Abstract
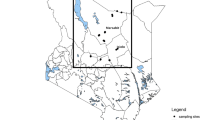
Brucellosis is a significant infection that causes abortion, decreased milk production, and sterility in livestock, which greatly affects the industry. This study aimed to determine the prevalence of Brucella in buffalo milk samples across various regions of Iran, utilizing serological, molecular, and cultural analyses. A total of 1860 buffalo milk samples were collected from industrial, semi-industrial, and traditional buffalo farms in four major buffalo breeding provinces. The milk ring test agglutination test (MRT) was initially conducted on all milk samples, followed by culture and molecular testing for positive and negative samples in MRT. The study revealed positive results for the presence of Brucella DNA in various provinces of Iran. The MRT had a relatively low sensitivity, with results ranging from 0 to 0.7% in different provinces. However, the AMOS PCR method showed a significantly higher presence of Brucella DNA, ranging from 13 to 46% in these provinces. The highest abundance of Brucella bacterial DNA was found in Ardabil province, while the lowest was in West Azerbaijan province. Brucella abortus was the most commonly detected bacteria, followed by Brucella melitensis. Interestingly, the B. abortus vaccine strain RB51 was detected in 26.3% of positive samples of B. abortus. The culture assay of milk samples further confirmed the presence of B. melitensis biovar 1 in one sample from Khuzestan province. Overall, the study emphasizes that the AMOS PCR method is the most sensitive in detecting Brucella-exposed milk, while the sensitivity of milk sample culture and MRT is relatively lower.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data and materials are available upon request.
Data Availability
The data supporting the results reported in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
References
Abbas B, Aldeewan A (2009) Occurrence and epidemiology of Brucella spp. in raw milk samples at Basrah province, Iraq. Bulg J Vet Med 12:136–142
Adams L, Templeton J (1998) Genetic resistance to bacterial diseases of animals. Rev sci tech 17:200–219. https://doi.org/10.20506/rst.17.1.1085
Adone R, Ciuchini F, Cerri D, Andreani E, Lillini E (1998) Isolation of Brucella melitensis biovar 1 from milk samples of seropositive buffaloes [Sicily]. Selezione Veterinaria (Italy)
Almashhadany D (2019) The significance of milk ring test for identifying Brucella antibodies in cows and buffaloes’ raw milk at Erbil governorate, Kurdistan region, Iraq. Iraqi J Vet Sci 33:395–400. https://doi.org/10.33899/ijvs.2019.163085
Alton G, Maw J, Rogerson B, McPherson G (1975) The serological diagnosis of bovine brucellosis: an evaluation of the complement fixation, serum agglutination and rose bengal tests. Aust Vet J 51(2):57–63. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-0813.1975.tb09404.x
Amoroso MG, Salzano C, Cioffi B, Napoletano M, Garofalo F, Guarino A, Fusco G (2011) Validation of a real-time PCR assay for fast and sensitive quantification of Brucella spp. in water buffalo milk. Food Control 22:1466–1470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2011.03.003
Averaimo D, De Massis F, Savini G, Garofolo G, Sacchini F, Abass A, Tittarelli M, Migliorati G, Petrini A (2022) Detection of Brucella abortus Vaccine strain RB51 in Water Buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) milk. Pathogens 11:748. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11070748
Azarkamand B, Pourmahdi Borujeni M, Gharibi D, Ghorbanpour M (2017) Comparison of serological methods for the diagnosis of brucellosis in water buffalo. Iran J Vet Res 13:5–12. https://doi.org/10.22055/IVJ.2017.36718.1612
Baltazar-Pérez J, Utrera-Quintana F, Camacho-Ronquillo J, González-Garduño R, Jiménez-Cortez H, Villa-Mancera A (2022) Prevalence of Neospora caninum, Toxoplasma gondii and Brucella abortus in water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis): climatic and environmental risk factors in eastern and southeast Mexico. Microb Pathog 173:105871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105871
Borriello G, Capparelli R, Bianco M, Fenizia D, Alfano F, Capuano F, Ercolini D, Parisi A, Roperto S, Iannelli D (2006) Genetic resistance to Brucella abortus in the water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis). Infect Immun 74:2115–2120. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.74.4.2115-2120.2006
Capparelli R, Borriello G, Marabelli R, Roperto S, Roperto F, Iannelli D (2007) The Nramp1 AA genotype confers susceptibility to Brucella abortus in water buffalo. Mamm Genome 18:137–143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-006-0103-x
Catozzi C (2020) Water buffalo microbiota and immunity during infectious diseases
Chand P, Rajpurohit B, Malhotra A, Poonia J (2005) Comparison of milk-ELISA and serum-ELISA for the diagnosis of Brucella melitensis infection in sheep. Vet Microbiol 108(3–4):305–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2005.04.006
Dadar M, Alamian S, Behrozikhah AM, Yazdani F, Kalantari A, Etemadi A, Whatmore AM (2019) Molecular identification of Brucella species and biovars associated with animal and human infection in Iran. Vet Res Forum 10:315–321. https://doi.org/10.30466/vrf.2018.89680.2171
Dadar M, Wareth G, Neubauer H (2021) Brucellosis in iranian buffalo. Ger J Vet Res 1:13–16. https://doi.org/10.51585/gjvr.2021.2.0009
Das V, Paranjape V, Corbel M (1990) Investigation of brucellosis-associated abortion in dairy buffaloes and cows in Bombay. Indian J Anim Sci 60:1193–1194
Dehkordi FS, Saberian S, Momtaz H (2012) Detection and segregation of Brucella abortus and Brucella melitensis in aborted bovine, ovine, Caprine, Buffaloes and Camelid fetuses by application of conventional and real-time polymerase chain reaction. Thai J Vet Med 42:13
Dehkordi FS, Khamesipour F, Momeni M (2014) Brucella abortus and Brucella melitensis in iranian bovine and buffalo semen samples: the first clinical trial on seasonal, senile and geographical distribution using culture, conventional and real-time polymerase chain reaction assays. Kafkas Univ Vet Fak Dergisi 20:821–828
Di Giannatale E, De Massis F, Ancora M, Zilli K, Alessiani A (2008) Typing of Brucella field strains isolated from livestock populations in Italy between 2001 and 2006. Vet Ital 44:383–388
Ewalt DR, Bricker BJ (2000) Validation of the abbreviated BrucellaAMOS PCR as a Rapid Screening Method for differentiation of Brucella abortus Field strain isolates and the vaccine strains, 19 and RB51. J Clin Microbiol 38:3085–3086. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.38.8.3085-3086.2000
Fusco G, Amoroso M, Tavano R, Corrado F, Conte F, Iovane G, Capuano F (2009) Identification of Brucella sp. by real time PCR in buffalo milk: preliminary data. In: XI Congresso Nazionale SI Di. LV, Parma, Italia, 30 settembre-2 ottobre 2009, 2009. Società Italiana di Diagnostica di Laboratorio Veterinaria (SIDiLV), pp 146–147
Gentile A (1957) Brucellosis in buffaloes. Vet Ital 8:591–596
Grandoni F, Signorelli F, Martucciello A, Napolitano F, De Donato I, Donniacuo A, Di Vuolo G, De Matteis G, Del Zotto G, Davis WC, De Carlo E (2023) In-depth immunophenotyping reveals significant alteration of lymphocytes in buffalo with brucellosis. Cytometry Part A 103:528–536. https://doi.org/10.1002/cyto.a.24710
Hamdy ME, Amin A (2002) Detection of Brucella species in the milk of infected cattle, sheep, goats and camels by PCR. VET J 163:299–305. https://doi.org/10.1053/tvjl.2001.0681
Hosein H, Rouby S, Menshawy A, AbdAl-Ghany A (2017) Sensitivity and specificity of the commonly used diagnostic procedures of bovine brucellosis. Vet Sci 3:45–52. https://doi.org/10.17582/journal.vsrr/2017.3.3.45.52
Hosein H, Zaki HM, Safwat NM, Menshawy AM, Rouby S, Mahrous A, Madkour BE-d (2018) Evaluation of the General Organization of Veterinary Services control program of animal brucellosis in Egypt: an outbreak investigation of brucellosis in buffalo. Veterinary World 11:748. https://doi.org/10.14202/vetworld.2018.748-757
Khan TI, Ehtisham-ul-Haque S, Waheed U, Khan I, Younus M, Ali S (2018) Milk Indirect-ELISA and milk Ring Test for Screening of Brucellosis in Buffaloes, Goats and Bulk Tank milk samples collected from two districts of Punjab, Pakistan. Pak Vet J 38:105–108. https://doi.org/10.29261/pakvetj/2018.021
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174. https://doi.org/10.2307/2529310
Lee PY, Costumbrado J, Hsu CY, Kim YH (2012) Agarose gel electrophoresis for the separation of DNA fragments. JoVE (Journal of Visualized Experiments) 20:e3923. https://doi.org/10.3791/3923-v
Longo M, Mallardo K, Montagnaro S, De Martino L, Gallo S, Fusco G, Galiero G, Guarino A, Pagnini U, Iovane G (2009) Shedding of Brucella abortus rough mutant strain RB51 in milk of water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis). Prev Vet Med 90:113–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prevetmed.2009.03.007
López-Goñi I, García-Yoldi D, Marin C, De Miguel M, Munoz P, Blasco J, Jacques I, Grayon M, Cloeckaert A, Ferreira A (2008) Evaluation of a multiplex PCR assay (Bruce-ladder) for molecular typing of all Brucella species, including the vaccine strains. J Clin Microbiol 46:3484–3487. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.00837-08
Mahajan S, Agrawal R, Pande N (2011) A comparative evaluation of different diagnostic tests for brucellosis in buffaloes. Buffalo Bull 30:75–78
Marianelli C, Martucciello A, Tarantino M, Vecchio R, Iovane G, Galiero G (2008) Evaluation of molecular methods for the detection of Brucella species in water buffalo milk. J Dairy Sci 91:3779–3786. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2008-1233
Martínez D, Thompson C, Draghi G, Canavesio V, Jacobo R, Zimmer P, Elena S, Nicola AM, de Echaide ST (2014) Pheno-and genotyping of Brucella abortus biovar 5 isolated from a water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) fetus: first case reported in the Americas. Vet Microbiol 173:172–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2014.07.011
Mazzeo A, Tremonte P, Rossi N, Ferrara C, Mascolo C, Lombardi SJ, Sorrentino E (2023) Modulation of the One Health Approach to Tackle Brucellosis in Buffaloes and cattle in two Italian Territories with different characteristics. J Buffalo Sci 12:55–69. https://doi.org/10.6000/1927-520X.2023.12.07
Moreno E, Middlebrook EA, Altamirano-Silva P, Al Dahouk S, Araj GF, Arce-Gorvel V, Arenas-Gamboa Á, Ariza J, Barquero-Calvo E, Battelli G, Bertu WJ (2023) If you’re not confused, you’re not paying attention: Ochrobactrum is not Brucella. J Clin Microbiol 61:e00438–e00423. https://doi.org/10.1128/jcm.00438-23
Nowroozi-Asl A, Oliaei A, Poormahmood-Shalgahian M (2007) A serological survey of brucella spp. in water buffalo in Khoozestan province, Iran. Ital J Anim Sci 6:825–827. https://doi.org/10.4081/ijas.2007.s2.825
Özen H, İlhan Z, Usta M, Karaman M, İlhan F (2021) Brucellosis in a water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) herd in Balikesir province of Turkey: a bacteriological and pathological investigation. Thai J Vet Med 51:133–140. https://he01.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/tjvm/article/view/247441
Radostits O, Gay C, Hinchcliff K, Constable P (2007) Diseases associated with bacteria. Veterinary Medicine: a textbook of the diseases of cattle, horses, sheep, pigs, and goats. Can Vet J 10:1007–1060
Rijpens NP, Jannes G, Van Asbroeck M, Rossau R, Herman L (1996) Direct detection of Brucella spp. in raw milk by PCR and reverse hybridization with 16S-23S rRNA spacer probes. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:1683–1688. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.62.5.1683-1688.1996
Romero C, Lopez-Goñi I (1999) Improved method for purification of bacterial DNA from bovine milk for detection of Brucella spp. by PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:3735–3737. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.65.8.3735-3737.1999
Sadhu DB, Panchasara H, Chauhan H, Sutariya D, Parmar V, Prajapati H (2015) Seroprevalence and comparison of different serological tests for brucellosis detection in small ruminants. Vet World 8:561. https://doi.org/10.14202/vetworld.2015.561-566
Sousa MG, Salvarani FM, Bomjardim HA, Brito MF, Barbosa JD (2017) Brucellosis in water buffaloes. Pesqui Vet Bras 37:234–240. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0100-736x2017000300006
Sreevatsan S, Bookout JB, Ringpis F, Perumaalla VS, Ficht TA, Adams LG, Hagius SD, Elzer PH, Bricker BJ, Kumar GK (2000) A multiplex approach to molecular detection of Brucella abortus and/or Mycobacterium bovis infection in cattle. J Clin Microbiol 38:2602–2610. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.38.7.2602-2610.2000
Vemulapalli R, McQuiston JR, Schurig GG, Sriranganathan N, Halling SM, Boyle SM (1999) Identification of an IS711 element interrupting the wboA gene of Brucella abortus vaccine strain RB51 and a PCR assay to distinguish strain RB51 from other Brucella species and strains. Clin Diagn lab Immunol 6:760–764. https://doi.org/10.1128/CDLI.6.5.760-764.1999
Xavier M, Paixão T, Poester F, Lage A, Santos R (2009) Pathological, immunohistochemical and bacteriological study of tissues and milk of cows and fetuses experimentally infected with Brucella abortus. J Comp Pathol 140:149–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcpa.2008.10.004
Acknowledgements
The authors would like thanks Amin Nemati Azar, Jafar Shirazi, Mehran Pedernejad, Mohammad Antik Chi for kindly providing the milk samples from differnt parts of Iran.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the Razi vaccine and serum research institute (Grant # 3-18-1857-005-000134).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Maryam Dadar and Akram Bahrainipour designed and funded the study; Maryam Dadar, Akram Bahrainipour, Karim Amiri, Faranak Abnaroodheleh and Saeed Alamian performed the experiments; Maryam Dadar and Ali Reza Yousefi analyzed and interpreted the results; The first draft and final draft of the manuscript was written by Maryam Dadar and all authors commented and contributed to the preparation of the final manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All milk samples were obtained following the procedures on Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee from Iranian veterinary organization by Ethics Committee (Approval number, 99030922; Approval date, 22Feb2020). All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations. Before beginning work on the present study, we contacted the buffalo owners and written informed consent was obtained from the owners for the participation of their animals in this study. During collecting milk specimens, these animals were not disturbed.
Consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from the buffalo owners.
Consent to publish
Buffalo-owners signed informed consent regarding publishing their animals’ data.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dadar, M., Bahreinipour, A., Alamian, S. et al. Serological, cultural, and molecular analysis of Brucella from Buffalo milk in various regions of Iran. Vet Res Commun 48, 427–436 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-023-10228-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-023-10228-5