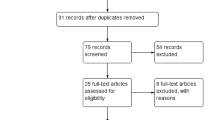
Abstract
Introduction
This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) use in hypospadias repair through systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies.
Methods
A systematic literature search was performed in May 2021. Comparative studies assessing the surgical outcome of hypospadias repair between control versus HBOT utilization were identified and evaluated according to Cochrane collaboration recommendations. The assessed outcome includes hypospadias repair failures and graft failure for staged repair using a buccal graft. Relative risk with corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI) were extrapolated. A random-effect model was used to generate pooled effect estimates. Heterogeneity and inter-study variability were assessed using Chi-square and I-square. Subgroup analysis was performed according to primary repair versus redo-hypospadias with buccal graft. PROSPERO registration (CRD42021251423).
Results
Five comparative studies with 576 cases (301 HBOT versus 275 controls) were included. Overall pooled effect estimates showed that the HBOT group has significantly lesser hypospadias repair failure (RR 0.52, 95%CI 0.37, 0.72). Subgroup analysis on the use of HBOT for graft take showed lesser graft failure compared to the control group (RR 0.20, 95% CI 0.05, 0.75), while the use of HBOT for primary and redo single staged hypospadias repair showed lesser complication rate (RR 0.56, 95%CI 0.40, 0.78). Based on ROBINS-I assessment, all included comparative studies are determined to be of serious risk of bias mainly due to presence of confounding.
Conclusion
The currently available low-quality of evidence suggests that compared to control groups, HBOT as an adjunctive intervention to complicated hypospadias repair was able to reduce surgical outcome failure and graft failure rates.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhat A, Mandal AK (2008) Acute postoperative complications of hypospadias repair. Indian J Urol 24(2):241
Guo S, Dipietro LA (2010) Factors affecting wound healing. J Dent Res 89(3):219–229. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034509359125
Chua ME, Rong M, Tuba-Ang K, Silangcruz JMA, Tanseco PP, Ming JMC, Kim KH, Hui CC, Farhat WA (2019) The impact of sex hormones on genital wound healing in mice: a comparative study. J Pediatr Urol 15(6):635–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpurol.2019.09.001
Snodgrass W, Bush NC (2017) Re-operative urethroplasty after failed hypospadias repair: how prior surgery impacts risk for additional complications. J Pediatr Urol 13:289
Bassetto F, Bosco G, Brambullo T, Kohlscheen E, Tocco Tussardi I, Vindigni V, Tiengo C (2019) Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in plastic surgery practice: case series and literature overview. G Chir 40(4):257–275
Huang X, Liang P, Jiang B, Zhang P, Yu W, Duan M, Guo L, Cui X, Huang M, Huang X (2020) Hyperbaric oxygen potentiates diabetic wound healing by promoting fibroblast cell proliferation and endothelial cell angiogenesis. Life Sci 259:118
Villanueva C (2019) Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in complex hypospadias repairs-expensive gimmicks or game changing advances? J Urol 202(3):467–468. https://doi.org/10.1097/JU.0000000000000397
Hanna MK (2020) Comment on, hyperbaric oxygen for pediatric hypospadias cripples, evaluating the advantages regarding graft take. J Pediatr Urol 16(4):519–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpurol.2020.05.157
Higgins JPT , Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page M et al (20199) The Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 6, updated 2019. https://methods.cochrane.org/bias/resources/rob-2-revised-cochrane-risk-bias-tool-randomized-trials. Accessed July 2019
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Prisma Group (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6(7):e1000097
Sterne JA, Hernán MA, Reeves BC et al (2016) ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ 12(355):i419
The Cochrane Collaboration (2014) Review manager (RevMan) [computer program]. Version 5. The Nordic Cochrane Centre, Copenhagen
Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins JP, Rothstein HR (2010) A basic introduction to fixed-effect and random-effects models for meta-analysis. Res Synth Methods 1(2):97–111. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.12
Takeshima N, Sozu T, Tajika A, Ogawa Y, Hayasaka Y, Furukawa TA (2014) Which is more generalizable, powerful, and interpretable in meta-analyses, mean difference or standardized mean difference? BMC Med Res Methodol 21(14):30. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-14-30
Bush N, Snodgrass W (2019) Hyperbaric oxygen therapy improves oral graft take in hypospadias staged tubularized autograft reoperations. J Urol 202(3):617–622. https://doi.org/10.1097/JU.0000000000000145
Chang C, White C, Katz A, Hanna MK (2020) Management of ischemic tissues and skin flaps in re-operative and complex hypospadias repair using vasodilators and hyperbaric oxygen. J Pediatr Urol 16(5):672.e1-672.e8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpurol.2020.07.034
Lei W, Li S, Wang J, Dai SX (2011) Hyperbaric oxygen auxiliary therapy ameliorating postoperative dermal wound healing of hypospadias. J Appl Clin Pediatr 11:726
Kara O, Malkoc E, Dursun F, Mutluoglu M, Aktas Z, Memis A, Soydan H, Ates F (2017) The effectiveness of adjuvant hyperbaric oxygen therapy in adults who underwent hypospadias surgery. J Clin Anal Med 8(1):60–63
Neheman A, Rappaport YH, Verhovsky G, Bush N, Snodgrass W, Lang E, Zisman A, Efrati S (2020) Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for pediatric “hypospadias cripple”-evaluating the advantages regarding graft take. J Pediatr Urol 16(2):163.e1-163.e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpurol.2020.01.002
Kleban S, Baynosa RC (2020) The effect of hyperbaric oxygen on compromised grafts and flaps. Undersea Hyperb Med 47(4):635–648
Francis A, Baynosa RC (2017) Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for the compromised graft or flap. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle) 6:23
Thom SR (2011) Hyperbaric oxygen–its mechanisms and efficacy. Plast Reconstr Surg, suppl 127:131S
Perrins DJ (1967) Influence of hyperbaric oxygen on the survival of split skin grafts. Lancet 1(7495):868–871. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91428-6
Citrome L, Ketter TA (2013) When does a difference make a difference? Interpretation of number needed to treat, number needed to harm, and likelihood to be helped or harmed. Int J Clin Pract 67(5):407–411
Cook RJ, Sackett DL (1995) The number needed to treat: a clinically useful measure of treatment effect. BMJ 310(6977):452–454
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Sultan S, Glasziou P, Akl EA, Alonso-Coello P et al (2011) GRADE guidelines: 9. Rating up the quality of evidence. J Clin Epidemiol 64(12):1311–1316
Anand S, Krishnan N, Bajpai M (2021) Utility and safety of hyperbaric oxygen therapy as a rescue treatment in complicated cases of hypospadias: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Pediatr Urol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpurol.2021.10.004
Mustafa RA, Santesso N, Brozek J, Akl EA, Walter SD, Norman G et al (2013) The GRADE approach is reproducible in assessing the quality of evidence of quantitative evidence syntheses. J Clin Epidemiol 66(7):736–742
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Montori V, Vist G, Kunz R, Brozek J et al (2011) GRADE guidelines: 5. Rating the quality of evidence–publication bias. J Clin Epidemiol 64(12):1277–1282
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist G, Kunz R, Brozek J, Alonso-Coello P et al (2011) GRADE guidelines: 4. Rating the quality of evidence–study limitations (risk of bias). J Clin Epidemiol 64(4):407–415
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Nothing to Disclose from all authors.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
Not Applicable.
Informed consent
Not Applicable.
Review registration
PROSPERO (CRD42021251423).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Appendix A
Appendix A
Database: OVID Medline Epub Ahead of Print, In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations, Ovid MEDLINE(R) Daily and Ovid MEDLINE(R) 1946 to Present Search Strategy: May 24, 2021.
-
1.
Exp hypospadias/ (5118)
-
2.
hypospadia*.ti,ab,kf. (6705)
-
3.
(hypospadias adj2 (correction* or repair* or procedure* or modif*)).ti,ab,kf. (1902)
-
4.
Or/1–3 (7569)
-
5.
(hyperbar$ adj oxygen$).ti,ab. (10,220)
-
6.
high pressure oxygen$.ti,ab. (229)
-
7.
exp Hyperbaric Oxygenation/ (12,100)
-
8.
oxygen.ti,ab,kf. (512,544)
-
9.
or/5–8 (517,161)
-
10.
4 AND 9 (33)
Embase Classic + Embase 1947 to 2021 May 21.
-
11.
Exp hypospadias/ (11,305)
-
12.
hypospadia*.ti,ab,kw. (9360)
-
13.
(hypospadias adj2 (correction* or repair* or procedure* or modif*)).ti,ab,kw. (2534)
-
14.
Or/1–3 (12,473)
-
15.
(hyperbar$ adj oxygen$).ti,ab. (13,715)
-
16.
high pressure oxygen$.ti,ab. (381)
-
17.
exp Hyperbaric Oxygen/ (3462)
-
18.
oxygen.ti,ab,kw. (655,432)
-
19.
or/5–8 (658,264)
-
20.
4 AND 9 (58)
PUBMed (13)
(“hyperbaric”[All Fields] OR “hyperbarics”[All Fields]) AND (“cell respiration”[MeSH Terms] OR (“cell”[All Fields] AND “respiration”[All Fields]) OR “cell respiration”[All Fields] OR “oxygenation”[All Fields] OR “oxygen”[MeSH Terms] OR “oxygen”[All Fields] OR “oxygen s”[All Fields] OR “oxygenate”[All Fields] OR “oxygenated”[All Fields] OR “oxygenates”[All Fields] OR “oxygenating”[All Fields] OR “oxygenations”[All Fields] OR “oxygenative”[All Fields] OR “oxygenator s”[All Fields] OR “oxygenators”[MeSH Terms] OR “oxygenators”[All Fields] OR “oxygenator”[All Fields] OR “oxygene”[All Fields] OR “oxygenic”[All Fields] OR “oxygenous”[All Fields] OR “oxygens”[All Fields]) AND (“hypospadias”[MeSH Terms] OR “hypospadias”[All Fields] OR “hypospadia”[All Fields])
Scopus (17) Proquest (10) Cochrane Library (2)
Hyperbaric AND Oxygen AND Hypospadias
Clinicaltrials.gov (0)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chua, M.E., Kim, J.J.K., Ming, J.M. et al. The utilization of hyperbaric oxygenation therapy in hypospadias repair: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Urol Nephrol 54, 273–285 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-021-03096-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-021-03096-y