Abstract
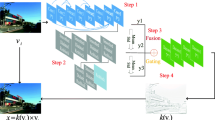
Atmospheric turbulence is one of the causes of quality degradation in long-range imaging and its removal from degraded frame sequences is considered an ill-posed problem. There have been numerous attempts to address this problem. However, there is still room for improving the quality of the restored images. In contrast to the previous approaches to address this problem, in this paper, we propose a data-driven approach. First, an end-to-end deep convolutional autoencoder is trained using natural images and its encoder part is exploited to extract high-level features from all the frames in a sequence that are distorted by atmospheric turbulence. Then, the binary search algorithm and the unsupervised K-means clustering method are jointly exploited to analyze these high-level features to find the best set of frames that can help accurately reconstruct the original high-quality image. After removing the geometric distortion from the selected frames, the saliency map of the average set of the selected frames is calculated and used with the original selected frames to train an end-to-end multi-scale saliency-guided deep convolutional autoencoder network to fuse the registered frames. This network uses different scales of the input frames and their saliency maps for better fusion performance. Specifically, the fusion network learns how to fuse these sets of frames and also exploit information from their saliency map to generate an image with more details of the scene. Finally, this fused image is post-processed to boost the visual quality of the output fused image. The experimental results on both synthetically and naturally distorted sequences show the superiority of our method compared to the state-of-the-art methods.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abadi, M., Barham, P., Chen, J., Chen, Z., Davis, A., Dean, J., et al. (2016). TensorFlow: A system for large-scale machine learning. Proceedings of the Operating systems Design and Implementation, 16, 265–283.
Aittala, M., & Durand, F. (2018). Burst image deblurring using permutation invariant convolutional neural networks. Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV) (pp. 731–747).
Anantrasirichai, N., Achim, A., Kingsbury, N., & Bull, D. (2013). Atmospheric turbulence mitigation using complex wavelet-based fusion. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing (TIP), 22(6), 2398–2408.
Aubailly, M., Vorontsov, M., Carhart, G., & Valley, M. (2008). Image enhancement by local information fusion with pre-processing and composed metric, Atmospheric Optics: Models, Measurements, and Target-in-the-Loop Propagation II.
Aubailly, M., Vorontsov, M., Carhart, G., & Valley, M. (2009). Automated video enhancement from a stream of atmospherically-distorted images: the lucky-region fusion approach. Atmospheric
Baig, M., Koltun, V., & Torresani, L. (2017). Learning to inpaint for image compression. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 30, 1246–1255.
Bookstein, Fred L. (1989). Principal warps: Thin-plate splines and the decomposition of deformations. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (PAMI), 11(6), 567–585.
Cai, B., Xu, X., Jia, K., Qing, C., & Tao, D. (2016). Dehazenet: An end-to-end system for single image haze removal. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing (TIP), 25(11), 5187–5198.
Chandler, D., & Hemami, S. (2007). VSNR: A wavelet-based visual signal-to-noise ratio for natural images. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing (TIP), 16(9), 2284–2298.
Chen, G., Gao, Z., Wang, Q., & Luo, Q. (2020). Blind de-convolution of images degraded by atmospheric turbulence. Applied Soft Computing, 89, 106–131.
Chen, H., & Kingsbury, N. (2011). Efficient registration of nonrigid 3-d bodies. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 21(1), 262–272.
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L., Li, K., & Fei-Fei, L. (2009). Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 248–255).
Fried, D. (1978). Probability of getting a lucky short-exposure image through turbulence. Journal of Optical Society of America, 68(12), 1651–1658.
Fu, H., Gong, M., Wang, C., Batmanghelich, K., & Tao, D. (2018). Deep ordinal regression network for monocular depth estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 2002–2011).
Gao, J., Anantrasirichai, N., & Bull, D. (2019). Atmospheric turbulence removal using convolutional neural network, arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.11350.
Godard, C., Mac A., & Brostow, G. (2017). Unsupervised monocular depth estimation with left-right consistency. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 270–279).
Gonzalez, R., & Woods, R. (2002). Digital image processing (2nd ed., Vol. 455). Publishing House of Electronics Industry.
Gopalakrishnan, V., Hu, Y., & Rajan, D. (2010). Random walks on graphs for salient object detection in images. IEEE Transactions on Image processing (TIP), 19(12), 3232–3242.
Halder, K., Tahtali, M., & Anavatti, S. (2015). Geometric correction of atmospheric turbulence-degraded video containing moving objects. Optics Express, 23(4), 5091–5101.
Harmeling, S., Hirsch, M., Sra, S., & Schölkopf, B. (2009). Online blind deconvolution for astronomical imaging. In IEEE International conference on computational photography (ICCP) (pp. 1–7).
Hyun, K., Mu Lee, K., Scholkopf, B., & Hirsch, M. (2017). Online video deblurring via dynamic temporal blending network. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (pp. 4038–4047).
Ioffe, S., & Szegedy, C. (2015). Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift, arXiv preprint arXiv:1502.03167.
John, S., & Vorontsov, M. (2005). Multiframe selective information fusion from robust error estimation theory. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing (TIP), 14(5), 577–584.
Kim, J., Sim, J., & Kim, C. (2013). Multiscale saliency detection using random walk with restart. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 24(2), 198–210.
Kingma, D., & Ba, J. (2014). Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In Proceedings of the international conference on learning representations (ICLR).
Lau, C., Souri, H., & Chellappa, R. (2020). ATFaceGAN: Single face image restoration and recognition from atmospheric turbulence. In IEEE international conference on automatic face and gesture recognition (pp. 32–39).
Lau, C., Lai, Y., & Lui, L. (2019). Restoration of atmospheric turbulence-distorted images via RPCA and quasiconformal maps. Inverse Problems, 35, 7.
Li, B., Peng, X., Wang, Z., Xu, J., & Feng, D. (2018). End-to-end united video dehazing and detection. In Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence.
Lou, Y., Kang, S., Soatto, S., & Bertozzi, A. (2013). Video stabilization of atmospheric turbulence distortion. Inverse Problem and Imaging, 7(3), 839–861.
Mannos, J., & Sakrison, D. (1974). The effects of a visual fidelity criterion of the encoding of images. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 20(4), 525–536.
Nah, S., Hyun K., & Mu Lee, K. (2017). Deep multi-scale convolutional neural network for dynamic scene deblurring. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 3883–3891).
Niu, Y., Geng, Y., Li, X., & Liu, F. (2012). Leveraging stereopsis for saliency analysis. In IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 454–461).
Noroozi, M., Chandramouli, P., & Favaro, P. (2017). Motion deblurring in the wild. In German conference on pattern recognition (pp. 65–77).
Pearson, J. (1976). Atmospheric turbulence compensation using coherent optical adaptive techniques. Applied Optics, 15(3), 622–631.
Roggemann, M., Stoudt, C., & Welsh, B. (1994). Image-spectrum signal-to-noise-ratio improvements by statistical frame selection for adaptive-optics imaging through atmospheric turbulence. Optical Engineering, 33(10), 3254–3265.
Selesnick, I., Baraniuk, R., & Kingsbury, N. (2005). The dual-tree complex wavelet transform. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 22(6), 123–151.
Shan, Q., Jia, J., & Agarwala, A. (2008). High-quality motion deblurring from a single image. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 27(3), 73.
Shimizu, M., Yoshimura, S., Tanaka, M., & Okutomi, M. (2008). Super-resolution from image sequence under influence of hot-air optical turbulence. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 1–8).
Su, S., Delbracio, M., Wang, J., Sapiro, G., Heidrich, W., & Wang, O. (2017). Deep video deblurring for hand-held cameras. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 1279–1288).
Tyson, R. (2000). Introduction to Adaptive Optics (Vol. 41). SPIE press.
Wang, W., Wang, Y., Huang, Q., & Gao, W. (2010). Measuring visual saliency by site entropy rate. In IEEE Computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 2368–2375).
Wang, Z., Bovik, A., Sheikh, H., & Simoncelli, E. (2004). Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing (TIP), 13(4), 600–612.
Wang, M., Mai, J., Cai, R., Liang, Y., & Wan, H. (2018). Single image deraining using deep convolutional networks. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 77(19), 25905–25918.
Xie, Y., Zhang, W., Tao, D., Hu, W., Qu, Y., & Wang, H. (2016). Removing turbulence effect via hybrid total variation and deformation-guided kernel regression. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing (TIP), 25(10), 4943–4958.
Xue, B., Liu, Y., Cui, L., Bai, X., Cao, X., & Zhou, F. (2016). Video stabilization in atmosphere turbulent conditions based on the Laplacian-Riesz pyramid. Optics Express, 24(24), 28092–28103.
Yan, R., & Shao, L. (2016). Blind image blur estimation via deep learning. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing (TIP), 25(4), 1910–1921.
Yitzhaky, Y., Dror, I., & Kopeika, N. (1997). Restoration of atmospherically blurred images according to weather-predicted atmospheric modulation transfer function. Optical Engineering, 36, 3064–3072.
Zhang, C., Xue, B., Zhou, F., & Xiong, W. (2018). removing atmospheric turbulence effects in unified complex steerable pyramid framework. IEEE Access, 6, 75855–75867.
Zhang, K., Zuo, W., Chen, Y., Meng, D., & Zhang, L. (2017). Beyond a gaussian denoiser: Residual learning of deep cnn for image denoising. IEEE transactions on image processing, 26(7), 3142–3155.
Zhu, X., & Milanfar, P. (2010). Image reconstruction from videos distorted by atmospheric turbulence. In Visual Information Processing and Communication.
Zhu, X., & Milanfar, P. (2011). Stabilizing and deblurring atmospheric turbulence. In IEEE International conference on computational photography (ICCP) (pp. 1–8).
Zhu, X., & Milanfar, P. (2012). Removing atmospheric turbulence via space-invariant deconvolution. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (PAMI), 35(1), 157–170.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Yasuhiro Mukaigawa.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fazlali, H., Shirani, S., BradforSd, M. et al. Atmospheric Turbulence Removal in Long-Range Imaging Using a Data-Driven-Based Approach. Int J Comput Vis 130, 1031–1049 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-022-01584-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-022-01584-x