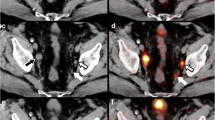
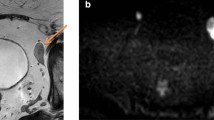
Abstract
Purpose
To assess the negative predictive value of PSMA PET scan for lymph node staging in patients undergoing robotic radical prostatectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection.
Materials and methods
A retrospective analysis of patients who underwent robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy with pelvic lymph node dissection and had a preoperative negative PSMA PET scan for metastasis was performed. The documented pre-operative variables studied included age, BMI, PSA at diagnosis, Gleason score, and biopsy ISUP grades. Patients were categorised as low, intermediate and high risk according to the D Amico classification. The post-op variables included were number of lymph nodes harvested, number of positive nodes, positivity rate, size of the node metastasis, T staging and ISUP grading.
Results
The overall negative predictive value of PSMA PET scan was 71.6%. Further sub-classification according to risk stratification demonstrated a NPV of 58.02%, 92.7% and 90% for high, intermediate and low risk, respectively.
Conclusion
Pelvic lymph node dissection cannot be excluded based on a negative preop PSMA PET/CT scan.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Ms Carmel Regeela Mainu TT, Mr. Adarsh M Kurup.
References
Mottet N, van den Bergh RCN, Briers E et al (2021) EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer-2020 update. Part 1: screening, diagnosis, and local treatment with curative intent. Eur Urol 79:243–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2020.09.042
Hövels AM, Heesakkers RA, Adang EM, Jager GJ, Strum S, Hoogeveen YL, Severens JL, Barentsz JO (2008) The diagnostic accuracy of CT and MRI in the staging of pelvic lymph nodes in patients with prostate cancer: a meta-analysis. Clin Radiol 63:387–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crad.2007.05.022
Briganti A, Abdollah F, Nini A, Suardi N, Gallina A, Capitanio U, Bianchi M, Tutolo M, Passoni NM, Salonia A, Colombo R, Freschi M, Rigatti P, Montorsi F (2012) Performance characteristics of computed tomography in detecting lymph node metastases in contemporary patients with prostate cancer treated with extended pelvic lymph node dissection. Eur Urol 61:1132–1138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2011.11.008
Hofman MS, Lawrentschuk N, Francis RJ, proPSMA Study Group Collaborators et al (2020) Prostate-specific membrane antigen PET/CT in patients with high-risk prostate cancer before curative-intent surgery or radiotherapy (proPSMA): a prospective, randomised, multicentre study. Lancet 395:1208–1216. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30314-7
Bouchelouche K, Turkbey B, Choyke PL (2016) PSMA PET and radionuclide therapy in prostate cancer. Semin Nucl Med 46:522–535. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2016.07.006
Sweat SD, Pacelli A, Murphy GP, Bostwick DG (1998) Prostate-specific membrane antigen expression is greatest in prostate adenocarcinoma and lymph node metastases. Urology 52:637–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0090-4295(98)00278-7
Perera M, Papa N, Roberts M, Williams M, Udovicich C, Vela I, Christidis D, Bolton D, Hofman MS, Lawrentschuk N, Murphy DG (2020) Gallium-68 prostate-specific membrane antigen positron emission tomography in advanced prostate cancer-updated diagnostic utility, sensitivity, specificity, and distribution of prostate-specific membrane antigen-avid lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Urol 77:403–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2019.01.049
Sachpekidis C, Bäumer P, Kopka K, Hadaschik BA, Hohenfellner M, Kopp-Schneider A, Haberkorn U, Dimitrakopoulou-Strauss A (2018) 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT in the evaluation of bone metastases in prostate cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 45:904–912. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-018-3936-0
Afshar-Oromieh A, Babich JW, Kratochwil C, Giesel FL, Eisenhut M, Kopka K, Haberkorn U (2016) The rise of PSMA ligands for diagnosis and therapy of prostate cancer. J Nucl Med 57(Suppl 3):79S-89S. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.115.170720
Mohler JL, Antonarakis ES, Armstrong AJ et al (2019) Prostate cancer, version 2.2019, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 17:479–505. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2019.0023
Gandaglia G, Fossati N, Zaffuto E et al (2017) Development and internal validation of a novel model to identify the candidates for extended pelvic lymph node dissection in prostate cancer. Eur Urol 72:632–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2017.03.049
Marra G, Valerio M, Heidegger I et al (2020) EAU-yau prostate cancer working party. Management of patients with node-positive prostate cancer at radical prostatectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection: a systematic review. Eur Urol Oncol. 3:565–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euo.2020.08.005
Luiting HB, van Leeuwen PJ, Busstra MB et al (2020) Use of gallium-68 prostate-specific membrane antigen positron-emission tomography for detecting lymph node metastases in primary and recurrent prostate cancer and location of recurrence after radical prostatectomy: an overview of the current literature. BJU Int 125:206–214. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.14944
Petersen LJ, Zacho HD (2020) PSMA PET for primary lymph node staging of intermediate and high-risk prostate cancer: an expedited systematic review. Cancer Imaging 23(20):10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40644-020-0290-9
Barbosa ÁRG, Amaral BS, Lourenço DB, Bianco B, Gushiken FA, Apezzato M, Silva JF, Cunha MLD, Filippi RZ, Baroni RH, Lemos GC, Carneiro A (2022) Accuracy of 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT and PET-MRI in lymph node staging for localized prostate cancer. Einstein 20:eAO6599. https://doi.org/10.31744/einstein_journal/2022AO6599
Klingenberg S, Jochumsen MR, Ulhøi BP, Fredsøe J, Sørensen KD, Borre M, Bouchelouche K (2021) 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT for primary lymph node and distant metastasis nm staging of high-risk prostate cancer. J Nucl Med 62:214–220. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.120.245605
Franklin A, Yaxley WJ, Raveenthiran S, Coughlin G, Gianduzzo T, Kua B, McEwan L, Wong D, Delahunt B, Egevad L, Samaratunga H, Brown N, Parkinson R, Roberts MJ, Yaxley JW (2021) Histological comparison between predictive value of preoperative 3-T multiparametric MRI and 68 Ga-PSMA PET/CT scan for pathological outcomes at radical prostatectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection for prostate cancer. BJU Int 127:71–79. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.15134
Hope TA, Eiber M, Armstrong WR, Juarez R, Murthy V, Lawhn-Heath C, Behr SC, Zhang L, Barbato F, Ceci F, Farolfi A, Schwarzenböck SM, Unterrainer M, Zacho HD, Nguyen HG, Cooperberg MR, Carroll PR, Reiter RE, Holden S, Herrmann K, Zhu S, Fendler WP, Czernin J, Calais J (2021) Diagnostic accuracy of 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET for pelvic nodal metastasis detection prior to radical prostatectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection: a multicenter prospective phase 3 imaging trial. JAMA Oncol 1(7):1635–1642. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.3771
Budäus L, Leyh-Bannurah SR, Salomon G, Michl U, Heinzer H, Huland H, Graefen M, Steuber T, Rosenbaum C (2016) Initial Experience of (68)Ga-PSMA PET/CT Imaging in High-risk Prostate Cancer Patients Prior to Radical Prostatectomy. Eur Urol 69:393–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2015.06.010
Van Leeuwen PJ, Emmett L, Ho B, Delprado W, Ting F, Nguyen Q, Stricker PD (2017) Prospective evaluation of 68Gallium-prostate-specific membrane antigen positron emission tomography/computed tomography for preoperative lymph node staging in prostate cancer. BJU Int 119:209–215. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.13540
Öbek C, Doğanca T, Demirci E, Ocak M, Kural AR, Yıldırım A, Yücetaş U, Demirdağ Ç, Erdoğan SM, Kabasakal L (2017) Members of urooncology association, Turkey. The accuracy of 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT in primary lymph node staging in high-risk prostate cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 44(11):1806–1812. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-017-3752-y
Noto B, Büther F, Auf der Springe K, Avramovic N, Heindel W, Schäfers M, Allkemper T, Stegger L (2017) Impact of PET acquisition durations on image quality and lesion detectability in whole-body 68Ga-PSMA PET-MRI. EJNMMI Res 7:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13550-017-0261-8
Ingvar J, Hvittfeldt E, Trägårdh E, Simoulis A, Bjartell A (2022) Assessing the accuracy of [18F]PSMA-1007 PET/CT for primary staging of lymph node metastases in intermediate- and high-risk prostate cancer patients. EJNMMI Res 9(12):48. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13550-022-00918-7
Jansen BHE, Bodar YJL, Zwezerijnen GJC, Meijer D, van der Voorn JP, Nieuwenhuijzen JA, Wondergem M, Roeleveld TA, Boellaard R, Hoekstra OS, van Moorselaar RJA, Oprea-Lager DE, Vis AN (2021) Pelvic lymph-node staging with 18F-DCFPyL PET/CT prior to extended pelvic lymph-node dissection in primary prostate cancer - the SALT trial. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 48:509–520. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-020-04974-w
Meijer D, van Leeuwen PJ, Roberts MJ, Siriwardana AR, Morton A, Yaxley JW, Samaratunga H, Emmett L, van de Ven PM, van der Poel HG, Donswijk ML, Boellaard TN, Schoots IG, Oprea-Lager DE, Coughlin GD, Vis AN (2021) External validation and addition of prostate-specific membrane antigen positron emission tomography to the most frequently used nomograms for the prediction of pelvic lymph-node metastases: an international multicenter study. Eur Urol 80:234–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2021.05.006
Funding
Intramural funds from Aster DM healthcare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Adiyat, K.T., Pooleri, G.K., Cherian, D.T. et al. Negative predictive value of PSMA PET scan for lymph node staging in patients undergoing robotic radical prostatectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection. Int Urol Nephrol 55, 1453–1457 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-023-03595-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-023-03595-0