Abstract
Purpose
It is unclear which time-points of intradialytic blood pressure (BP) best predict prognosis. Thus, it is important to assess the association between different time-points of intradialytic BP and prognosis in clinical practice.
Methods
We recruited patients who underwent hemodialysis from January 2014 to June 2014. Data about dialysis were collected, including intradialytic BP. Cox regression analysis was performed to examine the association between different time-points of intradialytic BP and clinical events, with a follow-up through December 31, 2019. The primary endpoint was all-cause mortality.
Results
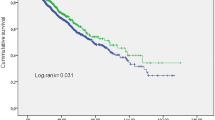
A total of 216 patients were recruited and 62 (30.7%) patients died (6.1 per 100-person year) during the follow-up. Intradialytic SBP varied greatly in fatalities. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression models indicated that the adjusted hazard ratio for death was 1.80 and 5.06 when intradialytic systolic blood pressure (SBP) variation was analyzed in increments of 20 mmHg. Furthermore, we divided intradialytic SBP variation into three categories: < 15 mmHg, 15 ~ 30 mmHg, ≥ 30 mmHg. Kaplan–Meier analysis indicated that both all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality increased significantly for patients with intradialytic SBP variation over 30 mmHg (P = 0.006 and 0.021). Univariate and multivariate Cox regression models indicated that the adjusted hazard ratio for death was 3.78 and 12.62 as intradialytic SBP variation ≥ 30 mmHg vs. intradialytic SBP variation < 15 mmHg.
Conclusion
Intradialytic SBP variation, rather than BP of specific intradialytic time-points, has the potential to predict long-term mortality in hemodialysis patients. BP stability is crucial for patients’ prognosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal and Rajiv (2005) Hypertension and survival in chronic hemodialysis patients-past lessons and future opportunities. Kidney Int 67(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00050.x
Daugirdas JT (2001) Pathophysiology of dialysis hypotension: an update. Am J Kidney Dis 38(4 Suppl 4):S11-17. https://doi.org/10.1053/ajkd.2001.28090
Sherman RA (2002) Intradialytic hypotension: an overview of recent, unresolved and overlooked issues. Semin Dialysis 15(3):141–143. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1525-139x.2002.00002.x
Andrulli S, Colzani S, Mascia F, Lucchi L, Stipo L, Bigi MC, Crepaldi M, Redaelli B, Albertazzi A, Locatelli F (2002) The role of blood volume reduction in the genesis of intradialytic hypotension. Am J Kidney Dis 40(6):1244–1254. https://doi.org/10.1053/ajkd.2002.36894
Inrig JK (2010) Intradialytic hypertension: a less-recognized cardiovascular complication of hemodialysis. Am J Kidney Dis 55(3):580–589. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2009.08.013
Teng J, Tian J, Lv WL, Zhang XY, Zou JZ, Fang Y, Yu J, Shen B, Liu ZH, Ding XQ (2015) Inappropriately elevated endothelin-1 plays a role in the pathogenesis of intradialytic hypertension. Hemodial Int 19(2):279–286. https://doi.org/10.1111/hdi.12238
Agarwal R, Light RP (2010) Intradialytic hypertension is a marker of volume excess. Nephrol Dialysis Transplant 25(10):3355–3361. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfq210
Chou KJ, Lee PT, Chen CL, Chiou CW, Hsu CY, Chung HM, Liu CP, Fang HC (2006) Physiological changes during hemodialysis in patients with intradialysis hypertension. Kidney Int 69(10):1833–1838. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ki.5000266
Flythe JE, Xue H, Lynch KE, Curhan GC, Brunelli SM (2015) Association of mortality risk with various definitions of intradialytic hypotension. J Am Soc Nephrol 26(3):724–734. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2014020222
Yu J, Liu Z, Shen B, Teng J, Zou J, Ding X (2018) Intradialytic hypotension as an independent risk factor for long-term mortality in maintaining hemodialysis patients: a 5-year follow-up cohort study. Blood Purif 45(4):320–326. https://doi.org/10.1159/000486231
Stefansson BV, Brunelli SM, Cabrera C, Rosenbaum D, Anum E, Ramakrishnan K, Jensen DE, Stalhammar NO (2014) Intradialytic hypotension and risk of cardiovascular disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 9(12):2124–2132. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.02680314
Inrig JK, Patel UD, Toto RD, Szczech LA (2009) Association of blood pressure increases during hemodialysis with 2-year mortality in incident hemodialysis patients: a secondary analysis of the Dialysis Morbidity and Mortality Wave 2 Study. Am J Kidney Dis 54(5):881–890. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2009.05.012
Yang CY, Yang WC, Lin YP (2012) Postdialysis blood pressure rise predicts long-term outcomes in chronic hemodialysis patients: a four-year prospective observational cohort study. BMC Nephrol 13:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2369-13-12
Lertdumrongluk P, Streja E, Rhee CM, Sim JJ, Gillen D, Kovesdy CP, Kalantar-Zadeh K (2015) Changes in pulse pressure during hemodialysis treatment and survival in maintenance dialysis patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 10(7):1179–1191. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.09000914
Hara M, Tanaka S, Taniguchi M, Fujisaki K, Torisu K, Masutani K, Hirakata H, Nakano T, Tsuruya K, Kitazono T (2018) Prognostic value of predialysis blood pressure and risk threshold on clinical outcomes in hemodialysis patients: the Q-Cohort Study. Medicine 97(51):e13485. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000013485
Rootjes PA, de Roij van Zuijdewijn CLM, Grooteman MPC, Bots ML, Canaud B, Blankestijn PJ, van Ittersum FJ, Maduell F, Morena M, Peters SAE, Davenport A, Vernooij RWM, Nube MJ, Investigators HDFPP (2020) Long-term peridialytic blood pressure patterns in patients treated by He. Kidney Int Rep 5(4):503–510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ekir.2020.01.007
Han YC, Tu Y, Zhou LT, Pan MM, Wang B, Liu H, Tang RN, Liu BC (2019) Peridialysis BP levels and risk of all-cause mortality: a dose-response meta-analysis. J Hum Hypertens 33(1):41–49. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-018-0103-9
Tsuruya K, Kanda E, Nomura T, Iseki K, Hirakata H (2020) Postdialysis blood pressure is a better predictor of mortality than predialysis blood pressure in Japanese hemodialysis patients: the Japan Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study. Hypertens Res. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-020-0425-1
Somes GW, Pahor M, Shorr RI, Cushman WC, Applegate WB (1999) The role of diastolic blood pressure when treating isolated systolic hypertension. Arch Intern Med 159(17):2004–2009. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.159.17.2004
Tatsuya S, Yoshiharu T, Masamitsu F, Enyu I (2004) Hemodialysis-associated hypotension as an independent risk factor for two-year mortality in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 66(3):1212–1220. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.00812.x
K/DOQI Workgroup (2005) K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for cardiovascular disease in dialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 45(null): S1–153
Chou JA, Streja E, Nguyen DV, Rhee CM, Obi Y, Inrig JK, Amin A, Kovesdy CP, Sim JJ, Kalantar-Zadeh K (2018) Intradialytic hypotension, blood pressure changes and mortality risk in incident hemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dialysis Transplant 33(1):149–159. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfx037
Assimon MM, Flythe JE (2015) Intradialytic blood pressure abnormalities: the highs, the lows and all that lies between. Am J Nephrol 42(5):337–350. https://doi.org/10.1159/000441982
van der Sande FM, Dekker MJ, Leunissen KML, Kooman JP (2018) Novel insights into the pathogenesis and prevention of intradialytic hypotension. Blood Purif 45(1–3):230–235. https://doi.org/10.1159/000485160
Nongnuch A, Campbell N, Stern E, El-Kateb S, Fuentes L, Davenport A (2015) Increased postdialysis systolic blood pressure is associated with extracellular overhydration in hemodialysis outpatients. Kidney Int 87(2):452–457. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2014.276
Vasan RS, Larson MG, Leip EP, Evans JC, O’Donnell CJ, Kannel WB, Levy D (2001) Impact of high-normal blood pressure on the risk of cardiovascular disease. New Engl J Med 345(18):1291–1297. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa003417
Foley RN, Herzog CA, Collins AJ (2002) Blood pressure and long-term mortality in United States hemodialysis patients USRDS Waves 3 and 4 study. Kidney Int 62(5):1784–1790. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.2002.00636.x
Zager PG, Nikolic J, Brown RH, Campbell MA, Hunt WC, Peterson D, Van Stone J, Levey A, Meyer KB, Klag MJ, Johnson HK, Clark E, Sadler JH, Teredesai P (1998) “U” curve association of blood pressure and mortality in hemodialysis patients. Medical directors of dialysis clinic, Inc. Kidney Int 54(2):561–569. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.1998.00005.x
Losito A, Del Vecchio L, Del Rosso G, Locatelli F (2016) Postdialysis hypertension: associated factors, patient profiles, and cardiovascular mortality. Am J Hypertens 29(6):684–689. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajh/hpv162
Rothwell PM (2010) Limitations of the usual blood-pressure hypothesis and importance of variability, instability, and episodic hypertension. The Lancet 375(9718):938–948. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(10)60309-1
Chang TI, Flythe JE, Brunelli SM, Muntner P, Greene T, Cheung AK, Chertow GM (2014) Visit-to-visit systolic blood pressure variability and outcomes in hemodialysis. J Hum Hypertens 28(1):18–24. https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2013.49
Shafi T, Sozio SM, Bandeen-Roche KJ, Ephraim PL, Luly JR, St Peter WL, McDermott A, Scialla JJ, Crews DC, Tangri N, Miskulin DC, Michels WM, Jaar BG, Herzog CA, Zager PG, Meyer KB, Wu AW, Boulware LE (2014) Predialysis systolic BP variability and outcomes in hemodialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 25(4):799–809. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2013060667
Flythe JE, Inrig JK, Shafi T, Chang TI, Cape K, Dinesh K, Kunaparaju S, Brunelli SM (2013) Association of intradialytic blood pressure variability with increased all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients treated with long-term hemodialysis. Am J Kidney Dis 61(6):966–974. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2012.12.023
Lu J, Zhu M, Liu S, Zhu M, Pang H, Lin X, Ni Z, Qian J, Cai H, Zhang W (2017) The relationship between survival rate and intradialytic blood pressure changes in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Ren Fail 39(1):417–422. https://doi.org/10.1080/0886022X.2017.1305407
Inrig JK, Oddone EZ, Hasselblad V, Gillespie B, Patel UD, Reddan D, Toto R, Himmelfarb J, Winchester JF, Stivelman J, Lindsay RM, Szczech LA (2007) Association of intradialytic blood pressure changes with hospitalization and mortality rates in prevalent ESRD patients. Kidney Int 71(5):454–461. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ki.5002077
Flythe JE, Kunaparaju S, Dinesh K, Cape K, Feldman HI, Brunelli SM (2012) Factors associated with intradialytic systolic blood pressure variability. Am J Kidney Dis 59(3):409–418. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2011.11.026
Burton JO, Jefferies HJ, Selby NM, McIntyre CW (2009) Hemodialysis-induced cardiac injury: determinants and associated outcomes. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4(5):914–920. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.03900808
Chesterton LJ, Selby NM, Burton JO, Fialova J, Chan C, McIntyre CW (2010) Categorization of the hemodynamic response to hemodialysis: the importance of baroreflex sensitivity. Hemodial Int 14(1):18–28. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1542-4758.2009.00403.x
Leypoldt JK, Cheung AK, Delmez JA, Gassman JJ, Levin NW, Lewis JA, Lewis JL, Rocco MV (2002) Relationship between volume status and blood pressure during chronic hemodialysis. Kidney Int 61(1):266–275. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.2002.00099.x
Flythe JE, Kimmel SE, Brunelli SM (2011) Rapid fluid removal during dialysis is associated with cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Kidney Int 79(2):250–257. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2010.383
Movilli E, Gaggia P, Zubani R, Camerini C, Vizzardi V, Parrinello G, Savoldi S, Fischer MS, Londrino F, Cancarini G (2007) Association between high ultrafiltration rates and mortality in uraemic patients on regular haemodialysis. A 5-year prospective observational multicentre study. Nephrol Dialysis Transplant 22(12):3547–3552. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfm466
Saran R, Bragg-Gresham JL, Levin NW, Twardowski ZJ, Wizemann V, Saito A, Kimata N, Gillespie BW, Combe C, Bommer J, Akiba T, Mapes DL, Young EW, Port FK (2006) Longer treatment time and slower ultrafiltration in hemodialysis: associations with reduced mortality in the DOPPS. Kidney Int 69(7):1222–1228. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ki.5000186
Agarwal R, Sinha AD, Pappas MK, Abraham TN, Tegegne GG (2014) Hypertension in hemodialysis patients treated with atenolol or lisinopril: a randomized controlled trial. Nephrol Dialysis Transplant 29(3):672–681. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gft515
Miskulin DC, Gassman J, Schrader R, Gul A, Jhamb M, Ploth DW, Negrea L, Kwong RY, Levey AS, Singh AK, Harford A, Paine S, Kendrick C, Rahman M, Zager P (2018) BP in dialysis: results of a pilot study. J Am Soc Nephrol 29(1):307–316. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2017020135
Rajiv A, Andersen MJ, Howard PJ (2008) On the importance of pedal edema in hemodialysis patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 3(1):153–158. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.03650807
Onofriescu M, Hogas S, Voroneanu L, Apetrii M, Nistor I, Kanbay M, Covic AC (2014) Bioimpedance-guided fluid management in maintenance hemodialysis: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Am J Kidney Dis 64(1):111–118. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2014.01.420
Loutradis C, Sarafidis PA, Ekart R, Papadopoulos C, Sachpekidis V, Alexandrou ME, Papadopoulou D, Efstratiadis G, Papagianni A, London G, Zoccali C (2019) The effect of dry-weight reduction guided by lung ultrasound on ambulatory blood pressure in hemodialysis patients: a randomized controlled trial. Kidney Int 95(6):1505–1513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2019.02.018
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to all participating patients and dialysis staff of Blood Purification Center, Division of Nephrology, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University. This study is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 81903969), the Youth Foundation of Zhongshan Hospital (Grant no. 2019ZSQN22), Shanghai "science and technology innovation plan" technical standard project (No. 19DZ2205600), as well as by Shanghai Municipal Hospital Frontier Technology Project supported by Shanghai ShenKang Hospital Development Center (No. SHDC12018127).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has any competing interests to declare, financial or otherwise.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by our institution’s clinical research ethics review board (Ethics Committee of Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University) and was conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki principles. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J., Chen, X., Wang, Y. et al. Intradialytic systolic blood pressure variation can predict long-term mortality in patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Int Urol Nephrol 53, 785–795 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02701-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02701-w