Abstract
Background
Both regional citrate anticoagulation (RCA) and heparin are used as anticoagulants during membrane therapeutic plasma exchange (mTPE). However, there are few reports of comparisons of the two methods. The aim of this study was to compare different anticoagulants in mTPE and observe the effectiveness, safety, and advantages of RCA.
Methods
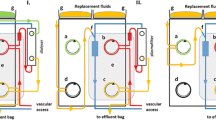
We retrospectively included 85 patients who underwent mTPE in the past 1 year, and divided them into three groups. Patients with no bleeding tendency were administered heparin anticoagulation; patients with bleeding tendency/with liver dysfunction/who had undergone an operation were treated with RCA, or did not receive anticoagulation. In the heparin group, low-dose heparin anticoagulation was administered; in the RCA group, 4% sodium citrate solution was administered, and 10% calcium gluconate solution was pumped from the venous circuit tube. The peripheral blood platelet count, prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), and electrolytes were detected before and after treatment in all patients.
Results
A total of 255 sessions of mTPE were performed in 85 patients (2–7 times/case) with 120 sessions of heparin anticoagulation, 93 sessions of RCA, and 42 sessions of no anticoagulation. Compared with pretreatment values, the platelet count decreased by 53.7% and the PT and APTT increased (p < 0.05) in the heparin group after treatment. There were no differences in platelet count and PT before and after treatment in the RCA group. In the RCA group, the patients did not experience hypocalcemia or hypercalcemia, and no separator clotting occurred.
Conclusion
RCA is safe, feasible, and effective in mTPE, especially for patients with bleeding tendency and frequent monitoring is needed. It is worth widely developing and applying it in clinical practice.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen X, Chen N (2013) Plasma exchange in the treatment of rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis. Contrib Nephrol 181:240–247
Nakanishi T, Suzuki N, Kuragano T, Nagasawa Y, Hasuike Y (2014) Current topics in therapeutic plasmapheresis. Clin Exp Nephrol 18(1):41–49
Láinez-Andrés JM, Gascón-Giménez F, Coret-Ferrer F, Casanova-Estruch B, Santonja JM (2015) Therapeutic plasma exchange: applications in neurology. Rev Neurol 60(3):120–131
Kindgen-Milles D, Brandenburger T, Dimski T (2018) Regional citrate anticoagulation for continuous renal replacement therapy. Curr Opin Crit Care 24(6):450–454
Janssen MJ (1996) The bleeding risk in chronic haemodialysis. Preventive strategies in high-risk patients. Neth J Med 48:198–207
Lee G, Arepally GM (2012) Anticoagulation techniques in apheresis: from heparin to citrate and beyond. Clin Apher 27(3):117–125
Maharaj S, Chang S, Seegobin K, Morales J, Aysola A, Rana F, Shaikh M (2018) Temporality of heparin-induced antibodies: a retrospective study in outpatients undergoing hemodialysis on unfractionated heparin. Exp Hematol Oncol 7:23
Mollison PL (2000) The introduction of citrate as an anticoagulant for transfusion and of glucose as a red cell preservative. Br J Haematol 108:13–18
Oudemans-van Straaten HM, Fiaccadori E, Baldwin I (2010) Anticoagulation for renal replacement therapy: different methods to improve safety. Contrib Nephro 165:251–262
Antonic M, Gubensek J, Buturović-Ponikvar J, Ponikvar R (2009) Comparison of citrate anticoagulation during plasma exchange with different replacement solutions. Ther Apher Dial 13(4):322–326
van de Wetering J, Westendorp RG, van der Hoeven JG, Stolk B, Feuth JD, Chang PC (1996) Heparin use in continuous renal replacement procedures: the struggle between filter coagulation and patient hemorrhage. J Am Soc Nephrol 7:45–50
Monchi M (2017) Citrate pathophysiology and metabolism. Transfus Apher Sci 56(1):28–30
Uhl L, Maillet S, King S, Kruskall MS (1997) Unexpected citrate toxicity and severe hypocalcemia during apheresis. Transfusion 37:1063–1065
Hester JP, McCullough J, Mishler JM, Szymanski IO (1983) Dosage regimens for citrate anticoagulants. J Clin Apher 1:149–157
Sigler K, Lee J, Srivaths P (2018) Regional citrate anticoagulation with calcium replacement in pediatric apheresis. J Clin Apher 33(3):274–277
Crookston KP, Novak DJ (2010) Physiology of apheresis. In: McLeod BC, Szczepiorkowski ZM, Weinstein R, Winters JL (eds) Apheresis: principles and practice. AABBPress, Bethesda, pp 45–69
Marques MB, Huang ST (2001) Patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura commonly develop metabolic alkalosis during therapeutic plasma exchange. J Clin Apher 16:120–124
Wright S, Steinwandel U, Ferrari P (2011) Citrate anticoagulation using ACD solution A during long-term haemodialysis. Nephrology (Carlton) 16(4):396–402
Weiss R, Fischer MB, Weber V (2017) The impact of citrate concentration on adhesion of platelets and leukocytes to adsorbents in whole blood lipoprotein apheresis. J Clin Apher 32(6):375–383
Puppe B, Kingdon EJ (2014) Membrane and centrifugal therapeutic plasma exchange: practical difficulties in anticoagulating the extracorporeal circuit. Clin Kidney J 7:201–205
Brandenburger T, Dimski T, Slowinski T, Kindgen-Milles D (2017) Renal replacement therapy and anticoagulation. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol 31(3):387–401
Rodnitzky RL, Goeken JA (1982) Complications of plasma exchange in neurological patients. Arch Neurol 39:350–354
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81770730) and the Grant 2017JJ2352 from Hunan Provincial Natural Science Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Human and animal rights
The study protocol has been approved by the research institute’s committee on human research. The requirement of informed consent was waived by the review board (no. 2019011).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, F., Li, Z., Li, X. et al. Application of regional citrate anticoagulation in membrane therapeutic plasma exchange. Int Urol Nephrol 52, 2379–2384 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02581-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02581-0