Abstract
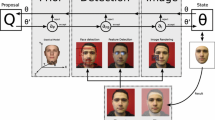
Faces in natural images are often occluded by a variety of objects. We propose a fully automated, probabilistic and occlusion-aware 3D morphable face model adaptation framework following an analysis-by-synthesis setup. The key idea is to segment the image into regions explained by separate models. Our framework includes a 3D morphable face model, a prototype-based beard model and a simple model for occlusions and background regions. The segmentation and all the model parameters have to be inferred from the single target image. Face model adaptation and segmentation are solved jointly using an expectation–maximization-like procedure. During the E-step, we update the segmentation and in the M-step the face model parameters are updated. For face model adaptation we apply a stochastic sampling strategy based on the Metropolis–Hastings algorithm. For segmentation, we apply loopy belief propagation for inference in a Markov random field. Illumination estimation is critical for occlusion handling. Our combined segmentation and model adaptation needs a proper initialization of the illumination parameters. We propose a RANSAC-based robust illumination estimation technique. By applying this method to a large face image database we obtain a first empirical distribution of real-world illumination conditions. The obtained empirical distribution is made publicly available and can be used as prior in probabilistic frameworks, for regularization or to synthesize data for deep learning methods.





















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Scalismo—a scalable image analysis and shape modelling software framework available as open source under https://github.com/unibas-gravis/scalismo.
Scalismo-faces—famework for shape modeling and model-based image analysis available as Open Source under https://github.com/unibas-gravis/scalismo-faces.
Tutorials on our Probabilistic Morphable Model framework http://gravis.dmi.unibas.ch/PMM/.
References
Aldrian, O., & Smith, W. A. (2013). Inverse rendering of faces with a 3D morphable model. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 35(5), 1080–1093.
Arthur, D., & Vassilvitskii, S. (2007). K-means++: The advantages of careful seeding. In Proceedings of the 18th annual ACM–SIAM symposium on discrete algorithms (pp. 1027–1035). Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics.
Barron, J. T., & Malik, J. (2015). Shape, illumination, and reflectance from shading. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 37(8), 1670–1687.
Basri, R., & Jacobs, D. W. (2003). Lambertian reflectance and linear subspaces. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 25(2), 218–233.
Blanz, V., & Vetter, T. (1999). A morphable model for the synthesis of 3D faces. In SIGGRAPH’99 proceedings of the 26th annual conference on computer graphics and interactive techniques (pp. 187–194). ACM Press.
Chan, T. F., & Vese, L. A. (2001). Active contours without edges. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 10(2), 266–277.
Dalca, A. V., Sridharan, R., Cloonan, L., Fitzpatrick, K. M., Kanakis, A., Furie, K. L., Rosand, J., Wu, O., Sabuncu, M., Rost, N. S., et al. (2014). Segmentation of cerebrovascular pathologies in stroke patients with spatial and shape priors. In Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention: MICCAI international conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention (Vol. 17, p. 773), NIH Public Access.
De Smet, M., Fransens, R., Van Gool, L. (2006). A generalized EM approach for 3D model based face recognition under occlusions. In 2006 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (Vol. 2, pp. 1423–1430). IEEE.
Dempster, A. P., Laird, N. M., & Rubin, D. B. (1977). Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B (Methodological), 39, 1–38.
Egger, B. (2017). Semantic morphable models. PhD thesis, University of Basel.
Egger, B., Schneider, A., Blumer, C., Forster, A., Schönborn, S., & Vetter, T. (2016). Occlusion-aware 3D morphable face models. In British machine vision conference (BMVC).
Egger, B., Schönborn, S., Blumer, C., Egger, B., Schönborn, S., Blumer, C., & Vetter, T. (2017). Probabilistic morphable models. In Statistical shape and deformation analysis: Methods, implementation and applications (p. 115).
Egger, B., Schönborn, S., Forster, A., & Vetter, T. (2014). Pose normalization for eye gaze estimation and facial attribute description from still images. In German conference on pattern recognition (pp. 317–327). Springer.
Fischler, M. A., & Bolles, R. C. (1981). Random sample consensus: A paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Communications of the ACM, 24(6), 381–395.
Gerig, T., Morel-Forster, A., Blumer, C., Egger, B., Lüthi M, Schönborn, S., & Vetter, T. (2017). Morphable face models—An open framework. Preprint arXiv:1709.08398.
Gross, R., Matthews, I., Cohn, J., Kanade, T., & Baker, S. (2010). Multi-PIE. Image and Vision Computing, 28(5), 807–813.
Huang, G. B., Ramesh, M., Berg, T., & Learned-Miller, E. (2007). Labeled faces in the wild: A database for studying face recognition in unconstrained environments. Tech. rep. 07-49, University of Massachusetts, Amherst.
Huang, R., Pavlovic, V., & Metaxas, D. N. (2004). A graphical model framework for coupling mrfs and deformable models. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2004. CVPR 2004 (Vol. 2, pp. II–739). IEEE.
Huber, P., Feng, Z. H., Christmas, W., Kittler, J., & Rätsch M (2015). Fitting 3D morphable face models using local features. In 2015 IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP) (pp. 1195–1199). IEEE.
Jourabloo, A., & Liu, X. (2016). Large-pose face alignment via CNN-based dense 3D model fitting. In CVPR.
Kortylewski, A. (2017). Model-based image analysis for forensic shoe print recognition. PhD thesis.
Kortylewski, A., Egger, B., Schneider, A., Gerig, T., Forster, A., & Vetter, T. (2017). Empirically analyzing the effect of dataset biases on deep face recognition systems. Preprint arXiv:1712.01619.
Köstinger, M., Wohlhart, P., Roth, P. M., & Bischof, H. (2011). Annotated facial landmarks in the wild: A large-scale, real-world database for facial landmark localization. In 2011 IEEE international conference on computer vision workshops (ICCV workshops) (pp. 2144–2151).
Kulkarni, T. D., Kohli, P., Tenenbaum, J. B., & Mansinghka, V. (2015) Picture: A probabilistic programming language for scene perception. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 4390–4399).
Le, T. H. N., Luu, K., & Savvides, M. (2015). Fast and robust self-training beard/moustache detection and segmentation. In 2015 international conference on biometrics (ICB) (pp. 507–512). IEEE.
Lüthi, M., Blanc, R., Albrecht, T., Gass, T., Goksel, O., Buchler, P., et al. (2012). Statismo—A framework for PCA based statistical models. The Insight Journal, 1, 1–18.
Maninchedda, F., Häne, C., Jacquet, B., Delaunoy, A., & Pollefeys, M. (2016). Semantic 3D reconstruction of heads. In European conference on computer vision (pp. 667–683). Springer.
Marschner, S. R., & Greenberg, D. P. (1997). Inverse lighting for photography. Color and Imaging Conference, Society for Imaging Science and Technology, 1997, 262–265.
Martinez, A. M., & Benavente, R. (1998). The AR face database. CVC technical report 24.
Morel-Forster, A. (2017). Generative shape and image analysis by combining Gaussian processes and MCMC sampling. PhD Thesis, University of Basel, Faculty of Science.
Murphy, K. P., Weiss, Y., & Jordan, M. I. (1999). Loopy belief propagation for approximate inference: An empirical study. In Proceedings of the 15th conference on uncertainty in artificial intelligence. (pp. 467–475). Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.
Murphy-Chutorian, E., & Trivedi, M. M. (2009). Head pose estimation in computer vision: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 31(4), 607–626.
Nguyen, M. H., Lalonde, J. F., Efros, A. A., & De la Torre, F. (2008) Image-based shaving. In Computer graphics forum (Vol. 27, pp. 627–635). Wiley Online Library.
Paysan, P., Knothe, R., Amberg, B., Romdhani, S., & Vetter, T. (2009). A 3D face model for pose and illumination invariant face recognition. In Proceedings of the 6th IEEE international conference on advanced video and signal based surveillance (AVSS) (pp 296–301). IEEE.
Pierrard, J. S., & Vetter, T. (2007). Skin detail analysis for face recognition. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2007. CVPR’07 (pp. 1–8). IEEE.
Ramamoorthi, R., & Hanrahan, P. (2001). An efficient representation for irradiance environment maps. In Proceedings of the 28th annual conference on computer graphics and interactive techniques (pp. 497–500). ACM.
Richardson, E., Sela, M., & Kimmel, R. (2016). 3D face reconstruction by learning from synthetic data. Preprint arXiv:1609.04387.
Romdhani, S., & Vetter, T. (2003). Efficient, robust and accurate fitting of a 3D morphable model. In 2003. Proceedings. 9th IEEE international conference on computer vision (pp. 59–66). IEEE.
Saito, S., Li, T., & Li, H. (2016). Real-time facial segmentation and performance capture from RGB input. In B. Leibe, J. Matas, N. Sebe, & M. Welling (Eds.), Computer vision—ECCV 2016: 14th European conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, October 11–14, 2016, Proceedings, Part VIII (pp. 244–261). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Schneider, A., Schönborn, S., Egger B, Frobeen, L., & Vetter, T. (2017). Efficient global illumination for morphable models. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 3865–3873).
Schönborn, S., Egger, B., Morel-Forster, A., & Vetter, T. (2017). Markov chain Monte Carlo for automated face image analysis. International Journal of Computer Vision, 123, 160–183.
Schönborn, S., Forster, A., Egger, B., & Vetter, T. (2013). A Monte Carlo strategy to integrate detection and model-based face analysis. In J. Weickert, M. Hein, & B. Schiele (Eds.), Pattern recognition (pp. 101–110). Berlin: Springer.
Shahlaei, D., & Blanz, V. (2015). Realistic inverse lighting from a single 2D image of a face, taken under unknown and complex lighting. In 2015 11th IEEE international conference and workshops on automatic face and gesture recognition (FG) (Vol. 1, pp. 1–8). IEEE.
Tewari, A., Zollhöfer M, Kim, H., Garrido, P., Bernard, F., Pérez, P., & Theobalt, C. (2017). Mofa: Model-based deep convolutional face autoencoder for unsupervised monocular reconstruction. Preprint arXiv:1703.10580.
Tu, Z., Chen, X., Yuille, A. L., & Zhu, S. C. (2005). Image parsing: Unifying segmentation, detection, and recognition. International Journal of Computer Vision, 63(2), 113–140.
Uřičář, M., Franc, V., Thomas, D., Akihiro, S., & Hlaváč, V. (2015). Real-time multi-view facial landmark detector learned by the structured output SVM. In 11th IEEE international conference and workshops on automatic face and gesture recognition (FG) (Vol. 02, pp. 1–8).
Wang, Y., Liu, Z., Hua, G., Wen, Z., Zhang, Z., & Samaras, D. (2007). Face re-lighting from a single image under harsh lighting conditions. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2007. CVPR’07 (pp. 1–8). IEEE.
Yildirim, I., Janner, M., Belledonne, M., Wallraven, C., Freiwald, W. A., & Tenenbaum, J. B. (2017). Causal and compositional generative models in online perception. In To be published at 39th annual conference of the cognitive science society.
Zhu, X., Lei, Z., Liu, X., Shi, H., & Li, S. Z. (2016). Face alignment across large poses: A 3D solution. In CVPR.
Zhu, X., Yan, J., Yi, D., Lei, Z., & Li, S. (2015). Discriminative 3D morphable model fitting. In Proceedings of 11th IEEE international conference on automatic face and gesture recognition FG2015. Ljubljana.
Zivanov, J., Forster, A., Schönborn, S., & Vetter, T. (2013). Human face shape analysis under spherical harmonics illumination considering self occlusion. In ICB-2013, 6th international conference on biometrics. Madrid.
Acknowledgements
Funding was provided by Schweizerischer Nationalfonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung (Grant No. SNF153297).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Edwin Hancock, Richard Wilson, Will Smith, Adrian Bors and Nick Pears.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Egger, B., Schönborn, S., Schneider, A. et al. Occlusion-Aware 3D Morphable Models and an Illumination Prior for Face Image Analysis. Int J Comput Vis 126, 1269–1287 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-018-1064-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-018-1064-8