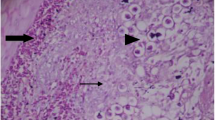
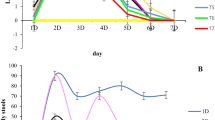
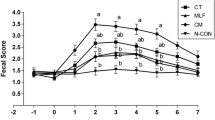
Abstract
Coccidiosis is an intestinal protozoan disease of sheep, that causes substantial economic losses in the industry due to its intestinal protozoan origins. Many anti-protozoan drugs including ionophores, triazines, and sulfonamides have been widely used to treat sheep coccidiosis. Still, anticoccidial resistance and drug residues in edible tissues have prompted an urgent search for alternatives. In this study, the anti-coccidial effectiveness of the Radix dichroae extract was compared to that of the conventional anti-coccidial drug diclazuril. Here, eighteen 45-day-old lambs naturally-infected with Eimeria spp. were randomly allocated in three groups: control group, Radix dichroae extract group and diclazuril group. The results showed that the body weight gain (BWG) during the treatment and withdrawal periods was considerably improved in the coccidiosis-infected sheep treated with Radix dichroae extract and diclazuril compared to the control group, respectively. Additionally, the Radix dichroae extract and diclazuril had fewer oocysts per gram (OPG) than the control group, showing similar anti-coccidial effects on days 14, 21, 28, 35 and 78, respectively. Furthermore, Radix dichroae extract and diclazuril treatment altered the structure and composition of gut microbiota, promoting the relative abundance of Actinobacteriota, Firmicutes, Alistipes, and Bifidobacterium, while decreasing the abundance of Bacteroidota, Marinilaceae, Helicobacteraceae, and Prevotella. Moreover, Spearman’s correlation analysis further revealed a correlation between the OPG and BWG and gut microorganisms. Collectively, the results indicated that Radix dichroae extract had similar anti-coccidial effects as diclazuril, and could regulate gut microbiota balance in growing lambs.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The bacterial 16 S rRNA sequencing data obtained from the fecal have been deposited in the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database under accession number PRJNA947373.
References
Acharya M, Burke JM, Miller JE, Terrill TH, Wood EL, Muir JP (2020) Quebracho tannins aid in the control of Eimeria spp. and gastrointestinal nematodes in lambs and goat kids. Vet Parasitol 288:109295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2020.109295
Andrews AH (2013) Some aspects of coccidiosis in sheep and goats. Small Ruminant Research 110:93–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2012.11.011
Bangoura B, Bhuiya MAI, Kilpatrick M (2022) Eimeria infections in domestic and wild ruminants with reference to control options in domestic ruminants. Parasitol Res 121:2207–2232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-022-07564-x
Bauer BU, Pomroy WE, Gueydon J, Gannac S, Scott I, Pfister K (2010) Comparison of the FLOTAC technique with the McMaster method and the Baermann technique to determine counts of Dictyocaulus eckerti L1 and strongylid eggs in faeces of red deer (Cervus elaphus). Parasitol Res 107:555–560. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-1893-z
Burke JM, Miller JE, Terrill TH, Orlik ST, Acharya M, Garza JJ, Mosjidis JA (2013) Sericea lespdeza as an aid in the control of Emeria spp. in lambs. Vet Parasitol 193:39–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.11.046
Cai H, Liao S, Li J, Liu Q, Luo S, Lv M, Lin X, Hu J, Zhang J, Qi N, Sun M (2022a) Single and combined Effects of Clostridium butyricum and Coccidiosis Vaccine on Growth Performance and the intestinal microbiome of broiler chickens. Front Microbiol 13:811428. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.811428
Cai H, Luo S, Zhou Q, Yan Z, Liu Q, Kang Z, Liao S, Li J, Lv M, Lin X, Hu J, Yu S, Zhang J, Qi N, Sun M (2022b) Effects of Bacillus subtilis and coccidiosis vaccine on growth indices and intestinal microbiota of broilers. Poult Sci 101:102091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psj.2022.102091
Cervantes-Valencia ME, Alcalá-Canto Y, Sumano-Lopez H, Ducoing-Watty AM, Gutierrez-Olvera L (2016) Effects of Curcuma longa dietary inclusion against Eimeria spp. in naturally-infected lambs. Small Ruminant Research 136:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2015.12.035
Chen P, Xu T, Zhang C, Tong X, Shaukat A, He Y, Liu K, Huang S (2022) Effects of Probiotics and Gut Microbiota on Bone metabolism in chickens: a review. Metabolites 12:1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12101000
de Souza Rodrigues F, Cezar AS, de Menezes FR, Sangioni LA, Vogel FSF, de Avila Botton S (2017) Efficacy and economic analysis of two treatment regimens using toltrazuril in lambs naturally infected with Eimeria spp. on pasture. Parasitol Res 116:2911–2919. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-017-5597-5
Dziarski R, Park SY, Kashyap DR, Dowd SE, Gupta D (2016) Pglyrp-regulated gut Microflora Prevotella falsenii, Parabacteroides distasonis and Bacteroides eggerthii enhance and Alistipes finegoldii attenuates colitis in mice. PLoS ONE 11:e0146162. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0146162
Fitzgerald PR (1980) The economic impact of coccidiosis in domestic animals. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med 24:121–143. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-8159.1994.tb02379.x
Flint HJ, Stewart CS (1999) Bacteroides and prevotella - encyclopedia of food microbiology. Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology 198–203
Guan Y, Yang H, Han S, Feng L, Wang T, Ge J (2017) Comparison of the gut microbiota composition between wild and captive sika deer (Cervus nippon hortulorum) from feces by high-throughput sequencing. AMB Express 7:212. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-017-0517-8
Hofer U (2014) Microbiome: pro-inflammatory Prevotella? Nat Rev Microbiol 12:5. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro3180
Huang G, Zhang S, Zhou C, Tang X, Li C, Wang C, Tang X, Suo J, Jia Y, El-Ashram S, Yu Z, Cai J, Gupta N, Suo X, Liu X (2018) Influence of Eimeria falciformis infection on gut microbiota and metabolic pathways in mice. Infect Immun 86:e00073–e00018. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00073-18
Huang SC, He YF, Chen P, Liu KL, Shaukat A (2023) Gut microbiota as a target in the bone health of livestock and poultry: roles of short-chain fatty acids. Anim Dis 3:23. https://doi.org/10.1186/s44149-023-00089-5
Iljazovic A, Roy U, Gálvez EJC, Lesker TR, Zhao B, Gronow A, Amend L, Will SE, Hofmann JD, Pils MC, Schmidt-Hohagen K, Neumann-Schaal M, Strowig T (2021) Perturbation of the gut microbiome by Prevotella spp. enhances host susceptibility to mucosal inflammation. Mucosal Immunol 14:113–124. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41385-020-0296-4
Iqbal A, Tariq KA, Wazir VS, Singh R (2013) Antiparasitic efficacy of Artemisia absinthium, toltrazuril and amprolium against intestinal coccidiosis in goats. J Parasit Dis 37:88–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-012-0137-9
Jiang F, Gao H, Qin W, Song P, Wang H, Zhang J, Liu D, Wang D, Zhang T (2021) Marked Seasonal Variation in structure and function of Gut Microbiota in Forest and Alpine musk deer. Front Microbiol 12:699797. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.699797
Jonsson NN, Piper EK, Gray CP, Deniz A, Constantinoiu CC (2011) Efficacy of toltrazuril 5% suspension against Eimeria bovis and Eimeria zuernii in calves and observations on the associated immunopathology. Parasitol Res 109(Suppl 1):S113–S128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2408-2
Kaboutari J, Arab HA, Ebrahimi K, Rahbari S (2014) Prophylactic and therapeutic effects of a novel granulated formulation of Artemisia extract on broiler coccidiosis. Trop Anim Health Prod 46:43–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-013-0444-x
Kaur K, Jain M, Kaur T, Jain R (2009) Antimalarials from nature. Bioorg Med Chem 17:3229–3256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2009.02.050
Le Sueur C, Mage C, Mundt HC (2009) Efficacy of toltrazuril (Baycox 5% suspension) in natural infections with pathogenic Eimeria spp. in housed lambs. Parasitol Res 104:1157–1162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-008-1305-9
Lee WJ, Hase K (2014) Gut microbiota-generated metabolites in animal health and disease. Nat Chem Biol 10:416–424. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1535
Leung JM, Graham AL, Knowles SCL (2018) Parasite-microbiota interactions with the Vertebrate Gut: synthesis through an ecological Lens. Front Microbiol 9:843. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00843
Lia L, Wu J, Lei Y, Kong F, Zhang R, Sun J, Wang L, Li Z, Shi J, Wang Y, Wei Y, Zhang K, Lei Z (2022) Oregano essential oils mediated intestinal microbiota and metabolites and improved growth performance and intestinal barrier function in Sheep. Front Immunol 13:908015. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.908015
Lin LX, Cao QQ, Zhang CD, Xu TT, Yue K, Li Q, Liu F, Wang X, Dong HJ, Huang SC, Jian FC (2022) Aflatoxin B1 causes oxidative stress and apoptosis in sheep testes associated with disrupting rumen microbiota. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 232:113225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113225
Lu C, Yan Y, Jian F, Ning C (2021) Coccidia-Microbiota interactions and their Effects on the host. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 11:751481. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2021.751481
Macfarlane GT, Steed H, Macfarlane S (2008) Bacterial metabolism and health-related effects of galacto-oligosaccharides and other prebiotics. J Appl Microbiol 104:305–344. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2007.03520.x
Madlala T, Okpeku M, Adeleke MA (2021) Understanding the interactions between Eimeria infection and gut microbiota, towards the control of chicken coccidiosis: a review. Parasite 28:48. https://doi.org/10.1051/parasite/2021047
Morishima H, Baba E, Fukata T, Arakawa A (1984) Effect of Eimeria tenella infection in chickens fed the feed artificially contaminated with Salmonella typhimurium. Poult Sci 63:1732–1737. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.0631732
Mundt HC, Dittmar K, Daugschies A, Grzonka E, Bangoura B (2009) Study of the comparative efficacy of toltrazuril and diclazuril against ovine coccidiosis in housed lambs. Parasitol Res 105 Suppl 1S141–S150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-009-1505-y
Odden A, Enemark HL, Ruiz A, Robertson LJ, Ersdal C, Nes SK, Tømmerberg V, Stuen S (2018) Controlled efficacy trial confirming toltrazuril resistance in a field isolate of ovine Eimeria spp. Parasit Vectors 11:394. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-018-2976-4
Ozbayram EG, Ince O, Ince B, Harms H, Kleinsteuber S (2018) Comparison of Rumen and Manure Microbiomes and Implications for the Inoculation of anaerobic digesters. Microorganisms 6:15. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6010015
Parker BJ, Wearsch PA, Veloo ACM, Rodriguez-Palacios A (2020) The Genus Alistipes: gut Bacteria with emerging implications to inflammation, Cancer, and Mental Health. Front Immunol 11:906. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.00906
Pérez-Fonseca A, Alcala-Canto Y, Salem AZ, Alberti-Navarro AB (2016) Anticoccidial efficacy of naringenin and a grapefruit peel extract in growing lambs naturally-infected with Eimeria spp. Vet Parasitol 232:58–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2016.11.009
Platzer B, Prosl H, Cieslicki M, Joachim A (2005) Epidemiology of Eimeria infections in an austrian milking sheep flock and control with diclazuril. Vet Parasitol 129:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2004.11.031
Rhee KJ, Wu S, Wu X, Huso DL, Karim B, Franco AA, Rabizadeh S, Golub JE, Mathews LE, Shin J, Sartor RB, Golenbock D, Hamad AR, Gan CM, Housseau F, Sears CL (2009) Induction of persistent colitis by a human commensal, enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis, in wild-type C57BL/6 mice. Infect Immun 77:1708–1718. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00814-08
Rolhion N, Chassaing B, Nahori MA, de Bodt J, Moura A, Lecuit M, Dussurget O, Bérard M, Marzorati M, Fehlner-Peach H, Littman DR, Gewirtz AT, Van de Wiele T, Cossart P (2019) A Listeria monocytogenes Bacteriocin can target the commensal Prevotella copri and modulate intestinal infection. Cell Host Microbe 26:691–701e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2019.10.016
Rostami F, Taherpour K, Ghasemi HA, Akbari Gharaei M, Shirzadi H (2021) Effects of Scrophularia striata hydroalcoholic extract in comparison to salinomycin on growth performance, intestinal health and immunity in broiler chickens following a mixed-species Eimeria challenge. Vet Parasitol 293:109417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2021.109417
Sandoval E, Morales G, Ybarra N, Borges J (2012) Comparison between two mcmaster egg counting slide used for the diagnostic of gastrointestinal nematode infection in ruminants. Zootecnia Trop 29:495–501
Schroeder BO, Birchenough GMH, Ståhlman M, Arike L, Johansson MEV, Hansson GC, Bäckhed F (2018) Bifidobacteria or Fiber protects against Diet-Induced microbiota-mediated colonic mucus deterioration. Cell Host Microbe 23:27–40e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2017.11.004
Tang S, Xin Y, Ma Y, Xu X, Zhao S, Cao J (2020) Screening of Microbes Associated with Swine Growth and Fat Deposition Traits across the intestinal tract. Front Microbiol 11:586776. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.586776
Velazquez-González MY, Loya-Olguin JL, Valdes-Garcia YS, Martinez-Gonzalez S, Avila-Ramos F, Escalera-Valente F, Gonzalez-Montaña JR (2022) Hura crepitans seeds for control of Eimeria spp. in lambs as an alternative to Conventional Therapies. Vet Sci 9:488. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9090488
Wang D, Zhou L, Li W, Zhou H, Hou G (2016) Anticoccidial effect of Piper sarmentosum extracts in experimental coccidiosis in broiler chickens. Trop Anim Health Prode 48:1071–1078. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-016-1034-5
Wang Y, Zhang H, Zhu L, Xu Y, Liu N, Sun X, Hu L, Huang H, Wei K, Zhu R (2018) Dynamic distribution of gut microbiota in goats at different Ages and Health States. Front Microbiol 9:2509. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02509
Wang L, Guo Z, Gong Z, Cai J, Yang F, Wei X, Niu B (2020) Efficacy of an oral solution prepared from the Ultrasonic Extract of Radix dichroae roots against Eimeria tenella in broiler chickens. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2020:3870902. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/3870902
Waters JL, Ley RE (2019) The human gut bacteria Christensenellaceae are widespread, heritable, and associated with health. BMC Biol 17:83. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12915-019-0699-4
Xu TT, Chen P, Zhang CD, Shaukat A, Lin LX, Yue K, Ding WL, Tong X, Liu KL, He YF, Xie JF, Liu F, Zhang C, Zhang HY, Huang SC (2023) Gut microbiome dysregulation drives bone damage in broiler tibial dyschondroplasia by disrupting glucose homeostasis. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 9:1. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41522-022-00360-6
Yoshida N, Yamashita T, Osone T, Hosooka T, Shinohara M, Kitahama S, Sasaki K, Sasaki D, Yoneshiro T, Suzuki T, Emoto T, Saito Y, Ozawa G, Hirota Y, Kitaura Y, Shimomura Y, Okamatsu-Ogura Y, Saito M, Kondo A, Kajimura S, Inagaki T, Ogawa W, Yamada T, Hirata KI (2021) Bacteroides spp. promotes branched-chain amino acid catabolism in brown fat and inhibits obesity. iScience 24:103342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2021.103342
Youn HJ, Noh JW (2001) Screening of the anticoccidial effects of herb extracts against Eimeria tenella. Vet Parasitol 96:257–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-4017(01)00385-5
Zamani S, Hesam Shariati S, Zali MR, Asadzadeh Aghdaei H, Sarabi Asiabar A, Bokaie S, Nomanpour B, Sechi LA, Feizabadi MM (2017) Detection of enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis in patients with ulcerative colitis. Gut Pathog 9:53. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13099-017-0202-0
Funding
This study was supported by the National Modern Agriculture Industry Technology System (No. CARS-38), the Scientific and Technological Support Project for Ecological Environment Protection and High-quality Development of the Yellow River Basin in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (No. 2021BEF02026), and the Special Support Fund for High-level Talents and skills improvement of Henan Agricultural University (No. 30501374 and SYS2023T08).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Pan Chen: Data curation, Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing – original draft. Shijie Li: Methodology, Data curation, Investigation. Lijun Zheng: Data curation, Methodology, Validation, Investigation. Zhanming Wang: Data curation, Methodology. Yanfeng He and Kaili Liu: Data analysis, Investigation. Manman Li and Yingmin Wang: Sample prepare, site resources. Aftab Shaukat: Writing – review & editing. Senyang Li: Investigation. Shucheng Huang: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Resources, Writing – review & editing. Fuchun Jian: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Resources. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All sheep experiments followed the animal welfare guidelines of Henan Agricultural University (Zhengzhou, China) (Permit No: 17–0126).
Consent to publish
All authors agree to the content of the paper for publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, P., Li, S., Zheng, L. et al. Effects of Radix dichroae extract supplementation on growth performance, oocysts output and gut microbiota in growing lambs with coccidiosis. Vet Res Commun 48, 279–290 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-023-10209-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-023-10209-8