Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the efficacy of dutasteride add-on treatment to tadalafil in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) suggestive of benign prostatic enlargement (BPE).
Methods
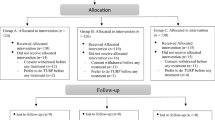
A prospective study was conducted in patients with BPE who had not been satisfied with tadalafil monotherapy for more than 3 months. Inclusion criteria were prostate volume (PV) ≥ 30 ml and IPSS ≥ 8 or QOL index ≥ 3 under administration of tadalafil without anticholinergic agent. Before and 24 weeks after dutasteride add-on treatment to tadalafil, we assessed IPSS, overactive bladder symptom score (OABSS), serum PSA and testosterone, and uroflowmetry (UFM) to compare these parameters before and after dutasteride add-on treatment. Using a propensity-score matching analysis, the efficacy of dutasteride add-on treatment to tadalafil was compared with the previous study of dutasteride add-on treatment to alpha blocker.
Results
Of 52 patients who were enrolled in this study, 48 patients completed the study (mean age: 72 ± 5 years old). Dutasteride add-on treatment to tadalafil significantly improved IPSS (from 16.4 ± 5.2 to 13.3 ± 6.4) and IPSS-QOL (from 4.0 ± 1.2 to 3.3 ± 1.1), and reduced PV from 55 ± 26 to 39 ± 22 ml. Propensity-score matching identified 42 matched pairs of patients. The improvement rate of IPSS and reduction rate of PV were similar between patients treated with dutasteride add-on treatment to tadalafil and dutasteride add-on treatment to alpha blocker. The logistic regression analysis showed that PV at baseline and reduction rate of PV after treatment were associated with the effective symptomatic outcome.
Conclusions
The dutasteride add-on is a reasonable treatment option for male patients with LUTS who are not satisfied with tadalafil monotherapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oelke M, Giuliano F, Mirone V, Xu L, Cox D, Viktrup L (2012) Monotherapy with tadalafil or tamsulosin similarly improved lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia in an international, randomised, parallel, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Eur Urol 61:917–925
Roehrborn CG, Siami P, Barkin J, Damião R, Major–Walker K, Nandy I, Morrill BB, Gagnier RP, Montorsi F, CombAT Study Group (2010) The effects of combination therapy with dutasteride and tamsulosin on clinical outcomes in men with symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia: 4-year results from the CombAT study. Eur Urol 57:123–131
Watanabe D, Yamashita A, Miura K, Mizushima A (2020) Effects on sexual function in Japanese patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia upon switching from combination therapy with α1 blocker and dutasteride to combination therapy with tadalafil and dutasteride. Aging Male 23:501–506
Kosilov KV, Kuzina IG, Kuznetsov V, Kosilova EK (2020) Improvement of the symptoms of lower urinary tract and sexual dysfunction with tadalafil and solifenacin after the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia with dutasteride. Prostate Int 8:78–84
Kosilov K, Kuzina I, Kuznetsov V, Barabash O, Fedorishcheva E (2022) Efficacy of a combination of dutasteride, tadalafil, and solifenacin in the treatment of previously unsuccessful patients. Asian J Urol 9:42–50
Wada N, Kita M, Hashizume K, Matsumoto S, Kakizaki H (2013) Urodynamic effects of dutasteride add-on therapy to alpha-adrenergic antagonist for patients with benign prostatic enlargement: prospective pressure-flow study. Neurourol Urodyn 32:1123–1127
Wada N, Hashizume K, Tamaki G, Kita M, Iwata T, Matsumoto S, Kakizaki H (2012) Add-on effect of dutasteride in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia treated with alpha blocker: its effect on overactive bladder. Act Urol Jpn 58:475–480
Homma Y, Yoshida M, Seki N, Yokoyama O, Kakizaki H, Gotoh M, Yamanishi T, Yamaguchi O, Takeda M, Nishizawa O (2006) Symptom assessment tool for overactive bladder syndrome–overactive bladder symptom score. Urology 68:318–323
Yamaguchi O, Nishizawa O, Takeda M, Yokoyama O, Homma Y, Kakizaki H, Obara K, Gotoh M, Igawa Y, Seki N, Yoshida M, Neurogenic Bladder Society (2009) Clinical guidelines for overactive bladder. Int J Urol 16:126–142
Homma Y, Kawabe K, Tsukamoto T, Yamaguchi O, Okada K, Aso Y, Watanabe H, Okajima E, Kumazawa J, Yamaguchi T, Ohashi Y (1996) Estimate criteria for efficacy of treatment in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Int J Urol 3:267–273
Oelke M, Bachmann A, Descazeaud A, Emberton M, Gravas S, Michel MC, Ndow J, Nordling J, de la Rosette JJ, European Association of Urology (2013) EAU guidelines on the treatment and follow-up of non-neurogenic male lower urinary tract symptoms including benign prostatic obstruction. Eur Urol 64:118–140
Homma Y, Gotoh M, Kawauchi A, Kojima Y, Masumori N, Nagai A, Saitoh T, Sakai H, Takahashi S, Ukimura O, Yamanishi T, Yokoyama O, Yoshida M, Maeda K (2017) Clinical guidelines for male lower urinary tract symptoms and benign prostatic hyperplasia. Int J Urol 24:716–729
Lerner LB, McVary KT, Barry MJ, Bixler BR, Dahm P, Das AK, Gandhi MC, Kaplan SA, Kohler TS, Martin L, Parsons JK, Roehrborn CG, Stoffel JT, Welliver C, Wilt TJ (2021) Management of lower urinary tract symptoms attributed to benign prostatic hyperplasia: AUA guideline part I-initial work-up and medical management. J Urol 206:806–817
Casabé A, Roehrborn CG, Da Pozzo LF, Zepeda S, Henderson RJ, Sorsaburu S, Henneges C, Wong DG, Viktrup L (2014) Efficacy and safety of the coadministration of tadalafil once daily with finasteride for 6 months in men with lower urinary tract symptoms and prostatic enlargement secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol 191:727–733
Gacci M, Corona G, Salvi M, Vignozzi L, McVary KT, Kaplan SA, Roehrborn CG, Serni S, Mirone V, Carini M, Maggi M (2012) A systematic review and meta-analysis on the use of phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors alone or in combination with α-blockers for lower urinary tract symptoms due to benign prostatic hyperplasia. Eur Urol 61:994–1003
Matsukawa Y, Kanada Y, Takai S, Inoue S, Majima T, Funahashi Y, Kato M, Yamamoto T, Gotoh M (2020) Pre-treatment serum testosterone level can be a useful factor to predict the improvement in bladder outlet obstruction by tadalafil for male patients with lower urinary tract symptoms induced by benign prostatic obstruction. Aging Male 23:641–647
Traish AM, Krakowsky Y, Doros G, Morgentaler A (2019) Do 5α-reductase inhibitors raise circulating serum testosterone levels? A comprehensive review and meta-analysis to explaining paradoxical results. Sex Med Rev 7:95–114
Ozcan L, Polat EC, Kocaaslan R, Onen E, Otunctemur A, Ozbek E (2017) Effects of taking tadalafil 5 mg once daily on erectile function and total testosterone levels in patients with metabolic syndrome. Andrologia 49(9). https://doi.org/10.1111/and.12751 (PMID: 28295481)
Egan KB, Miner MM, Suh M, McVary K, Ni X, Roehrborn CG, Wittert G, Wong DG, Rosen RC (2015) Do baseline estrogen and testosterone affect lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) prior to or after pharmacologic treatment with tadalafil? Andrology 3:1165–1172
Roehrborn CG, Boyle P, Nickel JC, Hoefner K, Andriole G, ARIA3001 ARIA3002 and ARIA3003 Study Investigators (2002) Efficacy and safety of a dual inhibitor of 5-alpha-reductase types 1 and 2 (dutasteride) in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology 60:434–441
Bechis SK, Otsetov AG, Ge R, Wang Z, Vangel MG, Wu CL et al (2015) Age and obesity promote methylation and suppression of 5α reductase 2: implications for personalized therapy of benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol 194:1031–1037
Kang PM, Kim YJ, Seo WT et al (2019) Correlation between 5-α reductase type 2 protein expression and methylation of 5-α reductase type 2 promotor gene of benign prostatic hyperplasia. World J Urol 37:709–718
Roehrborn CG (2008) Pathology of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Int J Impot Res 20:S11–S18
Hirayama K, Masui K, Hamada A, Shichiri Y, Masuzawa N, Hamada S (2005) Evaluation of intravesical prostatic protrusion as a predictor of dutasteride-resistant lower urinary tract symptoms/benign prostatic enlargement with a high likelihood of surgical intervention. Urology 86:565–569
Maeda T, Kikuchi E, Hasegawa M, Ando T, Matsushima M, Yuge K, Ito Y, Miyajima A, Oya M (2016) A prospective longitudinal survey of erectile function status in symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia patients treated with dutasteride. Aging Male 19:111–116
La Torre A, Giupponi G, Duffy D, Conca A, Cai T, Scardigli A (2016) Sexual dysfunction related to drugs: a critical review. part V: α-blocker and 5-ARI drugs. Pharmacopsychiatry 49:3–13
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Nothing to declare.
Ethical approval
Approval of the research protocol by an Institutional Reviewer Board: No. 16138.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained. Registry and the Registration No. of the study/trial: UMIN000034701.
Animal studies
N/A.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wada, N., Abe, N., Miyauchi, K. et al. Dutasteride add-on treatment to tadalafil for patients with benign prostatic enlargement is similarly effective as dutasteride add-on treatment to alpha blocker: a propensity-score matching analysis. Int Urol Nephrol 54, 1193–1198 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-022-03198-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-022-03198-1