Abstract
Objective
This review aimed to assess the utility of urinary N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase (uNAG) as a prognostic biomarker for nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods
The search for relevant studies was conducted across multiple databases, including PubMed (Medline), EMBASE, LILACS, CENTRAL, IBECS, and gray literature. We employed a random effects model to calculate the standardized mean difference and 95% confidence interval. Furthermore, we assessed heterogeneity using Cochrane's Q test and Higgins' I2 statistics.
Results
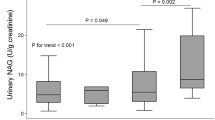
This review included a total of 16 articles involving 1669 patients, with 13 being case–control studies and three being cohorts. The meta-analysis conducted across all studies revealed significant heterogeneity. However, subgroup analysis of four studies indicated that an increase in uNAG among normoalbuminuric patients was associated with the development of macroalbuminuria (DMP = – 1.47; 95% CI = – 1.98 to 0.95; p < 0.00001; I2 = 45%). Conversely, it did not demonstrate effectiveness in predicting the development of microalbuminuria (DMP = 0.26; 95% CI = – 0.08 to 0.60; p = 0.13; I2 = 17%).
Conclusions
Elevated uNAG levels in normoalbuminuric patients may indicate an increased risk for the development of macroalbuminuria, but not microalbuminuria. However, the high heterogeneity observed among the studies highlights the necessity for further research to validate these findings.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
International Diabetes Federation (2021) International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice
DeFronzo RA, Ferrannini E, Groop L, Henry RR, Herman WH, Holst JJ, Hu FB, Kahn CR, Raz I, Shulman GI, Simonson DC, Testa MA, Weiss R (2015) Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Dis Prim 1:1–23 (PMID: 27189025)
Amorim RG, Guedes GS, Vasconcelos SML, Santos JCF (2019) Kidney disease in diabetes mellitus: cross-linking between hyperglycemia, redox imbalance and inflammation. Arq Bras Cardiol 112(5):577–587 (PMID: 31188964)
International K (2020) KDIGO 2020 clinical practice guideline for diabetes management in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 98(4):S1–S115 (PMID: 32998798)
Li L, Astor BC, Lewis J, Hu B, Appel LJ, Lipkowitz MS, Toto RD, Wang X, Wright JT, Greene TH (2012) Longitudinal progression trajectory of GFR among patients with CKD. Am J Kidney Dis 59(4):504–512 (PMID: 22284441)
American Association of Diabetes (2021) ADA standards of diabetes care 2021. Diabetes Care. pp S21–S226
Oshima M, Shimizu M, Yamanouchi M, Toyama T, Hara A, Furuichi K, Wada T (2021) Trajectories of kidney function in diabetes: a clinicopathological update. Nat Rev Nephrol 17(11):740–750
Levey AS, Grams ME, Inker LA (2022) Uses of GFR and albuminuria level in acute and chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med 386(22):2120–2128 (PMID: 35648704)
Weldegiorgis M, de Zeeuw D, Li L, Parving HH, Hou FF, Remuzzi G, Greene T, Heerspink HJL (2018) Longitudinal estimated GFR trajectories in patients with and without type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis 71(1):91–101
Vallon V, Thomson SC (2020) The tubular hypothesis of nephron filtration and diabetic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 16(6):317–336
Thomson SC, Vallon V, Blantz RC (2004) Kidney function in early diabetes: the tubular hypothesis of glomerular filtration. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 286(1):F8–F15 (PMID: 14656757)
Ix JH, Shlipak MG (2021) The promise of tubule biomarkers in kidney disease: a review. Am J Kidney Dis 78(5):719–727 (PMID: 34051308)
Lobato GR, Lobato MR, Thomé FS, Veronese FV (2017) Performance of urinary kidney injury molecule-1, neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin, and N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase to predict chronic kidney disease progression and adverse outcomes. Braz J Med Biol Res. https://doi.org/10.1590/1414-431X20176106. (PMID: 28380198)
Liu Q, Zong R, Li H, Yin X, Fu M, Yao L, Sun J, Yang F (2021) Distribution of urinary N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase and the establishment of reference intervals in healthy adults. J Clin Lab Anal 35(5):e23748
Nauta FL, Boertien WE, Bakker SJL, Van Goor H, Van Oeveren W, De Jong PE, Bilo H, Gansevoort RT (2011) Glomerular and tubular damage markers are elevated in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care 34(4):975–981 (PMID: 21307379)
Kalansooriya A, Jennings P, Haddad F, Holbrook I, Whiting PH (2007) Urinary enzyme measurements as early indicators of renal insult in type 2 diabetes. Br J Biomed Sci 64(4):153–156 (PMID: 18236735)
Omozee EB, Okaka EI, Edo AE, Obika LF (2019) Urinary N-acetyl-beta-d-glucosaminidase levels in diabetic adults. J Lab Physicians 11(1):001–004
Hiratsuka N, Shiba K, Nishida K, Iizima S, Kimura M, Kobayashi S (1998) Analysis of urinary albumin, transferrin, N-Acetyl-b-D-Glucosaminidase and b 2-microglobulin in patients with impaired glucose tolerance. J Clin Lab Anal 12(6):351–355
Yamanouchi T, Kawasaki T, Yoshimura T, Koshibu E, Ogata N, Funato H (1998) Relationship between Serum 1, 5-anhydroglucitol and urinary excretion of N-acetylglucosaminidase and albumin determined at onset of NIDDM with 3-year follow-up. Diabetes Care 21(4):619–624
Siddiqui K, Al-Malki B, George TP, Nawaz SS, Al Rubeaan K (2019) Urinary N-acetyl-beta-d-glucosaminidase (NAG) with neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) improves the diagnostic value for proximal tubule damage in diabetic kidney disease. 3 Biotech 9:66
Mohammadi-Karakani A, Asgharzadeh-Haghighi S, Ghazi-Khansari M, Hosseini R (2007) Determination of urinary enzymes as a marker of early renal damage in diabetic patients. J Clin Lab Anal 21(6):413–417 (PMID: 18022929)
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan SE, Chou R, Glanville J, Grimshaw JM, Hróbjartsson A, Lalu MM, Li T, Loder EW, Mayo-Wilson E, McDonald S, McGuinness LA, Stewart LA, Thomas J, Tricco AC, Welch VA, Whiting P, Moher D (2021) The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372:n71 (PMID: 33782057)
Akobeng AK (2005) Principles of evidence-based medicine. Arch Dis Child 90(8):837–840 (PMID: 16040884)
Fontenelles MJ, Simões MG, Farias SH, Fontenelles RGS (2009) Metodologia da pesquisa científica: diretrizes para elaboração de um protocolo de pesquisa. Rev Para Med 23(3):1–8
Wells GA, Shea B, O’Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, Tugwell P (2000) The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses
Deeks J, Higgins J, Altman D (2022) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 6.3
Jaljuli I, Benjamini Y, Shenhav L, Panagiotou O, Heller R (2023) Quantifying replicability and consistency in systematic reviews. Stat Biopharm Res 15(2):372–385
Morii T, Fujita H, Narita T, Shimotomai T, Fujishima H, Yoshioka N, Imai H, Kakei M, Ito S (2003) Association of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 with renal tubular damage in diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Complicat 17(1):11–15
Fujita H, Morii T, Koshimura J, Kato M, Miura T, Sasaki H, Narita T, Ito S, Kakei M (2006) Possible relationship between adiponectin and renal tubular injury in diabetic nephropathy. Endocr J 53(6):745–752
Yashima I, Hirayama T, Shiiki H, Kanauchi M, Dohi K (1999) Diagnostic significance of urinary immunoglobulin G in diabetic nephropathy. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi 41(8):787–796
Bouvet BR, Paparella CV, Arriaga SMM, Monje AL, Amarilla AM, Almará AM (2014) Avaliação da N-acetil-beta-D-glucosaminidase urinária como marcador de dano renal precoce em pacientes com diabetes melito tipo 2. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol 58(8):798–801 (PMID: 25465599)
Assal HS, Tawfeek S, Rasheed EA, El-Lebedy D, Thabet EH (2013) Serum cystatin C and tubular urinary enzymes as biomarkers of renal dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes 6:7–13
Miyauchi E, Hosojima H, Morimoto S (1995) Urinary angiotensin-converting enzyme activity in type 2 diabetes mellitus: its relationship to diabetic nephropathy. Acta Diabetol 32(3):193–197
Banu N, Hara H, Okamura M, Egusa G, Yamakido M (1995) Urinary excretion of type IV collagen and laminin in the evaluation of nephropathy in NIDDM: comparison with urinary albumin and markers of tubular dysfunction and/or damage. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 29(1):57–67
Piwowar A, Knapik-Kordecka M, Buczynska H, Warwas M (1999) Plasma cystatin C concentration in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: relation with nephropathy. Arch Immunol Ther Exp-Engl Ed 47:327–331
Ito S, Fujita H, Narita T, Yaginuma T, Kawarada Y, Kawagoe M, Sugiyama T (2001) Urinary copper excretion in type 2 diabetic patients with nephropathy. Nephron 88(4):307–312
Piwowar A, Knapik-Kordecka M, Fus I, Warwas M (2006) Urinary activities of cathepsin B, N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase, and albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Med Sci Monit: Int Med J Exp Clin Res 12(5):CR210–CR214
Fu WJ, Li BL, Wang SB, Chen ML, Deng RT, Ye CQ, Liu L, Fang AJ, Xiong SL, Wen S, Tang HH, Chen ZX, Huang ZH, Peng LF, Zheng L, Wang Q (2012) Changes of the tubular markers in type 2 diabetes mellitus with glomerular hyperfiltration. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 95(1):105–109 (PMID: 22015481)
Zhang Y, Yang J, Zheng M, Wang Y, Ren H, Xu Y, Chang B (2015) Clinical characteristics and predictive factors of subclinical diabetic nephropathy. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 123(2):132–138
Asare-Anane H, Twum F, Kwaku Ofori E, Torgbor EL, Amanquah SD, Osafo C (2016) urinary lysosomal enzyme activities and albuminuria in Ghanaian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Dis Markers. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2810639
Al-Hazmi SF, Gad HG, Alamoudi AA, Eldakhakhny BM, Binmahfooz SK, Alhozali AM (2020) Evaluation of early biomarkers of renal dysfunction in diabetic patients. Saudi Med J 41(7):690
Petrica L, Hogea E, Gadalean F, Vlad A, Vlad M, Dumitrascu V, Popescu R (2021) Long noncoding RNAs may impact podocytes and proximal tubule function through modulating miRNAs expression in early diabetic kidney disease of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Int J Med Sci 18(10):2093
Fufaa GD, Weil EJ, Nelson RG, Hanson RL, Bonventre JV, Sabbisetti V, Waikar SS, Mifflin TE, Zhang X, Xie D, Hsu CY, Feldman HI, Coresh J, Vasan RS, Kimmel PL, Liu KD (2015) Association of urinary KIM-1, L-FABP, NAG and NGAL with incident end-stage renal disease and mortality in American Indians with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 58(1):188–198 (PMID: 25316431)
Cianci R, Simeoni M, Gigante A, Marco Perrotta A, Ronchey S, Mangialardi N, Ferri C (2023) Renal stem cells, renal resistive index, and neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin changes after revascularization in patients with renovascular hypertension and ischemic nephropathy. Curr Pharm Des 29(2):133–138
Ruggenenti P, Cravedi P, Remuzzi G (2010) The RAAS in the pathogenesis and treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Nat Rev Nephrol 6(6):319–330
Alicic RZ, Rooney MT, Tuttle KR (2017) Diabetic kidney disease: challenges, progress, and possibilities. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 12(12):2032–2045 (PMID: 28522654)
Zhang Y, Yang J, Zheng M, Wang Y, Ren H, Xu Y, Yang Y, Cheng J, Han F, Yang X, Chen L, Shan C, Chang B (2015) Clinical characteristics and predictive factors of subclinical diabetic nephropathy. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 123(2):132–138 (PMID: 25607340)
Driza AR, Kapoula GV, Bagos PG (2021) Urinary N-Acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase (uNAG) as an indicative biomarker of early diabetic nephropathy in patients with diabetes mellitus (T1DM, T2DM): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetology 2(4):272–285
Kern EF, Erhard P, Sun W, Genuth S, Weiss MF (2010) Pathogenesis and treatment of kidney disease early urinary markers of diabetic kidney disease: a nested case-control study from the diabetes control and complications trial (DCCT). YAJKD 55:824–834
Sheira G, Noreldin N, Tamer A, Saad M (2015) Urinary biomarker N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase can predict severity of renal damage in diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Metab Disord. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40200-015-0133-6
Funding
The authors declare that the research was conducted without any commercial or financial relationships.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
dos Santos Bitencourt, A., Vargas Filho, R.L., da Silveira Prestes, G. et al. Evaluation of N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase as a prognostic marker for diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetics: systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Urol Nephrol 56, 1651–1661 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-023-03843-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-023-03843-3