Abstract
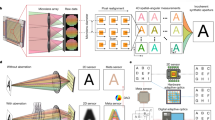
This paper introduces a 3D imaging framework that combines high-resolution photometric stereo and low-resolution depth. Our approach targets imaging scenarios based on either macro-lens photography combined with focal stacking or a large-format camera that are able to image objects with more than 600 samples per mm\(^2\). These imaging techniques allow photometric stereo algorithms to obtain surface normals at resolutions that far surpass corresponding depth values obtained with traditional approaches such as structured-light, passive stereo, or depth-from-focus. Our work offers two contributions for 3D imaging based on these scenarios. The first is a multi-resolution, patched-based surface reconstruction scheme that can robustly handle the significant resolution difference between our surface normals and depth samples. The second is a method to improve the initial normal estimation by using all the available focal information for images obtained using a focal stacking technique.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Also see http://carlos-hernandez.org/gallery/.
References
Agarwala, A., Dontcheva, M., Agrawala, M., Drucker, S., Colburn, A., Curless, B., et al. (2004). Interactive digital photomontage. ACM Transactions on Graphics (SIGGRAPH), 23(3), 294–302.
Agrawal, A., Raskar, R.,& Chellappa, R. (2006). What is the range of surface reconstructions from a gradient field? In European conference on computer vision (ECCV). Graz, Austria: Springer.
Agrawal, A., Xu, Y.,& Raskar, R. (2009). Invertible motion blur in video. ACM Transactions on Graphics (SIGGRAPH), 28(3), 1–8.
Anagramm and Digital Reproduction (1998). http://www.linhofstudio.com. Accesed 1 August 2011.
Banerjee, S., Sastry, P.,& Venkatesh, Y. (1992). Surface reconstruction from disparate shading: An integration of shape-from-shading and stereopsis. In 11th IAPR International conference on pattern recognition. The Hague, The Netherlands: IEEE Computer Society.
Bernardini, F., Rushmeier, H., Martin, I. M., Mittleman, J.,& Taubin, G. (2002). Building a digital model of Michelangelo’s Florentine Pieta. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, 22(1), 59–67.
Chen, C. Y., Klette, R.,& Chen, C. F. (2003). Shape from photometric stereo and contours. In Proceedings of computer analysis of images patterns (CAIP). Groningen, The Netherlands: Springer.
Cignoni, P., Rocchini, C.,& Scopigno, R. (1998). Metro: Measuring error on simplified surfaces. Computer Graphics Forum, 17(2), 167–174.
Darrell, T.,& Wohn, K. (1988). Pyramid based depth from focus. In Computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). Ann Arbor, MI: IEEE Computer Society.
Fua, P.,& Leclerc, Y. G. (1994). Using 3-dimensional meshes to combine image-based and geometry-based constraints. In European conference on computer vision (ECCV). Stockholm, Sweden: Springer.
Hausler, G. (1972). A method to increase the depth of focus by two step image processing. Optics Communications, 6(1), 38–42.
Hernández, C., Vogiatzis, G.,& Cipolla, R. (2008). Multi-view photometric stereo. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 30(3), 548–554.
Higo, T., Matsushita, Y., Joshi, N.,& Ikeuchi, K. (2009). A hand-held photometric stereo camera for 3D modeling. In Computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). Miami, FL: IEEE Computer Society.
Horn, B.,& Brooks, M. (1989). Shape from shading. Cambridge: MIT Press.
Ikeuchi, K. (1987). Determining a depth map using a dual photometric stereo. International Journal of Robotics Research, 6(1), 15–31.
Lange, H. (1999). Advances in the cooperation of shape from shading and stereo vision. In Proceedings 3DIM. Ottawa, Canada: IEEE Computer Society.
Lu, Z., Tai, Y. W., Ben-Ezra, M.,& Brown, M. S. (2010). A framework for ultra high resolution 3D imaging. In Computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). San Francisco, CA: IEEE Computer Society.
Malik, A. S.,& Choi, T. S. (2008). A novel algorithm for estimation of depth map using image focus for 3d shape recovery in the presence of noise. Pattern Recognition, 41(7), 2200–2225.
Nayar, S. K.,& Nakagawa, Y. (1994). Shape from focus. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 16(8), 824–831.
Nayar, S. K., Fang, X. S.,& Boult, T. (1997). Separation of reflection components using color and polarization. International Journal of Computer Vision, 21(3), 163–186.
Nehab, D., Rusinkiewicz, S., Davis, J.,& Ramamoorthi, R. (2005). Efficiently combining positions and normals for precise 3d geometry. ACM Transactions on Graphics (SIGGRAPH), 24(3), 536–543.
Reid, J. K.,& Scott, J. A. (2009). An out-of-core sparse cholesky solver. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, 36(2), 1–33.
Scharstein, D.,& Szeliski, R. (2002). A taxonomy and evaluation of dense two-frame stereo correspondence algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 47(1–3), 7–42.
Scharstein, D.,& Szeliski, R. (2003). High-accuracy stereo depth maps using structured light. In Computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). Madison, WI: IEEE Computer Society.
Seitz, S. M., Curless, B., Diebel, J., Scharstein, D.,& Szeliski, R. (2006). A comparison and evaluation of multi-view stereo reconstruction algorithms. In Computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). New York, NY: IEEE Computer Society.
Terzopoulos, D. (1988). The computation of visible-surface representations. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 10(4), 417–438.
Vlasic, D., Peers, P., Baran, I., Debevec, P., Popovi’c, J., Rusinkiewicz, S., et al. (2009). Dynamic shape capture using multi-view photometric stereo. ACM Transactions on Graphics (SIGGRAPH-ASIA), 28(5), 1–11.
Wholer, C. (2009). 3D computer vision: efficient methods and applications. New York: Springer.
Woodham, R. J. (1980). Photometric method for determining surface orientation from multiple images. Optical Engineering, 19(1), 139–144.
Wu, T. P.,& Tang, C. K. (2006). Visible surface reconstruction from normals with discontinuity consideration. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).
Wu, T. P., Sun, J., Tang, C. K.,& Shum, H. Y. (2008). Interactive normal reconstruction from a single image. ACM Transactions on Graphics (SIGGRAPH-ASIA), 27(5), 1–9.
Xiong, Y.,& Shafer, S. (1993). Depth from focusing and defocusing. In Computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). New York, NY: IEEE Computer Society.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Z., Tai, YW., Deng, F. et al. A 3D Imaging Framework Based on High-Resolution Photometric-Stereo and Low-Resolution Depth. Int J Comput Vis 102, 18–32 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-012-0589-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-012-0589-5