Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the safety and effectiveness of an individualized regional citrate anticoagulation (RCA) protocol for hemodialysis.
Methods
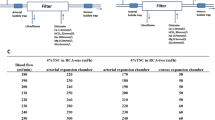
In this single-center, retrospective study, blood coagulation in the extracorporeal circulation, adverse reactions, in vivo ionized calcium (iCa2+) concentrations, and the infusion dose of citrate during RCA in hemodialysis were observed in 98 patients from February 2021 to March 2022.
Results
A total of 98 patients underwent RCA during hemodialysis 362 times, and blood coagulation occurred in the extracorporeal circulation 29 times. Among the 29 cases of coagulation, most of the patients exhibited hypercoagulability, and among approximately 80% of the treatments, the deviation between the actual infusion rate of citrate in the extracorporeal circulation and the theoretical value was ± 10%. After hemodialysis, pH values and bicarbonate ion (HCO3−) levels were clearly improved, and online conductivity monitoring (OCM) values and blood coagulation scores in the extracorporeal circulation were identical to those measured in similar studies.
Conclusion
An individualized RCA protocol for hemodialysis is safe, effective, simple, and inexpensive and can meet the needs of individualized treatment; therefore, its application is worthy of promotion.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Morita Y, Johnson RW, Dorn RE et al (1961) Regional anticoagulation during hemodialysis using citrate. Am J MedicalSci 242(1):32
Luo L, Fan M, Chen Q et al (2021) A simplified protocol for individualized regional citrate anticoagulation for hemodialysis: a single-center, randomized clinical study. Medicine 100(8):e24639
Buturovic-Ponikvar J, Cerne S, Gubensek J et al (2008) Regional citrate anticoagulation for hemodialysis: calcium-free Vs. calcium containing dialysate—a randomized trial. Int J Artif Organs 31(5):418–424
Tolwani A, Wille KM (2012) Advances in continuous renal replacement therapy: citrate anticoagulation update. Blood Purif 34(2):88–93
Oudemans-Van-Straaten H, Bosman RM, Van-Der-Voort P et al (2009) Citrate anticoagulation for continuous venovenous hemofiltration. Crit Care Med 37(2):545
Khwaja A (2012) KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin Pract 120(4):c179–c184
Kramer L, Bauer E, Joukhadar C et al (2003) Citrate pharmacokinetics and metabolism in cirrhotic and noncirrhotic critically ill patients. Crit Care Med 31(10):2450–2455
Hartmann J, Strobl K, Fichtinger U et al (2012) In vitro investigations of citrate clearance with different dialysis filters. Int J Artif Organs 35(5):352–359
Song L (2017) Calcium and bone metabolism indices. Adv Clin Chem 82:1–46
Umerah CO, Momodu II. Anticoagulation. 2021 Dec 27. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan–. PMID: 32809486.
Lin T, Song L, Huang R et al (2019) Modified regional citrate anticoagulation is optimal for hemodialysis in patients at high risk of bleeding: a prospective randomized study of three anticoagulation strategies. BMC Nephrol 20(1):472
Al Saran K, Sabry A, Abdulghafour M, Yehia A (2010) Online conductivity monitoring of dialysis adequacy versus Kt/V derived from urea reduction ratio: a prospective study from a Saudi Center. Ren Fail 32(1):36–40
Masud A, Costanzo EJ, Zuckerman R, Asif A (2018) The complications of vascular access in hemodialysis. Semin Thromb Hemost 44(1):57–59
Calatzis A, Toepfer M, Schramm W et al (2001) Citrate anticoagulation for extracorporeal circuits: effects on whole blood coagulation activation and clot formation. Nephron 89(2):233–236
Kozik-Jaromin J (2005) Citrate kinetics during regional citrate anticoagulation in extracorporeal organ replacement therapy. universität freiburg
Arepally, Gowthami, M (2017) Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood: J Am Soc Hematol 129(21):2864–2872
Debaugnies F, Azerad MA, Noubouossié D et al (2010) Evaluation of the procoagulant activity in the plasma of cancer patients using a thrombin generation assay. Thromb Res 126(6):531–535
LinnemannB L-L (2012) Risk factors, management and primary prevention of thrombotic complications related to the use of central venous catheters. Vasa 41(5):319–332
De Pietri L, Montalti R, Beqliomini B et al (2010) Thromboelastographic changes in liver and pancreatic cancer surgery: hypercoagulability, hypocoagulability or normocoagulability? Eur J Anaesthesiol 27(7):608–616
Saccullo G, Malato A, Raso S et al (2012) Cancer patients requiring interruption of long-term warfarin because of surgery or chemotherapy induced thrombocytopenia: the use of fixed sub-therapeutic doses of low-molecular weight heparin. Am J Hematol 87(4):388–391
Huang MJ, Wei RB, Li QP et al (2016) Hypercoagulable state evaluated by thromboelastography in patients with idiopathic membranous nephropathy. J Thrombosis Thrombolysis 41(2):321–327
Levi M, Tom V (2017) Coagulation and sepsis. Thrombosis Res 149:38–44
Liew N, Alemany G, Angchaisuksiri P et al (2017) Asian venous thromboembolism guidelines: updated recommendations for the prevention of venous thromboembolism. Int Angiol 36(1):1
Szamosfalvi B, Frinak S, Yee J (2010) Automated regional citrate anticoagulation: technological barriers and possible solutions. Blood Purif 29(2):204–209
Funding
This study was supported by Nanchang Medical and health science and technology Support Plan (2022-KJZC-027).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LL designed the study, organized the research, conducted the statistical analysis, and revised the paper; YF, FW, and MZ collected the data, conducted the statistical analysis, and wrote the paper. YG, ZH, TJ, and CG implemented the individualized protocol of regional citrate anticoagulation in hemodialysis, collected blood samples, and scored blood coagulation in the extracorporeal circulation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, Y., Wu, F., Zou, M. et al. An individualized regional citrate anticoagulation protocol for hemodialysis: a real-world retrospective study. Int Urol Nephrol 56, 295–302 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-023-03677-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-023-03677-z