Abstract
Purpose
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is one of the most serious complications of diabetes that leads to decline of renal function. Although numerous studies have revealed that microRNAs (miRNAs) play essential roles in the progression of DN, whether miR-365 is involved remains elusive.
Methods
The successful construction of DN model was confirmed by ELSIA, hematoxylin–eosin (HE) and Masson staining assay. The expression of miR-365 was detected through RT-qPCR. The levels of BDNF, p-TrkB, α-smooth muscle actin (SMA), collagen IV (Col.IV), transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) were evaluated by western blot, IF or ELISA assays. Luciferase reporter assay was used to detect the interaction between miR-365 and BDNF.
Results
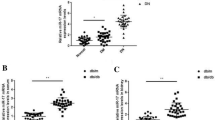
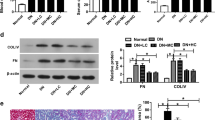
The DN mice model was induced by streptozotocin (STZ). Then miR-365 expression was found to upregulate in tissues of DN rat. Furthermore, elevated expression of miR-365 was found in high glucose (HG)-treated HK-2 cells. Silencing of miR-365 suppressed the accumulation of ECM components and secretion of inflammatory cytokines in HK-2 cells. In addition, it was demonstrated that miR-365 could target BDNF. The protein levels of BDNF and p-TrkB were negatively regulated by miR-365 in HK-2 cells. Moreover, inhibition of miR-365 suppressed the levels of SMA, Col.IV, TGF-β1, TNF-α, and IL-6, indicating the renal fibrosis was inhibited by miR-365 knockdown.
Conclusion
MiR-365 could regulate BDNF-TrkB signal axis in STZ induced DN fibrosis and renal function. The results of the current study might provide a promising biomarker for the treatment of DN in the future.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article, so the code availability is not applicable.
References
Fan Y, Li X, Xiao W, Fu J, Harris RC, Lindenmeyer M, Cohen CD, Guillot N, Baron MH, Wang N, Lee K, He JC, Schlondorff D, Chuang PY (2015) BAMBI elimination enhances alternative TGF-β signaling and glomerular dysfunction in diabetic mice. Diabetes 64:2220–2233
An L, Ji D, Hu W, Wang J, Jin X, Qu Y, Zhang N (2020) Interference of Hsa_circ_0003928 alleviates high glucose-induced cell apoptosis and inflammation in HK-2 cells via miR-151-3p/Anxa2. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 13:3157–3168
Helou N, Dwyer A, Shaha M, Zanchi A (2016) Multidisciplinary management of diabetic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JBI Database Syst Rev Implement Rep 14:169–207
Dai H, Liu Q, Liu B (2017) Research progress on mechanism of podocyte depletion in diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Res 2017:2615286
Loeffler I, Liebisch M, Wolf G (2012) Collagen VIII influences epithelial phenotypic changes in experimental diabetic nephropathy. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 303:F733-745
Tang F, Hao Y, Zhang X, Qin J (2017) Effect of echinacoside on kidney fibrosis by inhibition of TGF-β1/Smads signaling pathway in the db/db mice model of diabetic nephropathy. Drug Des Dev Ther 11:2813–2826
Gross JL, de Azevedo MJ, Silveiro SP, Canani LH, Caramori ML, Zelmanovitz T (2005) Diabetic nephropathy: diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Diabetes Care 28:164–176
Guo LM, Ding GF, Xu W, Ge H, Jiang Y, Chen XJ, Lu Y (2018) MiR-135a-5p represses proliferation of HNSCC by targeting HOXA10. Cancer Biol Ther 19:973–983
Hoch MJ, Bruno MT, Faustin A, Cruz N, Crandall L, Wisniewski T, Devinsky O, Shepherd TM (2019) 3T MRI whole-brain microscopy discrimination of subcortical anatomy, part 1: brain stem. Am J Neuroradiol 40:401–407
Ye Y, Li M, Chen L, Li S, Quan Z (2020) Circ-AK2 is associated with preeclampsia and regulates biological behaviors of trophoblast cells through miR-454-3p/THBS2. Placenta 103:156–163
Yi L, Zhou L, Luo J, Yang Q (2020) Circ-PTK2 promotes the proliferation and suppressed the apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia cells through targeting miR-330-5p/FOXM1 axis. Blood Cells Mol Dis 86:102506
Liu H, Wang X, Wang ZY, Li L (2020) Circ_0080425 inhibits cell proliferation and fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy via sponging miR-24-3p and targeting fibroblast growth factor 11. J Cell Physiol 235:4520–4529
Li M, Guo Q, Cai H, Wang H, Ma Z, Zhang X (2020) miR-218 regulates diabetic nephropathy via targeting IKK-β and modulating NK-κB-mediated inflammation. J Cell Physiol 235:3362–3371
Ding H, Xu Y, Jiang N (2020) Upregulation of miR-101a suppresses chronic renal fibrosis by regulating KDM3A via blockade of the YAP-TGF-β-Smad signaling pathway. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 19:1276–1289
Fan W, Peng Y, Liang Z, Yang Y, Zhang J (2019) A negative feedback loop of H19/miR-675/EGR1 is involved in diabetic nephropathy by downregulating the expression of the vitamin D receptor. J Cell Physiol 234:17505–17513
Zhu Y, Wen X, Zhao P (2018) MicroRNA-365 inhibits cell growth and promotes apoptosis in melanoma by targeting BCL2 and cyclin D1 (CCND1). Med Sci Monit 24:3679–3692
Yang X, Guan Y, Tian S, Wang Y, Sun K, Chen Q (2016) Mechanical and IL-1β responsive miR-365 contributes to osteoarthritis development by targeting histone deacetylase 4. Int J Mol Sci 17:436
Wang J, Zhou T, Liu J, Shangguan J, Liu X, Li Z, Zhou X, Ren Y, Wang C (2020) Application of (1)H-MRS in end-stage renal disease with depression. BMC Nephrol 21:225
Tsai YC, Kuo MC, Hung WW, Wu LY, Wu PH, Chang WA, Kuo PL, Hsu YL (2020) High glucose induces mesangial cell apoptosis through miR-15b-5p and promotes diabetic nephropathy by extracellular vesicle delivery. Mol Ther 28:963–974
Cho MH (2010) Renal fibrosis. Korean. J Pediatr 53:735–740
Humphreys BD (2018) Mechanisms of renal fibrosis. Annu Rev Physiol 80:309–326
Zhang M, Guo Y, Fu H, Hu S, Pan J, Wang Y, Cheng J, Song J, Yu Q, Zhang S, Xu JF, Pei G, Xiang X, Yang P, Wang CY (2015) Chop deficiency prevents UUO-induced renal fibrosis by attenuating fibrotic signals originated from Hmgb1/TLR4/NFκB/IL-1β signaling. Cell Death Dis 6:e1847
Zheng ZC, Zhu W, Lei L, Liu XQ, Wu YG (2020) Wogonin ameliorates renal inflammation and fibrosis by inhibiting NF-κB and TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling pathways in diabetic nephropathy. Drug Des Dev Ther 14:4135–4148
Wei TT, Yang LT, Guo F, Tao SB, Cheng L, Huang RS, Ma L, Fu P (2020) Activation of GPR120 in podocytes ameliorates kidney fibrosis and inflammation in diabetic nephropathy. Acta Pharmacol Sin 42:252–263
Xiang E, Han B, Zhang Q, Rao W, Wang Z, Chang C, Zhang Y, Tu C, Li C, Wu D (2020) Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells prevent the progression of early diabetic nephropathy through inhibiting inflammation and fibrosis. Stem Cell Res Ther 11:336
Chen Y, Liu L, Xing YY, Li Q, Zhao GH, Lu YY, Yang JJ (2020) Down-regulation of miR-365 suppresses cerebral ischemia injury by targeting IGF1R. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 34:1857–1862
Wang X, Gong S, Pu D, Hu N, Wang Y, Fan P, Zhang J, Lu X (2020) Up-regulation of miR-365 promotes the apoptosis and restrains proliferation of synoviocytes through downregulation of IGF1 and the inactivation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in mice with rheumatoid arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol 79:106067
Gao M, Li C, Xu M, Liu Y, Cong M, Liu S (2018) LncRNA MT1DP aggravates cadmium-induced oxidative stress by repressing the function of Nrf2 and is dependent on interaction with miR-365. Adv Sci (Weinh) 5:1800087
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Xie W, Lu Q, Wang K, Lu J, Gu X, Zhu D, Liu F, Guo Z (2018) miR-34b-5p inhibition attenuates lung inflammation and apoptosis in an LPS-induced acute lung injury mouse model by targeting progranulin. J Cell Physiol 233:6615–6631
Liu X, Liu L, Zhang H, Shao Y, Chen Z, Feng X, Fang H, Zhao C, Pan J, Zhang H, Zeng C, Cai D (2019) MiR-146b accelerates osteoarthritis progression by targeting alpha-2-macroglobulin. Aging (Albany NY) 11:6014–6028
Li P, Xu Y, Wang B, Huang J, Li Q (2020) miR-34a-5p and miR-125b-5p attenuate Aβ-induced neurotoxicity through targeting BACE1. J Neurol Sci 413:116793
He M, Wang J, Yin Z, Zhao Y, Hou H, Fan J, Li H, Wen Z, Tang J, Wang Y, Wang DW, Chen C (2019) MiR-320a induces diabetic nephropathy via inhibiting MafB. Aging (Albany NY) 11:3055–3079
Xu D, Gao Y, Hu N, Wu L, Chen Q (2017) miR-365 ameliorates dexamethasone-induced suppression of osteogenesis in MC3T3-E1 Cells by targeting HDAC4. Int J Mol Sci 18:977
Lin B, Feng DG, Wang F, Wang JX, Xu CG, Zhao H, Cheng ZY (2016) MiR-365 participates in coronary atherosclerosis through regulating IL-6. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 20:5186–5192
Li M, Liu L, Zang W, Wang Y, Du Y, Chen X, Li P, Li J, Zhao G (2015) miR-365 overexpression promotes cell proliferation and invasion by targeting ADAMTS-1 in breast cancer. Int J Oncol 47:296–302
Numakawa T, Suzuki S, Kumamaru E, Adachi N, Richards M, Kunugi H (2010) BDNF function and intracellular signaling in neurons. Histol Histopathol 25:237–258
Barbacid M (1994) The Trk family of neurotrophin receptors. J Neurobiol 25:1386–1403
Kallies G, Rapp MA, Fydrich T, Fehm L, Tschorn M, Terán C, Schwefel M, Pietrek A, Henze R, Hellweg R, Ströhle A, Heinzel S, Heissel A (2019) Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) at rest and after acute aerobic exercise in major depressive disorder. Psychoneuroendocrinology 102:212–215
Francis K, Dougali A, Sideri K, Kroupis C, Vasdekis V, Dima K, Douzenis A (2018) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in children with ASD and their parents: a 3-year follow-up. Acta Psychiatr Scand 137:433–441
Heitz U, Papmeyer M, Studerus E, Egloff L, Ittig S, Andreou C, Vogel T, Borgwardt S, Graf M, Eckert A, Riecher-Rössler A (2019) Plasma and serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels and their association with neurocognition in at-risk mental state, first episode psychosis and chronic schizophrenia patients. World J Biol Psychiatry 20:545–554
Funding
This research was supported by the Zhejiang Health Science and Technology Project (2021KY1130).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PZ: methodology, software, validation, and data curation. XL: methodology, software, validation, and writing-original draft. YL: software, validation, and methodology. JZ: software, methodology, and writing—review and editing. YS: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, and supervision. JH: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, and supervision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest concerning this article.
Ethics approval
The experiments involved in animals were performed according to the National Institutes of Health guide for the care and use of Laboratory animals.
Consent for publication
All authors agree to publish this article to this journal.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, P., Li, X., Li, Y. et al. Mechanism of miR-365 in regulating BDNF-TrkB signal axis of HFD/STZ induced diabetic nephropathy fibrosis and renal function. Int Urol Nephrol 53, 2177–2187 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-021-02853-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-021-02853-3