Abstract
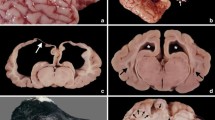
Akabane virus (AKAV) is known as a major teratogenic agent of ruminant fetuses. In this study, we investigated the relationship between porcine abnormal deliveries and AKAV by serology, pathology, and virology investigations using specimens from 16 stillborn fetuses delivered in southern Japan between 2013 and 2015. The major clinical manifestations in stillborn fetuses were hydranencephaly, arthrogryposis, spinal curvature, and both skeletal muscle and subcutaneous edema. Histologic examination of the specimens identified atrophy of skeletal muscle fibers accompanied by adipose replacement. Nonsuppurative encephalomyelitis and decreased neuronal density in the ventral horn of the spinal cord were shown in two separate fetuses, respectively. Neutralizing antibody titers to AKAV were detected in most of the tested fetuses (13/16). The AKAV sequences detected in the affected fetuses in 2013 and 2015 were highly identical and closely related to Japanese AKAV isolates which were isolated in 2013 and sorted into genogroup I of AKAV. Immunohistochemistry visualized AKAV antigens in the neuronal cells of the central nervous system of the fetuses. These findings indicate that AKAV was involved in the birth of abnormal piglets at the affected farm. The clinical manifestations and histopathological features in the stillborn fetuses were very similar to those in ruminant neonates affected by AKAV. To avoid misdiagnosis and to evaluate the precise impact of AKAV on pig reproduction, AKAV should be considered in differential diagnoses of reproductive failures in pigs.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data supporting the results of this study can be provided when requested with a valid reason.
References
Akashi H, Kaku Y, Kong XG, Pang H (1997) Sequence determination and phylogenetic analysis of the Akabane bunyavirus S RNA genome segment. J Gen Virol 78:2847–2851. https://doi.org/10.1099/0022-1317-78-11-2847
Althouse GC, Kauffold J, Rossow S (2019) Disease of the reproduction system. In: Zimmerman JJ, Karriker LA, Ramirez A, Schwartz KJ, Stevenson GW, Zhang J (eds) Diseases of swine, 11th edn. Wiley-Blackwell, Hoboken, pp 373–392
Elliott RM, Blakqori G (2011) Molecular biology of orthobunyaviruses. In: Phyusnin A, Elliott RM (eds) Bunyaviridae. Caister, Norfolk, pp 1–39
Haughey KG, Hartley WJ, Della-Porta AJ, Murray MD (1988) Akabane disease in sheep. Aust Vet J 65:136–140. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-0813.1988.tb14440.x
Hirashima Y, Kitahara S, Kato T, Shirafuji H, Tanaka S, Yanase T (2017) Congenital malformations of calves infected with Shamonda virus, southern Japan. Emerg Infect Dis 23:993–996. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2306.161946
Huang CC, Huang TS, Deng MC, Jong MH, Lin SY (2003) Natural infections of pigs with akabane virus. Vet Microbiol 94:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-1135(03)00062-2
Izumida A, Yasuhara H, Kubota M, Yoshiki K, Hirahara T, Kodama K, Sasaki N (1990) A survey of antibodies to arthropod-borne viruses among swine in Japan. J Jpn Vet Med Assoc 43:646–649 (in Japanese with English summary). https://doi.org/10.12935/jvma1951.43.646
Joo H, Chu RM (1999) Japanese B encephalitis. In: Straw B, D’Allaire S, Mengeling W, Taylor DJ (eds) Diseases of swine, 8th edn. Iowa State University Press, Ames, pp 173–178
Kawashima K, Tsunemitsu H, Horino R, Katsuda K, Shoji T, Onodera T, Haritani M, Murakami Y, Kubo M, Ikeda H, Kaku Y, Kimura K, Tanimura N (2003) Postweaning multisystemic wasting syndrome (PMWS) in pigs in Japan: Clinical manifestation of the diseased pigs, experimental infection of porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2), and epidemiological investigations of PCV2 and PMWS. Bull Natl Inst Anim Health 109:9–16 (in Japanese with English summary)
Kirkland PD, Barry RD, Harper PA, Zelski RZ (1988) The development of Akabane virus-induced congenital abnormalities in cattle. Vet Rec 122:582–586. https://doi.org/10.1136/vr.122.24.582
Kirkland PD (2015) Akabane virus infection. Rev Sci Tech 34:403–410. https://doi.org/10.20506/rst.34.2.2366
Kono Y, Kanno T, Shimizu M, Yamada S, Ohashi S, Nakamine M, Shirai J (1996) Nested PCR for detection and typing of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) virus in pigs. J Vet Med Sci 58:941–946. https://doi.org/10.1292/jvms.58.10_941
Kuhn JH, Adkins S, Alkhovsky SV et al (2022) 2022 taxonomic update of phylum Negarnaviricota (Riboviria: Orthornavirae), including the large orders Bunyavirales and Mononegavirales. Arch Virol 167:2857–2906. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-022-05546-z
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35:1547–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
Kurogi H, Inaba Y, Goto Y, Miura Y, Takahashi H (1975) Serologic evidence for etiologic role of Akabane virus in epizootic abortion-arthrogryposis-hydranencephaly in cattle in Japan, 1972–1974. Arch Virol 47:71–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01315594
Kurogi H, Inaba Y, Takahashi E, Sato K, Goto Y (1977a) Experimental infection of pregnant goats with Akabane virus. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 17:1–9
Kurogi H, Inaba Y, Takahashi E, Sato K, Satoda K (1977b) Congenital abnormalities in newborn calves after inoculation of pregnant cows with Akabane virus. Infect Immun 17:338–343. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.17.2.338-343.1977
Kurogi H, Akiba K, Inaba Y, Matumoto M (1987) Isolation of Akabane virus from the biting midge Culicoides oxystoma in Japan. Vet Microbiol 15:243–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-1135(87)90078-2
Lim SI, Kweon CH, Tark DS, Kim SH, Yang DK (2007) Sero-survey on Aino, Akabane, Chuzan, bovine ephemeral fever and Japanese encephalitis virus of cattle and swine in Korea. J Vet Sci 8:45–49. https://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2007.8.1.45
Maruyama S, Maruyama F, Tanaka Y, Itoh H, Uematsu N (1983) Experimental infection of pigs with Akabane virus. Uirusu 33:131–133 (in Japanese). https://doi.org/10.2222/jsv.33.131
Matsumori Y, Aizawa M, Sakai Y, Inoue D, Kodani M, Tsuha O, Beppu A, Hirashima Y, Kono R, Ohtani A, Yanase T, Shirafuji H, Kato T, Tanaka S, Yamakawa M (2018) Congenital abnormalities in calves associated with Peaton virus infection in Japan. J Vet Diagn Invest 30:855–861. https://doi.org/10.1177/1040638718796269
Morita K, Nabeshima T, Buerano CC (2015) Japanese encephalitis. Rev Sci Tech 34:441–452. https://doi.org/10.20506/rst.34.2.2370
Murakami S, Takahashi Y, Yoshida S, Fuke I, Ohmae K, Mori C, Takagi M, Takamizawa A, Okayama H (1994) Highly sensitive detection of viral RNA genomes in blood specimens by an optimized reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. J Med Virol 43:175–181. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.1890430215
Nishi D, Egashira T (2011) Serological survey of bovine ephemeral fever, Akabane, Aino, Chuzan, and Peaton viruses in swine in Saga Prefecture. J Jpn Vet Med Assoc 64:540–544 (in Japanese with English summary). https://doi.org/10.12935/jvma.64.540
Ogawa Y, Kato K, Tohya Y, Akashi H (2007) Sequence determination and functional analysis of the Akabane virus (family Bunyaviridae) L RNA segment. Arch Virol 152:971–979. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-006-0912-y
Ohashi S, Yoshida K, Yanase T, Kato T, Tsuda T (2004) Simultaneous detection of bovine arboviruses using single-tube multiplex reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. J Virol Methods 120:79–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jviromet.2004.04.006
Otani A, Iribe T, Murata F, Yanase T, Shirafuji H, Yamakawa M (2013) Application of real-time RT-PCR for diagnosis of Akabane disease. J Jpn Vet Med Assoc 66:398–402 (in Japanese with English summary). https://doi.org/10.12935/jvma.66.398
Oya A, Okuno T, Ogata T, Kobayashi I, Matsuyama T (1961) Akabane, a new arbor virus isolated in Japan. Jpn J Med Sci Biol 14:101–108. https://doi.org/10.7883/yoken1952.14.101
Parsonson IM, McPhee DA (1985) Bunyavirus pathogenesis. Adv Virus Res 30:279–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60453-4
Parsonson IM, Della-Porta AJ, Snowdon WA (1977) Congenital abnormalities in newborn lambs after infection of pregnant sheep with Akabane virus. Infect Immun 151:254–262. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.15.1.254-262.1977
Peperkamp NH, Luttikholt SJ, Dijkman R et al (2015) Ovine and bovine congenital abnormalities associated with intrauterine infection with Schmallenberg virus. Vet Pathol 52:1057–1066. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300985814560231
Soares RM, Durigon EL, Bersano JG, Richtzenhain LJ (1999) Detection of porcine parvovirus DNA by the polymerase chain reaction assay using primers to the highly conserved nonstructural protein gene, NS-1. J Virol Methods 78:191–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0166-0934(98)00177-3
Tsuda T, Yoshida K, Ohashi S, Yanase T, Sueyoshi M, Kamimura S, Misumi K, Hamana K, Sakamoto H, Yamakawa M (2004) Arthrogryposis, hydranencephaly and cerebellar hypoplasia syndrome in neonatal calves resulting from intrauterine infection with Aino virus. Vet Res 35:531–538. https://doi.org/10.1051/vetres:2004029
Wekesa SN, Inoshima Y, Murakami K, Sentsui H (2001) Genomic analysis of some Japanese isolates of Getah virus. Vet Microbiol 83:137–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-1135(01)00417-5
Yanase T, Yoshida K, Ohashi S, Kato T, Tsuda T (2003) Sequence analysis of the medium RNA segment of three Simbu serogroup viruses, Akabane, Aino, and Peaton viruses. Virus Res 93:63–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-1702(03)00066-2
Yanase T, Kato T, Kubo T, Yoshida K, Ohashi S, Yamakawa M, Miura Y, Tsuda T (2005) Isolation of bovine arboviruses from Culicoides biting midges (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) in southern Japan: 1985–2002. J Med Entomol 42:63–67. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmedent/42.1.63
Yanase T, Kato T, Hayama Y, Akiyama M, Itoh N, Horiuchi S, Hirashima Y, Shirafuji H, Yamakawa M, Tanaka S, Tsutsui T (2018) Transition of Akabane virus genogroups and its association with changes in the nature of disease in Japan. Transbound Emerg Dis 65:e434–e443. https://doi.org/10.1111/tbed.12778
Yanase T, Kato T, Hayama Y, Shirafuji H, Yamakawa M, Tanaka S (2019) Oral susceptibility of Japanese Culicoides (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) species to Akabane virus. J Med Entomol 56:533–539. https://doi.org/10.1093/jme/tjy201
Acknowledgements
We thank veterinary officers at Nagasaki Prefectural livestock hygiene service centers for excellent technical support and sampling.
Funding
This work was partially supported by a found from NARO.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: (Daisuke Inoue, Tohru Yanase); Methodology: (Daisuke Inoue, Kumiko Kimura, Tohru Yanase); Formal analysis and investigation: (Daisuke Inoue, Akimi Hayashima, Fumiko Suzuta, Yasuhiko Motomura, Yuta Kawamoto, Fumihiko Yoshino, Kotaro Morita, Yoshio Hirai, Shigeru Iwamatsu, Satoshi Nakazato, Kumiko Kimura, Tohru Yanase); Writing—original draft preparation: (Daisuke Inoue,); Writing—review and editing: (Kumiko Kimura, Tohru Yanase); Supervision: (Kumiko Kimura, Tohru Yanase).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Statement of animal rights
The use of all animals was with the consent of the participating farmers. This study was performed under guidelines provided by the animal health authority of Nagasaki Prefecture and NARO, and did not include any animal experiments or human specimens. Therefore, further approval by an ethics committee was not required.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Inoue, D., Hayashima, A., Suzuta, F. et al. Congenital malformations caused by Akabane virus in porcine fetuses in southern Japan. Vet Res Commun 48, 449–457 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-023-10230-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-023-10230-x