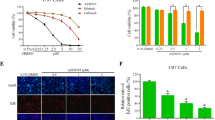
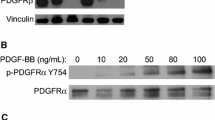
Abstract
Canine glioma is one of the most common brain tumors with poor prognosis, making effective chemotherapy highly desirable. Previous studies have suggested that ERBB4, a signaling molecule involving one of the epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFR), may be a promising therapeutic target. In this study, the anti-tumor effects of pan-ERBB inhibitors, which can inhibit the phosphorylation of ERBB4, were evaluated both in vitro and in vivo using a canine glioblastoma cell line. The results demonstrated that both afatinib and dacomitinib effectively reduced the expression of phosphorylated ERBB4, and significantly decreased the number of viable cells, ultimately prolonging the survival time of orthotopically xenografted mice. Further downstream of ERBB4, afatinib was found to suppress the expression of phosphorylated Akt and phosphorylated Extracellular signal-related kinases1 and 2 (ERK1/2) and induced apoptotic cell death. Thus, pan-ERBB inhibition is a promising therapeutic strategy for the treatment of canine gliomas.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Berens ME, Bjotvedt G, Levesque DC, Rief MD, Shapiro JR, Coons SW (1993) Tumorigenic, invasive, karyotypic, and immunocytochemical characteristics of clonal cell lines derived from a spontaneous canine anaplastic astrocytoma. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 29A:310–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02633959
Hampl JA, Camp SM, Mydlarz WK et al (2003) Potentiated gene delivery to tumors using herpes simplex virus/Epstein-Barr virus/RV tribrid amplicon vectors. Hum Gene Ther 14:611–626. https://doi.org/10.1089/104303403321618137
Hidalgo CE, Farré MA, Pumarola I, Battle M, Borrego MJF, Luján F-P, A (2022) Survival time after surgical debulking and temozolomide adjuvant chemotherapy in canine intracranial gliomas. Vet Sci 9:427. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9080427
Inoue S, Ichikawa T, Kurozumi K et al (2012) Novel animal glioma models that separately exhibit two different invasive and angiogenic phenotypes of human glioblastomas. World Neurosurg 78:670–682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2011.09.005
Lee S, Choi SH, Cho HR, Koh J, Park CK, Ichikawa T (2021) Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging features of a canine glioblastoma model. PLoS ONE 16:e0254448. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0254448
Longo JF, Brosius SN, Black L et al (2019) ErbB4 promotes malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor pathogenesis via ras-independent mechanisms. Cell Commun Signal 17:74. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-019-0388-5
Lucas LM, Dwivedi V, Senfeld JI et al (2022) The Yin and Yang of ERBB4: tumor suppressor and oncoprotein. Pharmacol Rev 74:18–47. https://doi.org/10.1124/pharmrev.121.000381
Noguchi S, Mori T, Hoshino Y et al (2011) MicroRNA-143 functions as a tumor suppressor in human bladder cancer T24 cells. Cancer Lett 307:211–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2011.04.005
Noguchi S, Inoue M, Ichikawa T et al (2021) The NRG3/ERBB4 signaling cascade as a novel therapeutic target for canine glioma. Exp Cell Res 400:112504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112504
Olayioye MA, Neve RM, Lane HA, Hynes NE (2000) The ErbB signaling network: receptor heterodimerization in development and cancer. EMBO J 19:3159–3167. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/19.13.3159
Onishi M, Ichikawa T, Kurozumi K et al (2013) Bimodal anti-glioma mechanisms of cilengitide demonstrated by novel invasive glioma models. Neuropathology 33:162–174. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1789.2012.01344.x
Pastwińska J, Karaś K, Karwaciak I, Ratajewski M (2022) Targeting EGFR in melanoma - the sea of possibilities to overcome drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1877:188754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2022.188754
Pitcher JL, Alexander N, Miranda PJ, Johns TG (2022) ErbB4 in the brain: focus on high grade glioma. Front Oncol 12:983514. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.983514
Rossmeisl JHJ, Pancotto TE (2020) Tumors of the nervous system. In: Vaill DM, Thamm DH, Liptak JM (eds) Withrow & MacEwen’s Small Animal Clinical Oncology, 6th edn. Elsevier, St Louis, pp 657–674
Torrini C, Nguyen TTT, Shu C et al (2022) Lactate is an epigenetic metabolite that drives survival in model systems of glioblastoma. Mol Cell 82:3061–3076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2022.06.030
Wu YT, Tan Hl, Huang Q, Sun XJ, Zhu X, Shen HM (2011) zVAD-induced necroptosis in L929 cells depends on autocrine production of TNFα mediated by the PKC-MAPKs-AP-1 pathway. Cell Death Differ 18:26–37
Yoshioka T, Shien K, Takeda T et al (2019) Acquired resistance mechanisms to afatinib in HER2-amplified gastric cancer cells. Cancer Sci 110:2549–2557. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.14089
Acknowledgements
We express our gratitude to Prof. Kazuhiko Kurozumi (Hamamatsu University School of Medicine) for providing the canine glioblastoma cell line. Additionally, we extend our thanks to Dr. Miyu Tanaka (Laboratory of Veterinary Pathology, Osaka Metropolitan University) for kindly assisting with the histological evaluation.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed to the conception and design of the study. Shunsuke Noguchi and Moeka Yasumura conducted material preparation, data collection, and analysis. Shunsuke Noguchi wrote the first draft of the manuscript, and all authors provided feedback on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Osaka Metropolitan University (14 May 2021/No. 21-129).
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Statement of Animal Ethics
Animal experiment protocol was approved by the Committee for Animal Research and Welfare of Osaka Prefecture University.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Noguchi, S., Yasumura, M. Potential therapeutic efficiency of pan-ERBB inhibitors for canine glioma. Vet Res Commun 47, 2207–2213 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-023-10117-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-023-10117-x