03012 [cs.GR], Stanford University — Princeton University — Toyota Technological Institute at Chicago.
Chen, L. C., Papandreou, G., Schroff, F., & Adam, H. (2017). Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv:1706.05587.
Chen, Z., & Zhang, H. (2019). Learning implicit fields for generative shape modeling. In CVPR, pp 5932–5941.
Cho, S., Hong, S., Jeon, S., Lee, Y., Sohn, K., & Kim, S. (2021). Cats: Cost aggregation transformers for visual correspondence. In Thirty-Fifth Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems.
Deng, Y., Yang, J., & Tong, X. (2021). Deformed implicit field: Modeling 3d shapes with learned dense correspondence. In CVPR, pp 10286–10296.
Dosovitskiy, A., Ros, G., Codevilla, F., Lopez, A., & Koltun, V. (2017). Carla: An open urban driving simulator. In Proc. CoRL.
Dumoulin, V., Perez, E., Schucher, N., Strub, F., Vries, H. d., Courville, A., & Bengio, Y. (2018). Feature-wise transformations. Distill https://doi.org/10.23915/distill.00011, https://distill.pub/2018/feature-wise-transformations.
Egger, B., Smith, W., Tewari, A., Wuhrer, S., Zollhöfer, M., Beeler, T., Bernard, F., Bolkart, T., Kortylewski, A., Romdhani, S., Theobalt, C., Blanz, V., & Vetter, T. (2020). 3d morphable face models–past, present, and future. TOG, 39, 1–38.
Eisenberger, M., Novotný, D., Kerchenbaum, G., Labatut, P., Neverova, N., Cremers, D., & Vedaldi, A. (2021). Neuromorph: Unsupervised shape interpolation and correspondence in one go. In CVPR.
Eslami, S. M. A., Rezende, D. J., Besse, F., Viola, F., Morcos, A. S., Garnelo, M., Ruderman, A., Rusu, A. A., Danihelka, I., Gregor, K., Reichert, D. P., Buesing, L., Weber, T., Vinyals, O., Rosenbaum, D., Rabinowitz, N. C., King, H., Hillier, C., Botvinick, M. M., … Hassabis, D. (2018). Neural scene representation and rendering. Science, 360, 1204–1210.
Fan, Z., Hu, X., Chen, C., & Peng, S. (2019). Boosting local shape matching for dense 3d face correspondence. In CVPR, pp 10936–10946.
Gafni, G., Thies, J., Zollhöfer, M., & Nießner, M. (2021). Dynamic neural radiance fields for monocular 4d facial avatar reconstruction. In CVPR, pp 8649–8658
Goodfellow, I. J., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B., Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., Courville, A. C., & Bengio, Y. (2014). Generative adversarial nets. In NIPS.
Gu, J., Liu, L., Wang, P., & Theobalt, C. (2022). Stylenerf: A style-based 3d aware generator for high-resolution image synthesis. In ICLR, https://openreview.net/forum?id=iUuzzTMUw9K.
Guo, Y., Chen, K., Liang, S., Liu, Y., Bao, H., & Zhang, J. (2021). Ad-nerf: Audio driven neural radiance fields for talking head synthesis. In ICCV.
Halimi, O., Litany, O., Rodola, E., Bronstein, A. M., & Kimmel, R. (2019). Unsupervised learning of dense shape correspondence. In CVPR, pp 4370–4379.
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2016). Deep residual learning for image recognition. In CVPR.
He, K., Fan, H., Wu, Y., Xie, S., & Girshick, R. (2019). Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning. arXiv.
Hong, S., Cho, S., Nam, J., Lin, S., & Kim, S. (2022a). Cost aggregation with 4d convolutional swin transformer for few-shot segmentation. In ECCV, Springer, pp 108–126.
Hong, Y., Peng, B., Xiao, H., Liu, L., & Zhang, J. (2022b). Headnerf: A real-time nerf-based parametric head model. In CVPR.
Jahanian, A., Chai, L., & Isola, P. (2020). On the “steerability” of generative adversarial networks. In ICLR.
Kaick, O. V., Zhang, H., Hamarneh, G., & Cohen-Or, D. (2011). A survey on shape correspondence. Computer Graphics Forum 30.
Karras, T., Laine, S., & Aila, T. (2019a). A style-based generator architecture for generative adversarial networks. In CVPR.
Karras, T., Laine, S., & Aila, T. (2019b). A style-based generator architecture for generative adversarial networks. In CVPR, pp 4396–4405.
Kingma, D. P., & Ba, J. (2015). Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In ICLR, arXiv:1412.6980.
Lan, Y., Meng, X., Yang, S., Loy, C. C., & Dai, B. (2023). E3dge: Self-supervised geometry-aware encoder for style-based 3d gan inversion. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).
Li, Z., & Snavely, N. (2018). Megadepth: Learning single-view depth prediction from internet photos. In ICCV, pp 2041–2050.
Li, Z., Niklaus, S., Snavely, N., & Wang, O. (2021). Neural scene flow fields for space-time view synthesis of dynamic scenes. In CVPR.
Litany, O., Remez, T., Rodolà, E., Bronstein, A., & Bronstein, M. (2017). Deep functional maps: Structured prediction for dense shape correspondence. In ICCV, pp 5660–5668.
Liu, C., Yuen, J., & Torralba, A. (2011). Sift flow: Dense correspondence across scenes and its applications. PAMI, 33, 978–994.
Liu, F., & Liu, X. (2020). Learning implicit functions for topology-varying dense 3d shape correspondence. In NIPS, Virtual.
Liu, Z., Luo, P., Wang, X., & Tang, X. (2015). Deep learning face attributes in the wild. In ICCV.
Loper, M., Mahmood, N., Romero, J., Pons-Moll, G., & Black, M. J. (2015). Smpl: A skinned multi-person linear model. TOG, 34(6), 1–16.
Lowe, D. G. (1999). Object recognition from local scale-invariant features. In Int. Conf. Comput. Vis., IEEE, vol 2, pp 1150–1157.
Mescheder, L., Oechsle, M., Niemeyer, M., Nowozin, S., & Geiger, A. (2019). Occupancy networks: Learning 3d reconstruction in function space. In CVPR, pp 4460–4470.
Mescheder, L. M., Geiger, A., & Nowozin, S. (2018). Which training methods for gans do actually converge? In ICML.
Mildenhall, B., Srinivasan, P. P., Tancik, M., Barron, J. T., Ramamoorthi, R., & Ng, R. (2020). Nerf: Representing scenes as neural radiance fields for view synthesis. In ECCV, Springer, pp 405–421.
Min, J., Lee, J., Ponce, J., & Cho, M. (2019). Spair-71k: A large-scale benchmark for semantic correspondence. arXiv:1908.10543.
Mu, J., De Mello, S., Yu, Z., Vasconcelos, N., Wang, X., Kautz, J., & Liu, S. (2022). Coordgan: Self-supervised dense correspondences emerge from gans. In CVPR.
Niemeyer, M., & Geiger, A. (2021). Giraffe: Representing scenes as compositional generative neural feature fields. In CVPR.
Noguchi, A., Sun, X., Lin, S., & Harada, T. (2021). Neural articulated radiance field. In ICCV.
Or-El, R., Luo, X., Shan, M., Shechtman, E., Park, J. J., & Kemelmacher-Shlizerman, I. (2021). StyleSDF: High-Resolution 3D-Consistent Image and Geometry Generation. In CVPR.
Pan, X., Dai, B., Liu, Z., Loy, C. C., & Luo, P. (2021). Do 2d gans know 3d shape? unsupervised 3d shape reconstruction from 2d image gans. In ICLR
Park, J. J., Florence, P., Straub, J., Newcombe, R., & Lovegrove, S. (2019). DeepSDF: Learning continuous signed distance functions for shape representation. In CVPR, IEEE, pp 165–174, https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00025, https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8954065/.
Park, K., Sinha, U., Barron, J.T., Bouaziz, S., Goldman, D. B., Seitz, S. M., & Martin-Brualla, R. (2021a). Nerfies: Deformable neural radiance fields. In ICCV.
Park, K., Sinha, U., Barron, J. T., Bouaziz, S., Goldman, D. B., Seitz, S. M., & Martin-Brualla, R. (2021b). Nerfies: Deformable neural radiance fields. In ICCV.
Park, K., Sinha, U., Hedman, P., Barron, J. T., Bouaziz, S., Goldman, D. B., Martin-Brualla, R., & Seitz, S. M. (2021c). Hypernerf: A higher-dimensional representation for topologically varying neural radiance fields. TOG 40(6).
Park, T., Zhu, J. Y., Wang, O., Lu, J., Shechtman, E., Efros, A. A., & Zhang, R. (2020). Swapping autoencoder for deep image manipulation. In NIPS.
Peebles, W., Zhu, J. Y., Zhang, R., Torralba, A., Efros, A., & Shechtman, E. (2022). Gan-supervised dense visual alignment. In CVPR.
Perez, E., Strub, F., De Vries, H., Dumoulin, V., & Courville, A. (2018). Film: Visual reasoning with a general conditioning layer. In AAAI, vol 32.
Pumarola, A., Corona, E., Pons-Moll, G., & Moreno-Noguer, F. (2020). D-NeRF: Neural Radiance Fields for Dynamic Scenes. In CVPR.
Qi, C., Su, H., Mo, K., & Guibas, L. (2017). Pointnet: Deep learning on point sets for 3d classification and segmentation. In CVPR, pp 77–85
Richardson, E., Alaluf, Y., Patashnik, O., Nitzan, Y., Azar, Y., Shapiro, S., & Cohen-Or, D. (2021). Encoding in style: a stylegan encoder for image-to-image translation. In CVPR.
Sahillioglu, Y. (2019). Recent advances in shape correspondence. The Visual Computer, 36, 1705–1721.
Schwarz, K., Liao, Y., Niemeyer, M., & Geiger, A. (2020). Graf: Generative radiance fields for 3d-aware image synthesis. In NIPS.
Shen, Y., Yang, C., Tang, X., & Zhou, B. (2020). Interfacegan: Interpreting the disentangled face representation learned by gans. PAMI PP.
Simonyan, K., & Zisserman, A. (2015). Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In CoRR, arXiv:1409.1556.
Sitzmann, V., Martel, J. N., Bergman, A. W., Lindell, D. B., & Wetzstein, G. (2020). Implicit neural representations with periodic activation functions. In NIPS.
Tancik, M., Srinivasan, P. P., Mildenhall, B., Fridovich-Keil, S., Raghavan, N., Singhal, U., Ramamoorthi, R., Barron, J. T., & Ng, R. (2020). Fourier features let networks learn high frequency functions in low dimensional domains. In NIPS.
Teed, Z., & Deng, J. (2020). Raft: Recurrent all-pairs field transforms for optical flow. In ECCV.
Tewari, A., Fried, O., Thies, J., Sitzmann, V., Lombardi, S., Sunkavalli, K., Martin-Brualla, R., Simon, T., Saragih, J., Nießner, M., Pandey, R., Fanello, S., Wetzstein, G., Zhu, J. Y., Theobalt, C., Agrawala, M., Shechtman, E., Goldman, D. B., & Zollhöfer, M. (2020). State of the Art on Neural Rendering. Computer Graphics Forum.
Tov, O., Alaluf, Y., Nitzan, Y., Patashnik, O., & Cohen-Or, D. (2021). Designing an encoder for stylegan image manipulation. arXiv.
Tritrong, N., Rewatbowornwong, P., & Suwajanakorn, S. (2021). Repurposing gans for one-shot semantic part segmentation. In CVPR.
Truong, P., Danelljan, M., Gool, L. V., & Timofte, R. (2020a). GOCor: Bringing globally optimized correspondence volumes into your neural network. In NIPS.
Truong, P., Danelljan, M., & Timofte, R. (2020b). Glu-net: Global-local universal network for dense flow and correspondences. In CVPR, pp 6257–6267.
Truong, P., Danelljan, M., Gool, L. V., & Timofte, R. (2021). Learning accurate dense correspondences and when to trust them. In CVPR, pp 5710–5720.
Wang, X., Bo, L., & Fuxin, L. (2019a). Adaptive wing loss for robust face alignment via heatmap regression. In ICCV
Wang, Y., Sun, Y., Liu, Z., Sarma, S. E., Bronstein, M., & Solomon, J. (2019). Dynamic graph cnn for learning on point clouds. TOG, 38, 1–12.
Wang, Z., Bagautdinov, T., Lombardi, S., Simon, T., Saragih, J., Hodgins, J., & Zollhofer, M. (2021). Learning compositional radiance fields of dynamic human heads. In CVPR, pp 5704–5713.
Wood, E., Baltrušaitis, T., Hewitt, C., Dziadzio, S., Johnson, M., Estellers, V., Cashman, T. J., & Shotton, J. (2021). Fake it till you make it: Face analysis in the wild using synthetic data alone. In Int. Conf. Comput. Vis.
Xu, J., & Wang, X. (2021). Rethinking self-supervised correspondence learning: A video frame-level similarity perspective. arXiv.
Yang, G., Belongie, S., Hariharan, B., & Koltun, V. (2021). Geometry processing with neural fields. In Thirty-Fifth Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems.
Yang, S., Jiang, L., Liu, Z., & Loy, C. C. (2022). Unsupervised image-to-image translation with generative prior. In CVPR.
Yu, A., Ye, V., Tancik, M., & Kanazawa, A. (2021). pixelnerf: Neural radiance fields from one or few images. In CVPR, pp 4578–4587.
Zhang, K., Zhang, Z., Li, Z., & Qiao, Y. (2016). Joint face detection and alignment using multitask cascaded convolutional networks. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 23, 1499–1503.
Zhang, K., Riegler, G., Snavely, N., & Koltun, V. (2020). Nerf++: Analyzing and improving neural radiance fields. arXiv.
Zhang, R., Isola, P., Efros, A. A., Shechtman, E., & Wang, O. (2018). The unreasonable effectiveness of deep features as a perceptual metric. In CVPR.
Zhang, W., Sun, J., & Tang, X. (2008). Cat head detection - how to effectively exploit shape and texture features. In ECCV.
Zhang, Y., Chen, W., Ling, H., Gao, J., Zhang, Y., Torralba, A., & Fidler, S. (2021a). Image gans meet differentiable rendering for inverse graphics and interpretable 3d neural rendering. In ICLR
Zhang, Y., Ling, H., Gao, J., Yin, K., Lafleche, J. F., Barriuso, A., Torralba, A., & Fidler, S. (2021b). Datasetgan: Efficient labeled data factory with minimal human effort. In CVPR.
Zheng, Y., Abrevaya, V. F., Bühler, M. C., Chen, X., Black, M. J., & Hilliges, O. (2022). I M Avatar: Implicit morphable head avatars from videos. In CVPR.
Zheng, Z., Yu, T., Dai, Q., & Liu, Y. (2021). Deep implicit templates for 3d shape representation. In CVPR, pp 1429–1439.
Zhou, P., Xie, L., Ni, B., & Tian, Q. (2021). CIPS-3D: A 3D-Aware Generator of GANs Based on Conditionally-Independent Pixel Synthesis. arXiv:2110.09788.
Zhou, T., Krähenbühl, P., Aubry, M., Huang, Q., & Efros, A. A. (2016). Learning dense correspondence via 3d-guided cycle consistency. In CVPR, pp 117–126
Acknowledgements
This study is supported under the RIE2020 Industry Alignment Fund Industry Collaboration Projects (IAF-ICP) Funding Initiative, as well as cash and in-kind contribution from the industry partner(s). It is also supported by Singapore MOE AcRF Tier 2 (MOE-T2EP20221-0011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Stephen Lin.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lan, Y., Loy, C.C. & Dai, B. Correspondence Distillation from NeRF-Based GAN. Int J Comput Vis 132, 611–631 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-023-01903-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-023-01903-w