Abstract
Introduction
Although it is known in the literature that the medical cost due to the complications of diabetes mellitus (DM) is high, data about the effect of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) on medical cost are limited.
Aims
The aim of this study is to investigate the cost of hospitalized patients with nephropathy due to type 2 DM, the parameters closely related to this cost and the effect of diabetic nephropathy stage on medical hospitalization costs.
Methods
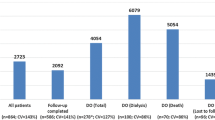
The study group consisted of 141 patients with DKD, and the control group consisted of 111 patients with DM without chronic complications in this retrospective study. The demographic characteristics, duration of diabetes and HbA1c values of the patients were recorded at the time of their first hospitalization, medical hospitalization costs, and the length of stay in hospital were recorded for a year from the date of hospitalization. The total medical hospitalization costs of the patients were divided into two groups as cost of medications and supplies and service cost. Patients with DKD were compared according to their dialysis status and nephropathy stages.
Results
While the average cost of a patient with DKD was 603 (283–1267) United States Dollars (USD), the average cost of a DM patient without complications was 222 (141–292) USD (p < 0.05). It was observed that the patients with DKD had higher medical hospitalization costs and length of stay in hospital compared to patients with diabetes without complications. In addition, it was observed that the medical hospitalization costs and the length of stay in hospital were significantly higher in patients undergoing dialysis than patients who did not undergo dialysis (p < 0.05 for each). An independent relation was found between average cost and duration of diabetes in patients with DKD (p < 0.05). No relation was found between diabetic nephropathy stage and medical hospitalization costs (p > 0.05 for each).
Conclusion
The estimated cost of treatment of DKD is higher than patients with uncomplicated diabetes. If preventive measures are not taken for DKD, it will continue to be a heavy economic burden.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P et al (2019) Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 157:107843
Williams R, Karuranga S, Malanda B et al (2020) Global and regional estimates and projections of diabetes-related health expenditure: results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 162:108072
Keskek SÖ, Kırım S, Yanmaz N et al (2014) Direct medical cost of type 1 and type 2 diabetes in Turkey. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries 34:77–81
Keskek SO, Kirim S, Yanmaz N (2014) Estimated costs of the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers in a tertiary hospital in Turkey. Pak J Med Sci 30(5):968–971
Menzin J, Korn JR, Cohen J et al (2010) Relationship between glycemic control and diabetes-related hospital costs in patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus. JMCP 16(4):264–275
Slabaugh SL, Curtis BH, Clore G et al (2015) Factors associated with increased healthcare costs in medicare advantage patients with type 2 diabetes enrolled in a large representative health insurance plan in the US. J Med Econ 18(2):106–112
Morsanutto A, Berto P, Lopatriello S et al (2006) Major complications have a impact on total annual medical cost of diabetes results of a database analysis. JDCJOURNAL 20:163–169
Pagano E, Bo S, Petrinco M et al (2009) Factors affecting hospitalization costs of in type 2 diabetic patients. JDCJOURNAL 23:1–6
Henriksson F, Agardh CD, Berne C et al (2000) Direct medical cost for patients with type 2 diabetes in Sweden. J Intern Med 248:387–396
Chan BSW, Tsang MW, Lee VWY et al (2007) Cost of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Hong Kong Chinese. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 45(8):455–468
Önsüz MF, Topuzoğlu A (2018) İstanbul İlinde Üç Hastanede Ayaktan İzlenen Tip II Diyabetik Hastalarda Glisemik Kontrolün Maliyet Etkinliğinin Değerlendirilmesi. Türk Dünyası Uygulama ve Araştırma Merkezi Halk Sağlığı Dergisi 3(2):1–14
Öcal EE, Önsüz MF (2018) Diyabet Hastalığının Ekonomik Yükü. Türk Dünyası Uygulama ve Araştırma Merkezi Halk Sağlığı Dergisi 3(1):24–31
Satman I, Ömer B, Tütüncü Y et al (2013) TURDEP—II Çalışma Grubu. Eur J Epidemiol 28(2):169–180
Rosenzweig JL (2008) Diyabet ve Sağlık Hizmeti Sistemi Ekonomik ve Sosyal Maliyetler. In: Kahn CR, Weir GC, King GL et al (eds) Joslin’s Diabetes mellitus 1. Medikal Yayıncılık Ltd Şti, Baskı, pp 777–792
The United States Renal Data System (USRDS) annual data report (2018): epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Bethesda: National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Shilpasree AS, Patil VS, Revanasiddappa M et al (2021) Renal Dysfunction in Prediabetes: Confirmed by Glomerular Hyperfiltration and Albuminuria. J Lab Physicians 13(3):257–262
Li R, Bilik D, Brown MB et al (2013) Medical costs associated with type 2 diabetes complications and comorbidities. Am J Manag Care 19(5):421–430
Schirr-Bonnans S, Costa N, Derumeaux-Burel H et al (2017) Cost of diabetic eye, renal and foot complications: a methodological review. Eur J Health Econ 18(3):293–312
Gordois A, Scuffham P, Makas A et al (2004) The health care costs of diabetic nephropathy in the United States and the United Kingdom. J Diabetes Complications 18(1):18–26
Davis WA, Knuiman MW, Hendrie D et al (2005) Determinants of diabetes attributable non–blood glucose—lowering medication costs in type 2 diabetes the Fremantle Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care 28:329–336
Lee HA, Fung KW, Msc BF (2003) Analyzing hospital length of stay, Mean or median regression? Med Care 41(5):681–686
Zhou Z, Chaudhari P, Yang H et al (2017) Healthcare resource use, costs, and disease progression associated with diabetic nephropathy in adults with type 2 diabetes: a retrospective observational study. Diabetes Ther 8(3):555–571
Vupputuri S, Kimes TM, Calloway MO et al (2014) The economic burden of progressive chronic kidney disease among patients with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Complications 28(1):10–16
Funding
We have not funding source for this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gülümsek, E., Keşkek, Ş.Ö. Direct medical cost of nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Int Urol Nephrol 54, 1383–1389 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-021-03012-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-021-03012-4