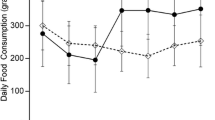
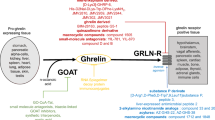
Abstract
Growth hormone and insulin like growth factor-1 plays an important role in the regulation of body composition and metabolism. Growth Hormone is released from the pituitary through a specific G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) called growth hormone secretagogue receptor 1a expressed in the hypothalamus. Ghrelin is a peptide hormone released from the cells in the stomach, which stimulates appetite and food intake in mammals, regulates gut motility, gastric acid secretion, taste sensation, circadian rhythm, learning and memory, oxidative stress, autophagy, glucose metabolism etc. When the release of the endogenous ligand GHSR-1a, i.e., ghrelin is malfunctioned or stopped, external substitutes are administrated to induce the stimulation of growth hormone and appetite. A class of compound known as ghrelin receptor agonists are developed as an external substitute of ghrelin for regulation and stimulation of growth hormone in frailty, for body weight gain, muscle mass gain, prevention of cachexia and for the treatment of chronic fatigue syndromes. Capromorelin [Entyce™ (Aratana Therapeutics, Leawood, KS, USA)] is the only FDA (Food and Drug Administration) approved (May 2016) drug used for stimulating appetite in dogs and was marketed in the fall of 2017. In 2020, USFDA approved Capromorelin [Elura™ (Elanco US Inc.)] for the management of weight loss in chronic kidney disease of cats. This article reviews the discovery of the ghrelin receptor agonist capromorelin, its efficacy, safety, clinical applications and aims to delineate its further scope of use in veterinary practice.


(adapted from IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY). Ghrelin receptor is a G-protein coupled receptor with seven transmembrane domains. GhSR utilizes distinct G-proteins such as Gα12/13, Gαi/0, Gαq/11 which activates secondary messengers. GHSR can lead to the formation of cyclic AMP (cAMP) or leads to activation of phospholipase C (PLC) that may function through calcium release. This signaling intricate mechanisms often involve rho guanine exchange factors that includes RhoA and associated kinase proteins. β-arrestins also gets activated by GHSR causing attenuation of the downstream signaling by receptor internalization
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data will be available upon request.
References
Agnew W, Korman R (2014) Pharmacological appetite stimulation: rational choices in the inappetent cat. J Feline Med Surg 16:749–756. https://doi.org/10.1177/1098612X14545273
Baldanzi G, Filigheddu N, Cutrupi S, Catapano F, Bonissoni S, Fubini A, Malan D, Baj G, Granata R, Broglio F, Papotti M, Surico N, Bussolino F, Isgaard J, Deghenghi R, Sinigaglia F, Prat M, Muccioli G, Ghigo E, Graziani A (2002) Ghrelin and des-acyl ghrelin inhibit cell death in cardiomyocytes and endothelial cells through ERK1/2 and PI 3-kinase/AKT. J Cell Biol 159:1029–1037. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200207165
Beiras-Fernandez A, Kreth S, Weis F, Ledderose C, Pöttinger T, Dieguez C, Beiras A, Reichart B (2010) Altered myocardial expression of ghrelin and its receptor (GHSR-1a) in patients with severe heart failure. Peptides 31:2222–2228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2010.08.019
Bowers CY (1998) Growth hormone-releasing peptide (GHRP). Cell Mol Life Sci 54:1316–1329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s000180050257
Bowers CY, Momany F, Reynolds GA, Chang D, Hong A, Chang K (1980) Structure-activity relationships of a synthetic pentapeptide that specifically releases growth hormone in vitro. Endocrinology 106:663–667. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo-106-3-663
Broglio F, Arvat E, Benso A, Gottero C, Muccioli G, Papotti M, van der Lely AJ, Deghenghi R, Ghigo E (2001) Ghrelin, a natural GH secretagogue produced by the stomach, induces hyperglycemia and reduces insulin secretion in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:5083–5086. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.86.10.8098
Brunetto MA, Gomes MOS, Andre MR, Teshima E, Gonçalves KNV, Pereira GT, Ferraudo AS, Carciofi AC (2010) Effects of nutritional support on hospital outcome in dogs and cats. J Vet Emerg Crit Care (San Antonio) 20:224–231. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-4431.2009.00507.x
Callaghan B, Kosari S, Pustovit RV, Sartor DM, Ferens D, Ban K, Baell J, Nguyen TV, Rivera LR, Brock JA, Furness JB (2014) Hypotensive effects of ghrelin receptor agonists mediated through a novel receptor. Br J Pharmacol 171:1275–1286. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.12527
Carpino PA, Lefker BA, Tole,r SM, Pan LC, Hadcock JR, Cook ER et al (2003) Pyrazoline-piperidine dipeptide growth hormone secretagogues (GHSs). Discovery of capromorelin. Bioorg Med Chem 11(4):581–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0968-0896(02)00433-9PMID12538023
Ceron-Romero N, Taofeek N, Thomas A, Vroonland E, Sanmartin K, Verghese M, Heinen E, Vizcarra JA (2021) Capromorelin, a ghrelin receptor agonist, increases feed intake and body weight gain in broiler chickens (Gallus gallus domesticus). Poult Sci 100:101204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psj.2021.101204
Chapman IM, Bach MA, Van Cauter E, Farmer M, Krupa D, Taylor AM, Schilling LM, Cole KY, Skiles EH, Pezzoli SS, Hartman ML, Veldhuis JD, Gormley GJ, Thorner MO (1996) Stimulation of the growth hormone (GH)-insulin-like growth factor I axis by daily oral administration of a GH secretogogue (MK-677) in healthy elderly subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81:4249–4257. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.81.12.8954023
Chuang J-C, Sakata I, Kohno D, Perello M, Osborne-Lawrence S, Repa JJ, Zigman JM (2011) Ghrelin directly stimulates glucagon secretion from pancreatic alpha-cells. Mol Endocrinol 25:1600–1611. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2011-1001
Costantini VJA, Vicentini E, Sabbatini FM, Valerio E, Lepore S, Tessari M, Sartori M, Michielin F, Melotto S, Bifone A, Pich EM, Corsi M (2011) GSK1614343, a novel ghrelin receptor antagonist, produces an unexpected increase of food intake and body weight in rodents and dogs. Neuroendocrinology 94:158–168. https://doi.org/10.1159/000328968
Cummings DE, Frayo RS, Marmonier C, Aubert R, Chapelot D (2004) Plasma ghrelin levels and hunger scores in humans initiating meals voluntarily without time- and food-related cues. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 287:E297–304. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00582.2003
Damian M, Marie J, Leyris J-P, Fehrentz J-A, Verdié P, Martinez J, Banères J-L, Mary S (2012) High constitutive activity is an intrinsic feature of ghrelin receptor protein: a study with a functional monomeric GHS-R1a receptor reconstituted in lipid discs. J Biol Chem 287:3630–3641. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.288324
Date Y, Kojima M, Hosoda H, Sawaguchi A, Mondal MS, Suganuma T, Matsukura S, Kangawa K, Nakazato M (2000) Ghrelin, a novel growth hormone-releasing acylated peptide, is synthesized in a distinct endocrine cell type in the gastrointestinal tracts of rats and humans. Endocrinology 141:4255–4261. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo.141.11.7757
Date Y, Nakazato M, Hashiguchi S, Dezaki K, Mondal MS, Hosoda H, Kojima M, Kangawa K, Arima T, Matsuo H, Yada T, Matsukura S (2002) Ghrelin is present in pancreatic alpha-cells of humans and rats and stimulates insulin secretion. Diabetes 51:124–129. https://doi.org/10.2337/diabetes.51.1.124
Deaver SE, Hoyer PB, Dial SM, Field ME, Collier RJ, Rhoads ML (2013) Localization of ghrelin and its receptor in the reproductive tract of Holstein heifers. J Dairy Sci 96:150–157. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2012-5506
Deboer MD, Zhu X, Levasseur PR, Inui A, Hu Z, Han G, Mitch WE, Taylor JE, Halem HA, Dong JZ, Datta R, Culler MD, Marks DL (2008) Ghrelin treatment of chronic kidney disease: improvements in lean body mass and cytokine profile. Endocrinology 149:827–835. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2007-1046
Dong X-Y, Xu J, Tang S-Q, Li H-Y, Jiang Q-Y, Zou X-T (2009) Ghrelin and its biological effects on pigs. Peptides 30:1203–1211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2009.03.001
Ferens DM, Yin L, Ohashi-Doi K, Habgood M, Bron R, Brock JA, Gale JD, Furness JB (2010) Evidence for functional ghrelin receptors on parasympathetic preganglionic neurons of micturition control pathways in the rat. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 37:926–932. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1681.2010.05409.x
Ferens DM, Habgood MD, Saunders NR, Tan YH, Brown DJ, Brock JA, Furness JB (2011) Stimulation of defecation in spinal cord-injured rats by a centrally acting ghrelin receptor agonist. Spinal Cord 49:1036–1041. https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2011.60
Gagnon J, Baggio LL, Drucker DJ, Brubaker PL (2015) Ghrelin is a Novel Regulator of GLP-1 secretion. Diabetes 64:1513–1521. https://doi.org/10.2337/db14-1176
Ge M, Cline E, Yang L, Mills SG (2008) Substituted pyrazoles as ghrelin receptor antagonists. WO2008008286A2
Hansen BS, Raun K, Nielsen KK, Johansen PB, Hansen TK, Peschke B, Lau J, Andersen PH, Ankersen M (1999) Pharmacological characterisation of a new oral GH secretagogue, NN703. Eur J Endocrinol 141:180–189. https://doi.org/10.1530/eje.0.1410180
Hayashi H, Yamakado M, Yamaguchi M, Kozakai T (2020) Leptin and ghrelin expressions in the gastrointestinal tracts of calves and cows. J Vet Med Sci 82:475–478. https://doi.org/10.1292/jvms.19-0680
Hayashida T, Murakami K, Mogi K, Nishihara M, Nakazato M, Mondal MS, Horii Y, Kojima M, Kangawa K, Murakami N (2001) Ghrelin in domestic animals: distribution in stomach and its possible role. Domest Anim Endocrinol 21:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0739-7240(01)00104-7
Holst B, Cygankiewicz A, Jensen TH, Ankersen M, Schwartz TW (2003) High constitutive signaling of the ghrelin receptor–identification of a potent inverse agonist. Mol Endocrinol 17:2201–2210. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2003-0069
Hosoda H, Kojima M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K (2000) Ghrelin and des-acyl ghrelin: two major forms of rat ghrelin peptide in gastrointestinal tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 279:909–913. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.2000.4039
Hosoda H, Kojima M, Kangawa K (2006) Biological, physiological, and pharmacological aspects of ghrelin. J Pharmacol Sci 100:398–410. https://doi.org/10.1254/jphs.crj06002x
Howard AD, Feighner SD, Cully DF, Arena JP, Liberator PA, Rosenblum CI, Hamelin M, Hreniuk DL, Palyha OC, Anderson J, Paress PS, Diaz C, Chou M, Liu KK, McKee KK, Pong SS, Chaung LY, Elbrecht A, Dashkevicz M, Heavens R, Rigby M, Sirinathsinghji DJ, Dean DC, Melillo DG, Patchett AA, Nargund R, Griffin PR, DeMartino JA, Gupta SK, Schaeffer JM, Smith RG, Van der Ploeg LH (1996) A receptor in pituitary and hypothalamus that functions in growth hormone release. Science 273:974–977. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.273.5277.974
Jennings JS, Wertz-Lutz AE, Pritchard RH, Weaver AD, Keisler DH, Bruns K (2011) Circulating ghrelin and leptin concentrations and growth hormone secretagogue receptor abundance in liver, muscle, and adipose tissue of beef cattle exhibiting differences in composition of gain. J Anim Sci 89:3954–3972. https://doi.org/10.2527/jas.2010-3597
Jiang H, Betancourt L, Smith RG (2006) Ghrelin amplifies dopamine signaling by cross talk involving formation of growth hormone secretagogue receptor/dopamine receptor subtype 1 heterodimers. Mol Endocrinol 20:1772–1785. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2005-0084
Kaiya H, Van Der Geyten S, Kojima M, Hosoda H, Kitajima Y, Matsumoto M, Geelissen S, Darras VM, Kangawa K (2002) Chicken ghrelin: purification, cDNA cloning, and biological activity. Endocrinology 143:3454–3463. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2002-220255
Kaiya H, Saito E-S, Tachibana T, Furuse M, Kangawa K (2007) Changes in ghrelin levels of plasma and proventriculus and ghrelin mRNA of proventriculus in fasted and refed layer chicks. Domest Anim Endocrinol 32:247–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.domaniend.2006.03.006
Khatib N, Gaidhane S, Gaidhane AM, Khatib M, Simkhada P, Gode D, Zahiruddin QS (2014) Ghrelin: Ghrelin as a Regulatory peptide in growth hormone secretion. J Clin Diagn Res 8:MC13–MC17. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2014/9863.4767
Kim MS, Yoon CY, Jang PG, Park YJ, Shin CS, Park HS, Ryu JW, Pak YK, Park JY, Lee KU, Kim SY, Lee HK, Kim YB, Park KS (2004) The mitogenic and antiapoptotic actions of ghrelin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol Endocrinol 18:2291–2301. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2003-0459
King MK, Gay DM, Pan LC, McElmurray JH, Hendrick JW, Pirie C, Morrison A, Ding C, Mukherjee R, Spinale FG (2001) Treatment with a growth hormone secretagogue in a model of developing heart failure: effects on ventricular and myocyte function. Circulation 103:308–313. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.103.2.308
Kojima M, Kangawa K (2010) Ghrelin: from gene to physiological function. Results Probl Cell Differ 50:185–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/400_2009_28
Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, Nakazato M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K (1999) Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 402:656–660. https://doi.org/10.1038/45230
Lieber RL, Jacks TM, Mohler RL, Schleim K, Haven M, Cuizon D, Gershuni DH, Lopez MA, Hora D, Nargund R, Feeney W, Hickey GJ (1997) Growth hormone secretagogue increases muscle strength during remobilization after canine hindlimb immobilization. J Orthop Res 15:519–527. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.1100150407
Longo KA, Govek EK, Nolan A, McDonagh T, Charoenthongtrakul S, Giuliana DJ, Morgan K, Hixon J, Zhou C, Kelder B, Kopchick JJ, Saunders JO, Navia MA, Curtis R, DiStefano PS, Geddes BJ (2011) Pharmacologic inhibition of ghrelin receptor signaling is insulin sparing and promotes insulin sensitivity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 339:115–124. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.111.183764
MacAndrew JT, Ellery SS, Parry MA, Pan LC, Black SC (2001) Efficacy of a growth hormone-releasing peptide mimetic in cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury. Eur J Pharmacol 432:195–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-2999(01)01475-3
Magistrelli D, Pinotti L, Rapetti L, Rosi F (2011) Ghrelin, insulin and pancreatic activity in the peri-weaning period of goat kids. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr 95:40–46. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0396.2009.00980.x
Mathews LS, Norstedt G, Palmiter RD (1986) Regulation of insulin-like growth factor I gene expression by growth hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 83:9343–9347. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.83.24.9343
Mathews LS, Hammer RE, Brinster RL, Palmiter RD (1988) Expression of insulin-like growth factor I in transgenic mice with elevated levels of growth hormone is correlated with growth. Endocrinology 123:433–437. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo-123-1-433
Mazzocchi G, Neri G, Rucinski M, Rebuffat P, Spinazzi R, Malendowicz LK, Nussdorfer GG (2004) Ghrelin enhances the growth of cultured human adrenal zona glomerulosa cells by exerting MAPK-mediated proliferogenic and antiapoptotic effects. Peptides 25:1269–1277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2004.05.011
McCoull W, Barton P, Broo A, Brown AJH, Clarke DS, Coope G, Davies RDM, Dossetter AG, Kelly EE, Knerr L, MacFaul P, Holmes JL, Martin N, Moore JE, Morgan D, Newton C, Österlund K, Robb GR, Rosevere E, Selmi N, Stokes S, Svensson TS, Ullah VBK, Williams EJ (2013) Identification of pyrazolo-pyrimidinones as GHS-R1a antagonists and inverse agonists for the treatment of obesity. Med Chem Commun 4:456–462. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2MD20340E
McKee KK, Palyha OC, Feighner SD, Hreniuk DL, Tan CP, Phillips MS, Smith RG, Van der Ploeg LH, Howard AD (1997) Molecular analysis of rat pituitary and hypothalamic growth hormone secretagogue receptors. Mol Endocrinol 11:415–423. https://doi.org/10.1210/mend.11.4.9908
Miqueo E, Chiarle A, Giuliodori MJ, Relling AE (2019) Association between prepartum metabolic status and resumption of postpartum ovulation in dairy cows. Domest Anim Endocrinol 69:62–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.domaniend.2019.04.005
Momany FA, Bowers CY, Reynolds GA, Hong A, Newlander K, Endocrinology 114, 1531. Bowers C. Y., Momany FA, Reynolds GA, Hong A (1984) (1984) On the in vitro and in ciao activity of a new synthetic hexapeptide that acts on the pituitary to specifically release growth hormone. Endocrinology 114: 1537–1545
Mousseaux D, Le Gallic L, Ryan J, Oiry C, Gagne D, Fehrentz J-A, Galleyrand J-C, Martinez J (2006) Regulation of ERK1/2 activity by ghrelin-activated growth hormone secretagogue receptor 1A involves a PLC/PKCvarepsilon pathway. Br J Pharmacol 148:350–365. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0706727
Müller TD, Nogueiras R, Andermann ML, Andrews ZB, Anker SD, Argente J, Batterham RL, Benoit SC, Bowers CY, Broglio F, Casanueva FF, D’Alessio D, Depoortere I, Geliebter A, Ghigo E, Cole PA, Cowley M, Cummings DE, Dagher A, Diano S, Dickson SL, Diéguez C, Granata R, Grill HJ, Grove K, Habegger KM, Heppner K, Heiman ML, Holsen L, Holst B, Inui A, Jansson JO, Kirchner H, Korbonits M, Laferrère B, LeRoux CW, Lopez M, Morin S, Nakazato M, Nass R, Perez-Tilve D, Pfluger PT, Schwartz TW, Seeley RJ, Sleeman M, Sun Y, Sussel L, Tong J, Thorner MO, van der Lely AJ, van der Ploeg LHT, Zigman JM, Kojima M, Kangawa K, Smith RG, Horvath T, Tschöp MH (2015) Ghrelin Mol Metab 4:437–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2015.03.005
Murray CDR, Martin NM, Patterson M, Taylor SA, Ghatei MA, Kamm MA, Johnston C, Bloom SR, Emmanuel AV (2005) Ghrelin enhances gastric emptying in diabetic gastroparesis: a double blind, placebo controlled, crossover study. Gut 54:1693–1698. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2005.069088
Nargund RP, Patchett AA, Bach MA, Murphy MG, Smith RG (1998) Peptidomimetic growth hormone secretagogues. Design considerations and therapeutic potential. J Med Chem 41:3103–3127. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm970342o
Patchett AA, Nargund RP, Tata JR, Chen MH, Barakat KJ, Johnston DB, Cheng K, Chan WW, Butler B, Hickey G (1995) Design and biological activities of L-163,191 (MK-0677): a potent, orally active growth hormone secretagogue. PNAS 92:7001–7005. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.92.15.7001
Pires J, Greathouse RL, Quach N, Huising MO, Crakes KR, Miller M, Gilor C (2021) The effect of the ghrelin-receptor agonist capromorelin on glucose metabolism in healthy cats. Domest Anim Endocrinol 74:106484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.domaniend.2020.106484
Puleo L, Marini P, Avallone R, Zanchet M, Bandiera S, Baroni M, Croci T (2012) Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of indolinone derivatives as novel ghrelin receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem 20:5623–5636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2012.07.018
Rhodes L, Zollers B, Wofford JA, Heinen E (2018) Capromorelin: a ghrelin receptor agonist and novel therapy for stimulation of appetite in dogs. Vet Med Sci 4:3–16. https://doi.org/10.1002/vms3.83
Richards MP, Poch SM, McMurtry JP (2006) Characterization of turkey and chicken ghrelin genes, and regulation of ghrelin and ghrelin receptor mRNA levels in broiler chickens. Gen Comp Endocrinol 145:298–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2005.09.013
Saito E, Kaiya H, Takagi T, Yamasaki I, Denbow DM, Kangawa K, Furuse M (2002) Chicken ghrelin and growth hormone-releasing peptide-2 inhibit food intake of neonatal chicks. Eur J Pharmacol 453:75–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-2999(02)02393-2
Saito E-S, Kaiya H, Tachibana T, Tomonaga S, Denbow DM, Kangawa K, Furuse M (2005) Inhibitory effect of ghrelin on food intake is mediated by the corticotropin-releasing factor system in neonatal chicks. Regul Pept 125:201–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regpep.2004.09.003
Seim I, Walpole C, Amorim L, Josh P, Herington A, Chopin L (2011) The expanding roles of the ghrelin-gene derived peptide obestatin in health and disease. Mol Cell Endocrinol 340:111–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2011.03.018
Sigalos JT, Pastuszak AW (2018) The safety and efficacy of growth hormone secretagogues. Sex Med Rev 6:45–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sxmr.2017.02.004
Sivertsen B, Lang M, Frimurer TM, Holliday ND, Bach A, Els S, Engelstoft MS, Petersen PS, Madsen AN, Schwartz TW, Beck-Sickinger AG, Holst B (2011) Unique interaction pattern for a functionally biased ghrelin receptor agonist. J Biol Chem 286:20845–20860. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.173237
Smith RG, Jiang H, Sun Y (2005) Developments in ghrelin biology and potential clinical relevance. Trends Endocrinol Metab 16:436–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2005.09.004
Song X, Jiao H, Zhao J, Wang X, Lin H (2019) Ghrelin serves as a signal of energy utilization and is involved in maintaining energy homeostasis in broilers. Gen Comp Endocrinol 272:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2018.11.017
Sugino T, Hasegawa Y, Kikkawa Y, Yamaura J, Yamagishi M, Kurose Y, Kojima M, Kangawa K, Terashima Y (2002) A transient ghrelin surge occurs just before feeding in a scheduled meal-fed sheep. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 295:255–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-291x(02)00654-x
Sugino T, Hasegawa Y, Kurose Y, Kojima M, Kangawa K, Terashima Y (2004) Effects of ghrelin on food intake and neuroendocrine function in sheep. Anim Reprod Sci 82–83:183–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anireprosci.2004.05.001
Sun Y, Wang P, Zheng H, Smith RG (2004) Ghrelin stimulation of growth hormone release and appetite is mediated through the growth hormone secretagogue receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:4679–4684. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0305930101
Vizcarra JA, Wright H, Vizcarra A (2012) The effect of passive immunization against ghrelin on feed and water intake in turkeys. Poult Sci 91:2305–2309. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.2012-02206
White HK, Petrie CD, Landschulz W, MacLean D, Taylor A, Lyles K, Study C, G et al (2009) Effects of an oral growth hormone secretagogue in older adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:1198–1206. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2008-0632
Wierup N, Björkqvist M, Weström B, Pierzynowski S, Sundler F, Sjölund K (2007) Ghrelin and motilin are cosecreted from a prominent endocrine cell population in the small intestine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:3573–3581. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2006-2756
Wofford JA, Zollers B, Rhodes L, Bell M, Heinen E (2018) Evaluation of the safety of daily administration of capromorelin in cats. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 41:324–333. https://doi.org/10.1111/jvp.12459
Yang L, Morriello G, Patchett AA, Leung K, Jacks T, Cheng K, Schleim KD, Feeney W, Chan WW, Chiu SH, Smith RG (1998) -[2(R)-(2-amino-2-methylpropionylamino)-3-(1H-indol-3-yl) propionyl]– 3-benzylpiperidine-3(S)-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (L-163,540): a potent, orally bioavailable, and short-duration growth hormone secretagogue. J Med Chem 41:1. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm9800191
Zollers B, Rhodes L, Smith RG (2016) Capromorelin increases food consumption, body weight, growth hormone, and sustained insulin-like growth factor 1 concentrations when administered to healthy adult Beagle dogs. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 40:140–147. https://doi.org/10.1111/jvp.12344
Zollers B, Huebner M, Armintrout G, Rausch-Derra LC, Rhodes L (2017) Evaluation of the safety in dogs of long-term, daily oral administration of capromorelin, a novel drug for stimulation of appetite. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 40:2 48–255. https://doi.org/10.1111/jvp.12358
Acknowledgements
The author acknowledges CSIR, India and CSIR-CDRI, Lucknow for providing the facilities. CSIR-CDRI communication number for this manuscript is 10636.
Funding
ND is supported by SERB-NPDF fellowship (PDF/2020/001806).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MR reviewed the literature and prepared the draft, NG and ND edited the manuscript and prepared the figures, and RG conceived the idea and edited the manuscript. ND and RG contributed equally to the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Animal ethical statement
No studies were conducted on animals for this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rathore, M., Das, N., Ghosh, N. et al. Insights on discovery, efficacy, safety and clinical applications of ghrelin receptor agonist capromorelin in veterinary medicine. Vet Res Commun 48, 1–10 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-023-10184-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-023-10184-0