Abstract
Purpose
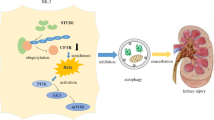
Oxidative damage is important in calcium oxalate (CaOx) stone development but occurs via multiple pathways. Studies have shown that klotho plays an essential role in ameliorating oxidative damage. This study aims to explore the role of klotho in CaOx stones and whether the underlying mechanism is related to the regulation of Keap1-Nrf2-ARE signaling.Methods.
Methods
The levels of GSH, SOD, CAT, MDA, and ROS were examined by ELISA. The klotho, Bcl-2, caspase-3, Keap1, Nrf2, HO-1, and NQO1 mRNA levels were measured by qRT‒PCR, and their protein levels were detected by Western blotting. Renal tissue apoptosis was examined by TUNEL staining, and crystal cell adherence and apoptosis in HKC cells were assessed based on the Ca2+ concentrations and by flow cytometry. The renal pathological changes and the adhesion of CaOx crystals in the kidneys were examined by hematoxylin–eosin and von Kossa staining, respectively.Results.
Results
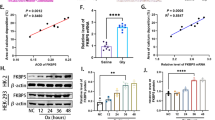
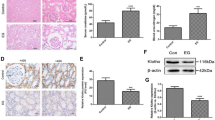
We constructed a CaOx kidney stone model in vitro. By regulating the klotho gene, klotho overexpression inhibited the CaOx‐induced promotion of crystal cell adherence and apoptosis in HKC cells, and these effects were reversed by klotho knockdown. Moreover, our in vivo assay demonstrated that klotho overexpression alleviated glyoxylate administration-induced renal oxidative damage, renal apoptosis, and crystal deposition in the kidneys of mice, and these effects were also associated with activation of the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway.Conclusion.
Conclusion
Klotho protein inhibits the oxidative stress response of HKC cells through the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway, reduces the apoptosis of and adhesion of CaOx crystals to HKC cells, and decreases the occurrence of CaOx kidney stones.
Clinical trial registration
20220304.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
References
Liu Y, Chen Y, Liao B et al (2018) Epidemiology of urolithiasis in Asia. Asian J Urol 5(4):205–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajur.2018.08.007
Kletzmayr A, Mulay SR, Motrapu M et al (2020) Inhibitors of calcium oxalate crystallization for the treatment of oxalate nephropathies. Adv Sci (Weinh). 7(8):1903337. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201903337
Erben RG (2018) α-Klotho’s effects on mineral homeostasis are fibroblast growth factor-23 dependent. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 27(4):229–235. https://doi.org/10.1097/MNH.0000000000000415
Chen K, Wang S, Sun QW et al (2021) Klotho Deficiency Causes Heart Aging via Impairing the Nrf2-GR Pathway. Circ Res 128(4):492–507. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317348
Neyra JA, Hu MC, Moe OW (2020) Klotho in clinical nephrology: diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 16(1):162–176. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.02840320
Khan SR, Canales BK, Dominguez-Gutierrez PR (2021) Randall’s plaque and calcium oxalate stone formation: role for immunity and inflammation. Nat Rev Nephrol 17:417–433. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41581-020-00392-1
Bellezza I (2018) Oxidative stress in age-related macular degeneration: Nrf2 as therapeutic target. Front Pharmacol 9:1280. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.01280
Romero A, San Hipólito-Luengo Á, Villalobos LA et al (2019) The angiotensin-(1–7)/Mas receptor axis protects from endothelial cell senescence via klotho and Nrf2 activation. Aging Cell 18(3):e12913. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12913
Cui W, Leng B, Wang G (2019) Klotho protein inhibits H2O2-induced oxidative injury in endothelial cells via regulation of PI3K/AKT/Nrf2/HO-1 pathways. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 97(5):370–376. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjpp-2018-0277
Yamamoto M, Kensler TW, Motohashi H (2018) The KEAP1-NRF2 system: a thiol-based sensor-effector apparatus for maintaining redox homeostasis. Physiol Rev 98:1169–1203. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00023.2017
Narula S, Tandon S, Baligar P, Singh SK, Tandon C (2017) Human kidney stone matrix: latent potential to restrain COM induced cytotoxicity and inflammatory response. Chem Biol Interact 278:114–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2017.10.018
Hu MC, Moe OW (2012) Klotho as a potential biomarker and therapy for acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Nephrol 8:423–429. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2012.92
Ni W, Zhang Y, Yin Z (2021) The protective mechanism of Klotho gene-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on acute kidney injury induced by rhabdomyolysis. Regen Ther 18:255–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reth.2021.07.003
Cheng MF, Chen LJ, Cheng JT (2010) Decrease of Klotho in the kidney of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Biomed Biotechnol 2010:513853. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/513853
Raeisi S, Ghorbanihaghjo A, Argani H, Dastmalchi S, Ghasemi B, Ghazizadeh T, Rashtchizadeh N, Nemati M, Abbasi MM, Bargahi N, Mota A, Vatankhah AM (2016) Effects of angiotensin II receptor blockade on soluble klotho and oxidative stress in calcineurin inhibitor nephrotoxicity in rats. Iran J Kidney Dis 10:358–363
Maltese G, Psefteli PM, Rizzo B, Srivastava S, Gnudi L, Mann GE, Siow RCM (2016) The anti-ageing hormone klotho induces Nrf2-mediated antioxidant defences in human aortic smooth muscle cells. J Cell Mol Med 21:621–627. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.12996
Shin EJ, Chung YH, Le HLT, Jeong JH, Dang DK, Nam Y, Wie MB, Nah SY, Nabeshima YI, Nabeshima T, Kim HC (2015) Melatonin attenuates memory impairment induced by Klotho gene deficiency via interactive signaling between MT2 receptor, ERK, and Nrf2-related antioxidant potential. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1093/ijnp/pyu105
Vasconcelos AR, Dos Santos NB, Scavone C, Munhoz CD (2019) Nrf2/ARE pathway modulation by dietary energy regulation in neurological disorders. Front Pharmacol 10:33–33. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.00033
Menshchikova EB, Zenkov NK, Tkachev VO, Lemza AE, Kandalintseva NV (2013) Protective effect of ARE-inducing phenol antioxidant TS-13 in chronic inflammation. Bull Exp Biol Med 155:330–334. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-013-2146-9
Jing X, Ren D, Wei X, Shi H, Zhang X, Perez RG, Lou H, Lou H (2013) Eriodictyol-7-O-glucoside activates Nrf2 and protects against cerebral ischemic injury. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 273:672–679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2013.10.018
Zhao M, Murakami S, Matsumaru D, Kawauchi T, Nabeshima Y-i, Motohashi H (2022) NRF2 pathway activation attenuates ageing-related renal phenotypes due to α-klotho deficiency. J Biochem 171:579–589. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvac014
Chen K, Wang S, Sun QW, Zhang B, Ullah M, Sun Z (2021) Klotho deficiency causes heart aging via impairing the Nrf2-GR pathway. Circ Res 128:492–507. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317348
Marquez-Exposito L, Tejedor-Santamaria L, Valentijn FA et al (2022) Oxidative stress and cellular senescence are involved in the aging kidney. Antioxidants (Basel) 11:301. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11020301
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Name of the fund: The role and Mechanism of Klotho protein in calcium oxalate stone formation by regulating Kear1-Nrf2-ARE signal Pathway No. 81760128).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This study was performed in collaboration with all authors. Murat Mahmut and Ma Bin conceived the outline and designed the study. Liu Ruo Tian and Murat Mahmut revised the manuscript. All the authors reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of The Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University (Urumqi, China).
Consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from all individual participants or legal guardians included in the study.
Consent to publish
All authors consent to publish.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmatjan, B., ruotian, L., rahman, A. et al. Klotho inhibits the formation of calcium oxalate stones by regulating the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway. Int Urol Nephrol 55, 263–276 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-022-03398-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-022-03398-9