Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the clinical characteristics of genuine- and induced-oligometastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (OM-CRPC) and assess the therapeutic effect of progressive-site directed therapy (PSDT).
Methods
We performed a retrospective analysis of 45 patients with OM-CRPC. Whole-body diffusion-weighted MRI (WB-DWI) was used to diagnose oligo-progressive disease. Based on the clinical and radiological findings, the OM-CRPCs were classified as genuine or induced. PSDT was performed with the intent to ablate all the progressive sites detected on WB-DWI with radiotherapy. Systemic therapy remained unchanged during and after PSDT.
Results
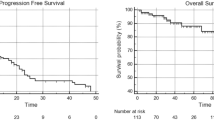
A total of 31 (69%) and 14 (31%) patients were diagnosed with genuine- and induced-OM-CRPC, respectively. The genuine-OM-CRPC group had significantly fewer patients treated with taxane-based chemotherapy and new hormonal drugs than the induced-OM-CRPC group. Of these, 26 OM-CRPC patients were treated with PSDT, and a 50% PSA decline was observed in 14 (93%) of 15 patients with genuine-OM-CRPC and 4 (36%) of 11 patients with induced-OM-CRPC (P = 0.033). Further, the duration of PSA-progression-free survival was significantly longer in the genuine-OM-CRPC group than in the induced-OM-CRPC group (8.7 vs. 5.8 months, P = 0.040).
Conclusions
PSDT can be a promising treatment option for genuine-OM-CRPC. The procedure might also be considered effective for induced-OM-CRPC, although there was less therapeutic benefit of PSDT in patients with induced-OM-CRPC than in patients with genuine-OM-CRPC.

Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Yes.
References
Hellman S, Weichselbaum RR (1995) Oligometastases. J Clin Oncol 13:8–10. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.1995.13.1.8
Ost P, Reynders D, Decaestecker K, Fonteyne V, Lumen N, De Bruycker A, Lambert B, Delrue L, Bultijnck R, Claeys T, Goetghebeur E, Villeirs G, De Man K, Ameye F, Billiet I, Joniau S, Vanhaverbeke F, De Meerleer G (2018) Surveillance or metastasis-directed therapy for oligometastatic prostate cancer recurrence: a prospective, randomized, multicenter phase II trial. J Clin Oncol 36:446–453. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2017.75.4853
Lecouvet FE, El Mouedden J, Collette L, Coche E, Danse E, Jamar F, Machiels JP, Vande Berg B, Omoumi P, Tombal B (2012) Can whole-body magnetic resonance imaging with diffusion-weighted imaging replace Tc 99m bone scanning and computed tomography for single-step detection of metastases in patients with high-risk prostate cancer. Eur Urol 62:68–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2012.02.020
Padhani AR, Lecouvet FE, Tunariu N, Koh DM, De Keyzer F, Collins DJ, Sala E, Schlemmer HP, Petralia G, Vargas HA, Fanti S, Tombal HB, de Bono J (2017) METastasis reporting and data system for prostate cancer: practical guidelines for acquisition, interpretation, and reporting of whole-body magnetic resonance imaging-based evaluations of multiorgan involvement in advanced prostate cancer. Eur Urol 71:81–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2016.05.033
Perera M, Papa N, Christidis D, Wetherell D, Hofman MS, Murphy DG, Bolton D, Lawrentschuk N (2016) Sensitivity, specificity, and predictors of positive 68Ga-prostate-specific membrane antigen positron emission tomography in advanced prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Urol 70:926–937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2016.06.021
Gillessen S, Attard G, Beer TM, Beltran H, Bjartell A, Bossi A, Briganti A, Bristow RG, Chi KN, Clarke N, Davis ID, de Bono J, Drake CG, Duran I, Eeles R, Efstathiou E, Evans CP, Fanti S, Feng FY, Fizazi K, Frydenberg M, Gleave M, Halabi S, Heidenreich A, Heinrich D, Higano CTS, Hofman MS, Hussain M, James N, Kanesvaran R, Kantoff P, Khauli RB, Leibowitz R, Logothetis C, Maluf F, Millman R, Morgans AK, Morris MJ, Mottet N, Mrabti H, Murphy DG, Murthy V, Oh WK, Ost P, O’Sullivan JM, Padhani AR, Parker C, Poon DMC, Pritchard CC, Reiter RE, Roach M, Rubin M, Ryan CJ, Saad F, Sade JP, Sartor O, Scher HI, Shore N, Small E, Smith M, Soule H, Sternberg CN, Steuber T, Suzuki H, Sweeney C, Sydes MR, Taplin ME, Tombal B, Türkeri L, van Oort I, Zapatero A, Omlin A (2020) Management of patients with advanced prostate cancer: report of the advanced prostate cancer consensus conference 2019. Eur Urol 77:508–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2016.06.021
deSouza NM, Liu Y, Chiti A, Oprea-Lager D, Gebhart G, Van Beers BE, Herrmann K, Lecouvet FE (2018) Strategies and technical challenges for imaging oligometastatic disease: recommendations from the European organisation for research and treatment of cancer imaging group. Eur J Cancer 91:153–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2017.12.012
Padhani AR, Liu G, Koh DM, Chenevert TL, Thoeny HC, Takahara T, Dzik-Jurasz A, Ross BD, Van Cauteren M, Collins D, Hammoud DA, Rustin GJ, Taouli B, Choyke PL (2009) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging as a cancer biomarker: consensus and recommendations. Neoplasia 11:102–125. https://doi.org/10.1593/neo.81328
Barnes A, Alonzi R, Blackledge M, Charles-Edwards G, Collins DJ, Cook G, Coutts G, Goh V, Graves M, Kelly C, Koh DM, McCallum H, Miquel ME, O’Connor J, Padhani A, Pearson R, Priest A, Rockall A, Stirling J, Taylor S, Tunariu N, van der Meulen J, Walls D, Winfield J, Punwani S (2018) UK quantitative WB-DWI technical workgroup: consensus meeting recommendations on optimisation, quality control, processing and analysis of quantitative whole-body diffusion-weighted imaging for cancer. Br J Radiol 91:20170577. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20170577
Lohaus F, Zöphel K, Löck S, Wirth M, Kotzerke J, Krause M, Baumann M, Troost EGC, Hölscher T (2019) Can local ablative radiotherapy revert castration-resistant prostate cancer to an earlier stage of disease. Eur Urol 75:548–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2018.11.050
Nozaki K, Kawai T, Fujimura T, Matsui H, Teshima T, Oshina T, Takahashi A, Sato Y, Yamada D, Azuma T, Hotta M, Nakajima K, Nakayama H, Minamimoto R, Kume H (2019) Carbon 11-choline positron emission tomography/computed tomography and palliative local therapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer. Int Urol Nephrol 51:1763–1769. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-019-02233-y
Triggiani L, Mazzola R, Magrini SM, Ingrosso G, Borghetti P, Trippa F, Lancia A, Detti B, Francolini G, Matrone F, Bortolus R, Fanetti G, Maranzano E, Pasqualetti F, Paiar F, Bonù ML, Magli A, Bruni A, Mazzeo E, Franzese C, Scorsetti M, Alongi F, Jereczek-Fossa BA, Ost P, Buglione M (2019) Metastasis-directed stereotactic radiotherapy for oligoprogressive castration-resistant prostate cancer: a multicenter study. World J Urol 37:2631–2637. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-019-02717-7
Yoshida S, Takahara T, Arita Y, Ishii C, Uchida Y, Nakagawa K, Toda K, Sakamoto T, Kijima T, Yokoyama M, Ishioka J, Matsuoka Y, Saito K, Yoshimura R, Fujii Y (2019) Progressive site-directed therapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer: localization of the progressive site as a prognostic factor. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 105:376–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.06.011
Guckenberger M, Lievens Y, Bouma AB, Collette L, Dekker A, deSouza NM, Dingemans AC, Fournier B, Hurkmans C, Lecouvet FE, Meattini I, Méndez Romero A, Ricardi U, Russell NS, Schanne DH, Scorsetti M, Tombal B, Verellen D, Verfaillie C, Ost P (2020) Characterisation and classification of oligometastatic disease: a European Society for radiotherapy and oncology and European organisation for research and treatment of cancer consensus recommendation. Lancet Oncol 21:e18–e28. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30718-1
Takahara T, Imai Y, Yamashita T, Yasuda S, Nasu S, Van Cauteren M (2004) Diffusion weighted whole body imaging with background body signal suppression (DWIBS): technical improvement using free breathing, STIR and high resolution 3D display. Radiat Med 22:275–282
Kwee TC, Takahara T, Ochiai R, Nievelstein RA, Luijten PR (2008) Diffusion-weighted whole-body imaging with background body signal suppression (DWIBS): features and potential applications in oncology. Eur Radiol 18:1937–1952. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-008-0968-z
Yoshida S, Takahara T, Arita Y, Toda K, Yoshimura R, Fujii Y (2020) Patterns of failure after progressive site-directed therapy in oligo-progressive castration-resistant prostate cancer. Int J Urol 27:634–635. https://doi.org/10.1111/iju.14249
Acknowledgment
None.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
Approved by the institutional review board (M2016-170).
Consent to participate
Waved by the institutional review board (M2016-170).
Consent for publication
Yes.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshida, S., Takahara, T., Arita, Y. et al. Genuine- and induced-oligometastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: clinical features and clinical outcomes after progressive site-directed therapy. Int Urol Nephrol 53, 1119–1125 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02762-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02762-x