Abstract
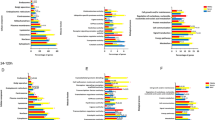
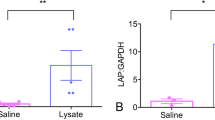
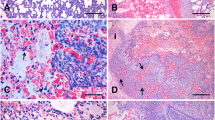
The addition of streptolysin-O (SLO) to the standard antibiotics regimen was shown to be superior to antibiotics alone after experimental infection of foals with Rhodoccocus equi (R. equi). The objective of this study is to investigate this response by determining the site-specific expression of extracellular matrix (ECM) and inflammatory response genes in biopsy samples taken from three distinct lung regions of the infected foals. Twenty-four foals were challenged by intrabronchial instillation of R. equi and assigned to four treatment groups: SLO/antibiotics adjunct therapy, antibiotics-only therapy (7.5 mg/kg clarithromycin and 5 mg/kg rifampin), SLO-only, and saline-only treatments. Treatments were administered twice daily for 16 days unless symptoms progressed to the point where the foals needed to be euthanized. Gene expressions were determined using custom-designed equine real-time qPCR arrays containing forty-eight genes from ECM remodeling and inflammation pathways. A non-parametric Wilcoxon signed-rank test for independent samples was applied to two pairs of time-matched comparison groups, SLO/antibiotics vs. antibiotics-only and SLO-only vs. saline-only, to document the significant differences in gene expressions within these groups. Several genes, MMP9, MMP2, TIMP2, COL1A1, COL12A1, ITGAL, ITGB1, FN1, CCL2, CCL3, CXCL9, TNFα, SMAD7, CD40, IL10, TGFB1, and TLR2, were significantly regulated compared to the unchallenged/untreated control foals. The results of this study demonstrate that enhancement of clinical responses by SLO is consistent with the changes in expression of critical genes in ECM remodeling and inflammatory response pathways.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida Cde S, Abramo C, Alves CC, Mazzoccoli L, Ferreira AP, Teixeira HC (2009) Anti-mycobacterial treatment reduces high plasma levels of CXC-chemokines detected in active tuberculosis by cytometric bead array. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 104(7):1039–1041
Alouf JE, Geoffroy C, Pattus F, Verger R (1984) Surface properties of bacterial sulfhydryl-activated cytolytic toxins. Interaction with monomolecular films of phosphatidylcholine and various sterols. Eur J Biochem 141:205–210
Bettelli E, Korn T, Kuchroo VK (2007) Th17: the third member of the effector T cell trilogy. Curr Opin Immunol 19(6):652–657
Bhakdi S, Tranum-Jensen J, Sziegoleit A (1985) Mechanism of membrane damage by streptolysin-O. Infect Immun 47:52–60
Chang JC, Wysocki A, Tchou-Wong KM, Moskowitz N, Zhang Y, Rom WN (1996) Effect of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and its components on macrophages and the release of matrix metalloproteinases. Thorax 51(3):306–311
Demmers S, Johannisson A, Gröndahl G, Jensen-Waern M (2001) Neutrophil functions and serum IgG in growing foals. Equine Vet J 33(7):676–680
Giguère S, Wilkie BN, Prescott JF (1999) Modulation of cytokine response of pneumonic foals by virulent Rhodococcus equi. Infect Immun 67(10):5041–5047
Greenlee KJ, Werb Z, Kheradmand F (2007) Matrix metalloproteinases in lung: multiple, multifarious, and multifaceted. Physiol Rev 87(1):69–98
Gröndahl G, Johannisson A, Jensen-Waern M (1997) Opsonic effect of equine plasma from different donors. Vet Microbiol 16(3-4):56, 227–35
Gröndahl G, Johannisson A, Demmers S, Jensen Waern M (1999) Influence of age and plasma treatment on neutrophil phagocytosis and CD18 expression in foals. Vet Microbiol 65(3):241–254
Halbur PG, Paul PS, Meng XJ, Lum MA, Andrews JJ, Rathje JA (1996) Comparative pathogenicity of nine US porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) isolates in a five-week-old cesarean-derived, colostrum-deprived pig model. J Vet Diagn Invest 8(1):11–20
Hall EH, Gurel V, Dahlberg AE, McMichael J, Brautigan DL (2011) Inhibition of human breast cancer Matrigel invasion by Streptolysin O activation of the EGF receptor ErbB1. Cell Signal 23(12):1972–1977
Harris JR, Adrian M, Bhakdi S, Palmer M (1998) Cholesterol-Streptolysin O interaction: an EM study of wild-type and mutant Streptolysin O. J Struct Biol 121:343–355
Hasan Z, Cliff JM, Dockrell HM, Jamil B, Irfan M, Ashraf M, Hussain R (2009) CCL2 responses to Mycobacterium tuberculosis are associated with disease severity in tuberculosis. PLoS One 29(12):e8459
Hedrich CM, Bream JH (2010) Cell type-specific regulation of IL-10 expression in inflammation and disease. Immunol Res 47(1–3):185–206
Henneke P, Takeuchi O, Malley R, Lien E, Ingalls RR, Freeman MW, Mayadas T, Nizet V, Akira S, Kasper DL, Golenbock DT (2002) Cellular activation, phagocytosis, and bactericidal activity against group B streptococcus involve parallel myeloid differentiation factor 88-dependent and independent signaling pathways. J Immunol 169(7):3970–3977
Hernandez-Pando R, Orozco H, Arriaga K, Pavön L, Rook G (2000) Treatment with BB-94, a broad spectrum inhibitor of zinc-dependent metalloproteinases, causes deviation of the cytokine profile towards type-2 in experimental pulmonary tuberculosis in Balb/c mice. Int J Exp Pathol 81(3):199–209
Hines SA, Stone DM, Hines MT, Alperin DC, Knowles DP, Norton LK, Hamilton MJ, Davis WC, McGuire TC (2003) Clearance of virulent but not avirulent Rhodococcus equi from the lungs of adult horses is associated with intracytoplasmic gamma interferon production by CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 10(2):208–215
Horohov DW, Loynachan AT, Page AE, Hughes K, Timoney JF, Fettinger M, Hatch T, Spaulding JG, McMichael J (2011) The use of streptolysin O (SLO) as an adjunct therapy for Rhodococcus equi pneumonia in foals. Vet Microbiol 154(1–2):156–162
Hrabec E, Strek M, Zieba M, Kwiatkowska S, Hrabec Z (2002) Circulation level of matrix metalloproteinase-9 is correlated with disease severity in tuberculosis patients. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 6(8):713–719
Huffnagle GB, Strieter RM, McNeil LK, McDonald RA, Burdick MD, Kunkel SL, Toews GB (1997) Macrophage inflammatory protein-1α (MIP-1α) is required for the effector phase of pulmonary cell-mediated immunity to a Cryptococcus neoformans infection. J Immunol 159:318–327
Izzo AA, Izzo LS, Kasimos J, Majka S (2004) A matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor promotes granuloma formation during the early phase of Mycobacterium tuberculosis pulmonary infection. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 84(6):387–396
Johnson MK, Geoffroy C, Alouf JE (1980) Binding of cholesterol by sulfhydryl-activated cytolysins. Infect Immun 27:97–101
Korn T, Oukka M, Kuchroo V, Bettelli E (2007) Th17 cells: effector T cells with inflammatory properties. Semin Immunol 19(6):362–371
Lyadova IV, Tsiganov EN, Kapina MA, Shepelkova GS, Sosunov VV, Radaeva TV, Majorov KB, Shmitova NS, van den Ham HJ, Ganusov VV, De Boer RJ, Racine R, Winslow GM (2010) In mice, tuberculosis progression is associated with intensive inflammatory response and the accumulation of Gr-1 cells in the lungs. PLoS One 5(5):e10469
Mamber SW, Long V, Rhodes RG, Pond-Tor S, Wheeler LR, Fredericks K, Vanscoy B, Sauniere JF, Steinschneider R, Laurent JC, McMichael J (2004) The use of streptolysin o for the treatment of scars, adhesions and fibrosis: initial investigations using murine models of scleroderma. Nonlinearity Biol Toxicol Med 2(2):67–87
Mamber SW, Gurel V, Rhodes RG, McMichael J (2011) Effects of stereptolysine o on extracellular matrix gene expression in normal human epidermal keratinocytes. Dose–response 9(4):554–578
McTaggart C, Yovich JV, Penhale J, Raidal SL (2001) A comparison of foal and adult horse neutrophil function using flow cytometric techniques. Res Vet Sci 71(1):73–79
Means TK, Wang S, Lien E, Yoshimura A, Golenbock DT, Fenton MJ (1999) Human toll-like receptors mediate cellular activation by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol 163(7):3920–3927
Meijer WG, Prescott JF (2004) Rhodococcus equi. Vet Res 35:383–396
Palmer M (2001) The family of thiol-activated, cholesterol-binding cytolysins. Toxicon 39:1681–1689
Park KJ, Hwang SC, Sheen SS, Oh YJ, Han JH, Lee KB (2005) Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in pleural effusions of tuberculosis and lung cancer. Respiration 72(2):166–175
Prescott JF (1987) Epidemiology of Rhodococcus equi infection in horses. Vet Microbiol 14:211–214
Price NM, Farrar J, Tran TT, Nguyen TH, Tran TH, Friedland JS (2001) Identification of a matrix-degrading phenotype in human tuberculosis in vitro and in vivo. J Immunol 166(6):4223–4230
Reuss SM, Chaffin KM, Cohen ND (2009) Extrapulmonary disorders associated with Rhodococcus equi infection in foals: a Retrospective Study of 150 Cases (1987–2007). J Am Vet Med Assoc 235(7):855–863
Sheen P, Ferrer P, Gilman RH, López-Llano J, Fuentes P, Valencia E, Zimic MJ (2009) Effect of pyrazinamidase activity on pyrazinamide resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 89(2):109–113
Taylor JL, Hattle JM, Dreitz SA, Troudt JM, Izzo LS, Basaraba RJ, Orme IM, Matrisian LM, Izzo AA (2006) Role for matrix metalloproteinase 9 in granuloma formation during pulmonary Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Infect Immun 74(11):6135–6144
Tomic-Canic M, Mamber SW, Stojadinovic O, Lee B, Radoja N, McMichael J (2007) Streptolysin O enhances keratinocyte migration and proliferation and promotes skin organ culture wound healing in vitro. Wound Repair Regen 15(1):71–79
Van den Steen PE, Dubois B, Nelissen I, Rudd PM, Dwek RA, Opdenakker G (2002) Biochemistry and molecular biology of gelatinase B or matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9). Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 37(6):375–536
Volkman HE, Pozos TC, Zheng J, Davis JM, Rawls JF, Ramakrishnan L (2010) Tuberculous granuloma induction via interaction of a bacterial secreted protein with host epithelium. Science 327(5964):466–469
Wada R, Kamada M, Anzai T, Nakanishi A, Kanemaru T, Takai S, Tsubaki S (1997) Pathogenicity and virulence of Rhodococcus equi in foals following intratracheal challenge. Vet Microbiol 56(3–4):301–312
Weinstock DM, Brown AE (2002) Rhodococcus equi: an emerging pathogen. Clin Infect Dis 34(10):1379–1385
Yamshchikov AV, Schuetz A, Lyon GM (2010) Rhodococcus equi infection. Lancet Infect Dis 10(5):350–359
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Christoph Schorl, Ph.D and Hilary E. Hartlaub at the Brown University’s Genomics and Proteomics Core Facility for providing access to real-time PCR machines, analysis software, and for other technical and scientific support. The authors also thank Asli Ascioglu, Ph.D for providing assistance with the statistical analysis of the data.
Conflict of Interest
Volkan Gurel, Ph.D, Kristyn Lambert and John McMichael, Ph.D are paid employees of Beech Tree Labs, Inc.
Ethical Standards
Experiments comply with current laws of the United States.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gurel, V., Lambert, K., Page, A.E. et al. Streptolysin-O/antibiotics adjunct therapy modulates site-specific expression of extracellular matrix and inflammatory genes in lungs of Rhodococcus equi infected foals. Vet Res Commun 37, 145–154 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-013-9557-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-013-9557-y