Abstract
Background
Present investigation aims to elucidate safety and efficacy of hemodialysis as well as peritoneal dialysis in treating end-stage diabetic nephropathy.
Methods
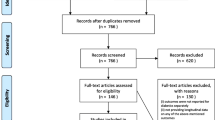
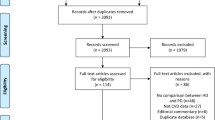
We searched various databases for articles from the database starting date to October 2019. The analysis involved studies that contained outcomes of hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis in the treatment of end-stage diabetic nephropathy. A total of 12 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with 932 participants were collected.
Results
Meta-analysis results suggested that comparing with peritoneal dialysis group, hemodialysis group had a higher incidence of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events and bleeding complications. There was no statistically significant difference regarding the infection (P = 0.71) or malnutrition (P = 0.53) incidence between the two forms of dialysis. Hemodialysis could better improve the levels of albumin [mean difference (MD) = 6.80, 95% CI = (4.17–9.44)] and hemoglobin [MD = 3.40, 95% CI = (0.94–5.86)] than peritoneal dialysis after 3 months or more.
Conclusions
In treating end-stage diabetic nephropathy patients, peritoneal dialysis had a lower incidence of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events, as well as bleeding complication than hemodialysis. However, hemodialysis could better improve albumin and hemoglobin levels than peritoneal dialysis after 3 months.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
National Kidney Foundation (2006) KDOQI clinical practice guidelines and clinical practice recommendations for vascular access, update 2006. Am J Kidney Dis 48:S177–S247
Jin DC, Yun SR, Seoung WL et al (2018) Current characteristics of dialysis therapy in Korea: 2016 registry data focusing on diabetic patients. Kidney Res Clin Pract 37:20–29
Xue J, Li HH, Zhou Q et al (2019) Comparison of peritoneal dialysis with hemodialysis on survival of diabetic patients with end-stage kidney disease: a meta-analysis of cohort studies. Ren Fail 41:521–531
Friedrich JO, Adhikari NKJ, Beyene J (2007) Inclusion of zero total event trials in meta-analyses maintains analytic consistency and incorporates all available data. BMC Med Res Methodol 7:5
Chen HG, Liao XY, Liu RG (2015) A comparative study of peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Clin Med Eng 22:17–19
Gao XM (2016) Comparison of hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis in patients with end-stage diabetic nephropathy. Psysiol Doctor 22:141–142
Hou CX (2018) Clinical effect of hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis on diabetic nephropathy. Guide China Med 16:149–150
Peng XF, Chen ZP, Xu JQ et al (2018) Comparative analysis of peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis in the treatment of end-stage diabetic nephropathy. Chronic Pathematology J 19:784–786
Shao HY, Chen K, Shen YL (2017) Comparison of peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Henan Med Res 26:1051–1052
Shi S (2018) Clinical efficacy and safety of peritoneal dialysis in the treatment of end-stage diabetic nephropathy. Inner Mongolia Med J 50:1204–1205
Wang JQ (2015) The effect of peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis on the prognosis of end-stage diabetic nephropathy. Med Inf 28:181–182
Wang XF, Chen J (2019) Analysis on the effect of peritoneal dialysis on end-stage diabetic nephropathy. Inner Mongolia Med J 51:518–520
Wang Y, Chen HX (2019) The effect of peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis in the treatment of end-stage diabetic nephropathy. Acta Med Sin 32:107–109
Yu XH, He GZ, Tu Q (2018) Comparative study of hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis in the treatment of end-stage diabetic nephropathy. Contemp Med 24:17–19
Zhang XH (2018) Comparison of hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis in the treatment of end-stage diabetic nephropathy. Health Requir 10:39
Zhu XD (2017) Effect of peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis on diabetic nephropathy. Contemp Med 23:89–90
Lee SY, Choi ME (2015) Urinary biomarkers for early diabetic nephropathy: beyond albuminuria. Pediatr Nephrol 30:1063–1075
Robert C, Stanton M (2014) Frontiers in diabetic kidney disease: introduction. Am J Kidney Dis 63:S1-2
Luke RG (1998) Chronic renal failure-a vasculopathic state. N Engl J Med 339:841–843
Mhairi S, Peter B, Maarter WT et al (2006) Vascular calcification and cardiovascular function in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transpl 21:707–714
Wang WN, Zhang WL, Sun T et al (2017) Effect of peritoneal dialysis versus hemodialysis on renal anemia in renal in end-stage disease patients: a meta-analysis. Ren Fail 39:59–66
Han SS, Park JY, Kang S et al (2015) Dialysis modality and mortality in the elderly: a meta-analysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 10:983–993
Cecile C, Davide B, Ionut N et al (2014) Dialysis modality choice in diabetic patients with end-stage kidney disease: a systematic review of the available evidence. Nephrol Dial Transpl 30:310–320
Kim YL, Cho JH, Choi JY et al (2013) Systemic and local impact of glucose and glucose degradation products in peritoneal dialysis solution. J Ren Nutr 23:218–222
Yan Y, Ye D, Yang L et al (2018) A meta-analysis of the association between diabetic patients and AVF failure in dialysis. Ren Fail 40:379–383
Yeates K, Zhu N, Vonesh E et al (2012) Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis are associated with similar outcomes for end-stage renal disease treatment in Canada. Nephrol Dial Transpl 27:3568–3575
Heaf JG, Wehberg S (2014) Relative survival of peritoneal dialysis and haemodialysis patients: effect of cohort and mode of dialysis initiation. PLoS ONE 9:e90119
Chang YT, Wu JL, Hsu CC et al (2014) Diabetes and end stage renal disease synergistically contribute to increased incidence of cardiovascular events: a nationwide follow-up study during 1998–2009. Diabetics Care 37:277–285
Icks A, Claessen H, Morbach S et al (2012) Time-dependent impact of diabetes on mortality in patients with stroke: survival up to 5 years in a health insurance population cohort in Germany. Diabetes Care 35:1868–1875
Tien KJ, Lin ZZ, Chio CC et al (2013) Epidemiology and mortality of new-onset diabetes after dialysis: Taiwan national cohort study. Diabetes Care 36:3027–3032
Sattar A, Argyropoulos C, Weissfeld L et al (2012) All-cause and cause-specific mortality associated with diabetes in prevalent hemodialysis patients. BMC Nephrol 13:3027–3032
Nesrallah GE, Lindsay RM, Cuerden MS et al (2012) Intensive hemodialysis associates with improved survival compared with conventional hemodialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol 23:696–705
Nadeau-Fredette AC, Hawley C, Pascoe E et al (2016) Predictors of transfer to home hemodialysis after peritoneal dialysis completion. Perit Dial Int 36:547–554
Cheng X, Nayyar S, Wang M et al (2013) Mortality rates among prevalent hemodialysis patients in Beijing: a comparison with USRDS data. Nephrol Dial Transpl 28:724–732
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11255_2022_3194_MOESM1_ESM.png
Supplementary file1 Supplementary Figure1. Study selection flow diagram. DKD, diabetic kidney disease; HD, hemodialysis; PD, peritoneal dialysis; RCTs, randomized controlled trials. (PNG 317 KB)
11255_2022_3194_MOESM2_ESM.png
Supplementary file2 Supplementary Figure 2. Risk of bias summary review authors’ judgments about each risk of bias item for each included study. (PNG 211 KB)
11255_2022_3194_MOESM4_ESM.png
Supplementary file4 Supplementary Figure 4. Forest plot based on comparison of albumin between hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis after excluding the one articles. (PNG 176 KB)
11255_2022_3194_MOESM5_ESM.png
Supplementary file5 Supplementary Figure 5. Publication bias according to Begg’s test funnel plots with plasma albumin. (PNG 38 KB)
11255_2022_3194_MOESM6_ESM.png
Supplementary file6 Supplementary Figure 6. Publication bias according to Egger’s test funnel plots with plasma albumin. (PNG 35 KB)
11255_2022_3194_MOESM7_ESM.png
Supplementary file7 Supplementary Figure 7. Publication bias according to Begg’s test funnel plots with hemoglobin. (PNG 36 KB)
11255_2022_3194_MOESM8_ESM.png
Supplementary file8 Supplementary Figure 8. Publication bias according to Egger’s test funnel plots with hemoglobin. (PNG 38 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, M., Xie, J., Lan, L. et al. Safety and efficacy of hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis in treating end-stage diabetic nephropathy: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int Urol Nephrol 54, 2901–2909 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-022-03194-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-022-03194-5