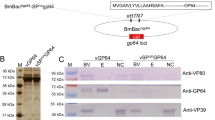
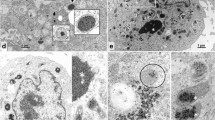
Abstract
Mitochondria play an essential role in intracellular energy metabolism. This study described the involvement of Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus (BmNPV) GP37 (BmGP37) in host mitochondria. Herein, the proteins associated with host mitochondria isolated from BmNPV-infected or mock-infected cells by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis were compared. One mitochondria-associated protein in virus-infected cells was identified as BmGP37 by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis. Furthermore, the BmGP37 antibodies were generated, which could react specifically with BmGP37 in the BmNPV-infected BmN cells. Western blot experiments showed that BmGP37 was expressed at 18 h post-infection and was verified as a mitochondria-associated protein. Immunofluorescence analysis demonstrated that BmGP37 localized to the host mitochondria during BmNPV infection. Furthermore, western blot analysis revealed that BmGP37 is a novel component protein of the occlusion-derived virus (ODV) of BmNPV. The present results indicated that BmGP37 is one of the ODV-associated proteins and may have important roles in host mitochondria during BmNPV infection.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Jehle JA, Blissard GW, Bonning BC, Cory JS, Herniou EA, Rohrmann GF, Theilmann DA, Vlak JM (2006) On the classification and nomenclature of baculoviruses: a proposal for revision. Arch Virol 151:1257–1266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-006-0763-6
Herniou EA, Luque T, Chen X, Vlak JM, Winstanley D, Cory JS, O’Reilly DR (2001) Use of whole genome sequence data to infer baculovirus phylogeny. J Virol 75:8117–8126. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.75.17.8117-8126.2001
Rohrmann GF (2013) Baculovirus Molecular Biology, 4th ed; National Center for Biotechnology Information: Bethesda (MD), USA, 2019, Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK543458/
Clem RJ (2005) The role of apoptosis in defense against baculovirus infection in insects. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 289:113–129. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-27320-4_5
Ikeda M, Kobayashi M (1999) Cell-cycle perturbation in Sf9 cells infected with Autographa californica nucleopolyhedrovirus. Virology 258:176–188. https://doi.org/10.1006/viro.1999.9706
Iwanaga M, Shimada T, Kobayashi M, Kang W (2007) Identification of differentially expressed host genes in Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus infected cells by using subtractive hybridization. Appl Entomol Zool 42:151–159. https://doi.org/10.1303/aez.2007.151
Nobiron I, O’Reilly DR, Olszewski JA (2003) Autographa californica nucleopolyhedrovirus infection of Spodoptera frugiperda cells: a global analysis of host gene regulation during infection, using a differential display approach. J Gen Virol 84:3029–3039. https://doi.org/10.1099/vir.0.19270-0
Xue J, Qiao N, Zhang W, Cheng RL, Zhang XQ, Bao YY, Xu YP, Gu LZ, Han JJ, Zhang CX (2012) Dynamic interactions between Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus and its host cells revealed by transcriptome analysis. J Virol 86:7345–7359. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.07217-12
Cha HJ, Dalal NG, Pham MQ, Kramer SF, Vakharia VN, Bentley WE (2002) Monitoring foreign protein expression under baculovirus p10 and polh promoters in insect larvae. Biotechniques 32(5):986–992. https://doi.org/10.2144/02325bm02
Bernal V, Carinhas N, Yokomizo AY, Carrondo MJT, Alves PM (2009) Cell density effect in the baculovirus-insect cells system: A quantitative analysis of energetic metabolism. Biotechnol Bioeng 104:162–180. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.22364
Lin YH, Tai CC, Brož V, Tang CK, Chen P, Wu CP, Li CH, Wu YL (2020) Adenosine receptor modulates permissiveness of baculovirus (budded virus) infection via regulation of energy metabolism in Bombyx mori. Front Immunol 11:763. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.00763
Iwanaga M, Kurihara M, Kobayashi M, Kang W (2002) Characterization of Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus orf68 gene that encodes a novel structural protein of budded virus. Virology 297:39–47. https://doi.org/10.1006/viro.2002.1443
Gomi S, Majima K, Maeda S (1999) Sequence analysis of the genome of Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus. J Gen Virol 80:1323–1337. https://doi.org/10.1099/0022-1317-80-5-1323
Iwanaga M, Takaya K, Katsuma S, Ote M, Tanaka S, Kamita SG, Kang W, Shimada T, Kobayashi M (2004) Expression profiling of baculovirus genes in permissive and nonpermissive cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 323:599–614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.08.114
Ogata M, Kameshima Y, Hattori T, Michishita K, Suzuki T, Kawagishi H, Totani K, Hiratake J, Usui T (2010) Lactosylamidine-based affinity purification for cellulolytic enzymes EG I and CBH I from Hypocrea jecorina and their properties. Carbohydr Res 345:2623–2629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2010.10.015
Tanaka Y, Suzuki T, Nakamura L, Nakamura M, Ebihara S, Kurokura T, Iigo M, Dohra H, Habu N, Konno N (2019) A GH family 28 endo-polygalacturonase from the brown-rot fungus Fomitopsis palustris: Purification, gene cloning, enzymatic characterization and effects of oxalate. Int J Biol Macromol 123:108–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.004
Iwanaga M, Shibano Y, Ohsawa T, Fujita T, Katsuma S, Kawasaki H (2014) Involvement of HSC70-4 and other inducible HSPs in Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus infection. Virus Res 179:113–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2013.10.028
Katou Y, Ikeda M, Kobayashi M (2006) Abortive replication of Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus in Sf9 and High Five cells: Defective nuclear transport of the virions. Virology 347:455–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2005.11.043
Gross CH, Wolgamot GM, Russell RL, Pearson MN, Rohrmann GF (1993) A 37-kilodalton glycoprotein from a baculovirus of Orgyia pseudotsugata is localized to cytoplasmic inclusion bodies. J Virol 67:469–475. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.67.1.469-475.1993
Phanis CG, Miller DP, Cassar SC, Tristem M, Thiem SM, O’Reilly DR (1999) Identification and expression of two baculovirus gp37 genes. J Gen Virol 80:1823–1831. https://doi.org/10.1099/0022-1317-80-7-1823
Copeland DE, Dalton AJ (1959) An association between mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum in cells of the pseudobranch gland of a teleost. J Biophys Biochem Cytol 25:393–396. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.5.3.393
Friedman JR, Lackner LL, West M, DiBenedetto JR, Nunnari J, Voeltz GK (2011) ER tubules mark sites of mitochondrial division. Science 334:358–362. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1207385
Zhou R, Yazdi AS, Menu P, Tschopp J (2011) A role for mitochondria in NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Nature 469:221–225. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09663
Hamasaki M, Furuta N, Matsuda A, Nezu A, Yamamoto A, Fujita N, Oomori H, Noda T, Haraguchi T, Hiraoka Y, Amano A, Yoshimori T (2013) Autophagosomes form at ER-mitochondria contact sites. Nature 495:389–393. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11910
Booth DM, Enyedi B, Geiszt M, Várnai P, Hajnóczky G (2016) Redox nanodomains are induced by and control calcium signaling at the ER-mitochondrial interface. Mol Cell 63:240–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2016.05.040
Cheng XW, Krell PJ, Arif BM (2001) P34.8 (GP37) is not essential for baculovirus replication. J Gen Virol 82:299–305. https://doi.org/10.1099/0022-1317-82-2-299
Zhang SZ, Zhu LB, Yu D, You LL, Wang J, Cao HH, Liu YX, Wang YL, Kong X, Toufeeq S, Xu JP (2020) Identification and functional analysis of BmNPV-interacting proteins from Bombyx mori (Lepidoptera) larval midgut based on subcellular protein levels. Front Microbiol 30:1481. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.01481
Chacinska A, Koehler CM, Milenkovic D, Lithgow T, Pfanner N (2009) Importing mitochondrial proteins: machineries and mechanisms. Cell 138:628–644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.08.005
Abe Y, Shodai T, Muto T, Mihara K, Torii H, Nishikawa S, Endo T, Kohda D (2000) Structural basis of presequence recognition by the mitochondrial protein import receptor Tom20. Cell 100:551–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80691-1
Yamano K, Yatsukawa Y, Esaki M, Hobbs AE, Jensen RE, Endo T (2008) Tom20 and Tom22 share the common signal recognition pathway in mitochondrial protein import. J Biol Chem 283:3799–3807. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M708339200
Fukasawa Y, Tsuji J, Fu SC, Tomii K, Horton P, Imai K (2015) MitoFates: improved prediction of mitochondrial targeting sequences and their cleavage sites. Mol Cell Proteomics 14:1113–1126. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M114.043083
Vialard JE, Yuen L, Richardson CD (1990) Identification and characterization of a baculovirus occlusion body glycoprotein which resembles spheroidin, an entomopoxvirus protein. J Virol 64:5804–5811. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.64.12.5804-5811.1990
Mitsuhashi W, Sato M, Hirai Y (2000) Involvement of spindles of an entomopoxvirus (EPV) in infectivity of the EPVs to their host insect. Arch Virol 145:1465–1471. https://doi.org/10.1007/s007050070103
Takemoto Y, Mitsuhashi W, Murakami R, Konishi H, Miyamoto K (2008) The N-terminal region of an entomopoxvirus fusolin is essential for the enhancement of peroral infection, whereas the C-terminal region is eliminated in digestive juice. J Virol 82:12406–12415. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01605-08
Wijonarko A, Hukuhara T (1998) Detection of a virus enhancing factor in the spheroid, spindle, and virion of an entomopoxvirus. J Invertebr Pathol 72:82–86. https://doi.org/10.1006/jipa.1998.4756
Li Z, Li C, Yang K, Wang L, Yin C, Gong Y, Pang Y (2003) Characterization of a chitin-binding protein GP37 of Spodoptera litura multicapsid nucleopolyhedrovirus. Virus Res 96:113–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-1702(03)00179-5
Wang P, Granados RR (1997) An intestinal mucin is the target substrate for a baculovirus enhancin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:6977–6982. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.94.13.6977
Liu X, Fang W, Fan R, Zhang L, Lei C, Zhang J, Nian W, Dou T, An S, Zhou L, Sun X (2019) Granulovirus GP37 facilitated ODVs cross insect peritrophic membranes and fuse with epithelia. Toxins (Basel) 11:145. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11030145
Liu X, Ma X, Lei C, Xiao Y, Zhang Z, Sun X (2011) Synergistic effects of Cydia pomonella granulovirus GP37 on the infectivity of nucleopolyhedroviruses and the lethality of Bacillus thuringiensis. Arch Virol 156:1707–1715. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-011-1039-3
Li X, Barrett J, Pang A, Klose RJ, Krell PJ, Arif BM (2000) Characterization of an overexpressed spindle protein during a baculovirus infection. Virology 268:56–67. https://doi.org/10.1006/viro.1999.0138
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from JSPS KAKENHI (grant no. 20K06069) to MI. The authors are grateful to Dr. Ikeda for the kind gift of anti-VP39 antibody. The authors would like to thank Enago (www.enago.jp) for the English language review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. The experiments were conceived and designed by SF and MI. The experiments were performed by SF, KF, TS, SK, and MI. The paper was written by MI and SK.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was performed in accordance with institutional committee protocols of Utsunomiya University.
Informed consent
There were no human participants in this study.
Research involving human and animal participants
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Edited by Sassan Asgari.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fujimoto, S., Fujimaki, K., Suzuki, T. et al. Expression and localization of Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus GP37. Virus Genes 59, 457–463 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-023-01983-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-023-01983-3