Abstract
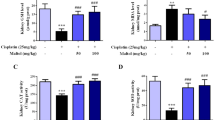
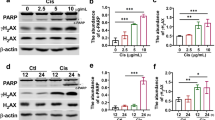
Acute kidney injury is a complex clinical disease that is associated with a high incidence of morbidity and mortality. Drug-induced acute kidney injury occurs in approximately 19–33% of hospitalized patients. Cisplatin, one of the most commonly used and effective chemotherapeutic drugs not only exerts anti-tumor effects but also causes renal toxicity damage, affecting its clinical application. Vinpocetine is an anti-inflammatory and antioxidant drug that predominately acts in the nervous system. In this study, we investigated the effects and mechanisms of vinpocetine in an animal model of cisplatin-induced acute renal injury. Rats were randomly divided into three experimental groups. During a 10-day trial, rats in the control group were administered a physiological saline solution; rats in the model group received a 5 mg/kg intraperitoneal injection of cisplatin; and rats in the cisplatin + vinpocetine group received a 5 mg/kg intraperitoneal injection of cisplatin as well as a 5 mg/kg dose of vinpocetine via gavage. We observed that following cisplatin administration, the rats exhibited an increase in blood urea and creatinine levels as well as an increase in their inflammation and oxidative stress levels. In renal tissue, cisplatin caused the morphological changes typical of acute tubular injury. Vinpocetine reduced the cisplatin-induced acute renal function damage and tubular injury. In both in vivo and in vitro experiments, we found that vinpocetine can confer protection of rat renal cells by inhibiting the NF–κB signaling pathway and activating the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. Therefore, vinpocetine is a promising therapeutic drug for the treatment of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stover EH, Konstantinopoulos PA, Matulonis UA, Swisher EM (2016) Biomarkers of response and resistance to DNA repair targeted therapies. Clin Cancer Res 22(23):5651–5660. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-16-0247
Dasari S, Tchounwou PB (2014) Cisplatin in cancer therapy: molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol 740:364–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.07.025
Kelland L (2007) The resurgence of platinum-based cancer chemotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 7(8):573–584. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2167
Sanchez-Gonzalez PD, Lopez-Hernandez FJ, Lopez-Novoa JM, Morales AI (2011) An integrative view of the pathophysiological events leading to cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Crit Rev Toxicol 41(10):803–821. https://doi.org/10.3109/10408444.2011.602662
Arany I, Safirstein RL (2003) Cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Semin Nephrol 23(5):460–464
Galgamuwa R, Hardy K, Dahlstrom JE, Blackburn AC, Wium E, Rooke M, Cappello JY, Tummala P, Patel HR, Chuah A, Tian L, McMorrow L, Board PG, Theodoratos A (2016) Dichloroacetate prevents cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity without compromising cisplatin anticancer properties. J Am Soc Nephrol JASN 27(11):3331–3344. https://doi.org/10.1681/asn.2015070827
Meng XM, Ren GL, Gao L, Yang Q, Li HD, Wu WF, Huang C, Zhang L, Lv XW, Li J (2018) NADPH oxidase 4 promotes cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury via ROS-mediated programmed cell death and inflammation. Lab Investig 98(1):63–78. https://doi.org/10.1038/labinvest.2017.120
Wang T, Zhang X, Li JJ (2002) The role of NF-kappaB in the regulation of cell stress responses. Int Immunopharmacol 2(11):1509–1520
Baichwal VR, Baeuerle PA (1997) Activate NF-kappa B or die? Curr Biol CB 7(2):R94–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0960-9822(06)00046-7
Pahl HL (1999) Activators and target genes of Rel/NF-kappaB transcription factors. Oncogene 18(49):6853–6866. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203239
Heckman PR, Wouters C, Prickaerts J (2015) Phosphodiesterase inhibitors as a target for cognition enhancement in aging and Alzheimer's disease: a translational overview. Curr Pharm Des 21(3):317–331. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612820666140826114601
Bagoly E, Feher G, Szapary L (2007) The role of vinpocetine in the treatment of cerebrovascular diseases based in human studies. Orv Hetil 148(29):1353–1358. https://doi.org/10.1556/oh.2007.28115
Tamaki N, Matsumoto S (1985) Agents to improve cerebrovascular circulation and cerebral metabolism–vinpocetine. Nihon Rinsho Jpn J Clin Med 43(2):376–378
Medina AE (2011) Therapeutic utility of phosphodiesterase type I inhibitors in neurological conditions. Front Neurosci 5:21. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2011.00021
Sharma S, Deshmukh R (2015) Vinpocetine attenuates MPTP-induced motor deficit and biochemical abnormalities in Wistar rats. Neuroscience 286:393–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.12.008
Gupta S, Sharma B (2014) Protective effects of phosphodiesterase-1 (PDE1) and ATP sensitive potassium (KATP) channel modulators against 3-nitropropionic acid induced behavioral and biochemical toxicities in experimental Huntingtons disease. Eur J Pharmacol 732:111–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.03.032
Ruiz-Miyazawa KW, Pinho-Ribeiro FA, Zarpelon AC, Staurengo-Ferrari L, Silva RL, Alves-Filho JC, Cunha TM, Cunha FQ, Casagrande R, Verri WA Jr (2015) Vinpocetine reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory pain and neutrophil recruitment in mice by targeting oxidative stress, cytokines and NF-kappaB. Chem Biol Interact 237:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2015.05.007
Jeon KI, Xu X, Aizawa T, Lim JH, Jono H, Kwon DS, Abe J, Berk BC, Li JD, Yan C (2010) Vinpocetine inhibits NF-kappaB-dependent inflammation via an IKK-dependent but PDE-independent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(21):9795–9800. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0914414107
Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Al-Nami MS (2019) Vinpocetine improves oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory mediators in acute kidney injury. Int J Prevent Med 10:142. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_5_19
Francescato HDC, Almeida LF, Reis NG, Faleiros CM, Papoti M, Costa RS, Coimbra TM (2018) Previous exercise effects in cisplatin-induced renal lesions in rats. Kidney Blood Pressure Res 43(2):582–593. https://doi.org/10.1159/000488964
Ibrahim ME, Bana EE, El-Kerdasy HI (2018) Role of bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells and the protective effect of silymarin in cisplatin-induced acute renal failure in rats. Am J Med Sci 355(1):76–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjms.2017.08.004
Moreno-Gordaliza E, Esteban-Fernandez D, Lazaro A, Aboulmagd S, Humanes B, Tejedor A, Linscheid MW, Gomez-Gomez MM (2018) Lipid imaging for visualizing cilastatin amelioration of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. J Lipid Res 59(9):1561–1574. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M080465
Choi YM, Kim HK, Shim W, Anwar MA, Kwon JW, Kwon HK, Kim HJ, Jeong H, Kim HM, Hwang D, Kim HS, Choi S (2015) Mechanism of cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity is correlated to impaired metabolism due to mitochondrial ROS generation. PLoS ONE 10(8):e0135083. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0135083
Pan H, Shen K, Wang X, Meng H, Wang C, Jin B (2014) Protective effect of metalloporphyrins against cisplatin-induced kidney injury in mice. PLoS ONE 9(1):e86057. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0086057
Latcha S, Jaimes EA, Patil S, Glezerman IG, Mehta S, Flombaum CD (2016) Long-term renal outcomes after cisplatin treatment. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol CJASN 11(7):1173–1179. https://doi.org/10.2215/cjn.08070715
Lebwohl D, Canetta R (1998) Clinical development of platinum complexes in cancer therapy: an historical perspective and an update. Eur J Cancer 34(10):1522–1534. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0959-8049(98)00224-x
Shiraishi F, Curtis LM, Truong L, Poss K, Visner GA, Madsen K, Nick HS, Agarwal A (2000) Heme oxygenase-1 gene ablation or expression modulates cisplatin-induced renal tubular apoptosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 278(5):F726–736. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.2000.278.5.F726
Zeng X, McMahon GM, Brunelli SM, Bates DW, Waikar SS (2014) Incidence, outcomes, and comparisons across definitions of AKI in hospitalized individuals. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol CJASN 9(1):12–20. https://doi.org/10.2215/cjn.02730313
Yang L, Xing G, Wang L, Wu Y, Li S, Xu G, He Q, Chen J, Chen M, Liu X, Zhu Z, Yang L, Lian X, Ding F, Li Y, Wang H, Wang J, Wang R, Mei C, Xu J, Li R, Cao J, Zhang L, Wang Y, Xu J, Bao B, Liu B, Chen H, Li S, Zha Y, Luo Q, Chen D, Shen Y, Liao Y, Zhang Z, Wang X, Zhang K, Liu L, Mao P, Guo C, Li J, Wang Z, Bai S, Shi S, Wang Y, Wang J, Liu Z, Wang F, Huang D, Wang S, Ge S, Shen Q, Zhang P, Wu L, Pan M, Zou X, Zhu P, Zhao J, Zhou M, Yang L, Hu W, Wang J, Liu B, Zhang T, Han J, Wen T, Zhao M, Wang H (2015) Acute kidney injury in China: a cross-sectional survey. Lancet (London, England) 386(10002):1465–1471. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(15)00344-x
Cao SS, Yan M, Hou ZY, Chen Y, Jiang YS, Fan XR, Fang PF, Zhang BK (2017) Danshen modulates Nrf2-mediated signaling pathway in cisplatin-induced renal injury. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Med Sci 37(5):761–765. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-017-1801-1
Guerrero-Hue M, Farre-Alins V, Palomino-Antolin A, Parada E, Rubio-Navarro A, Egido J, Egea J, Moreno JA (2017) Targeting Nrf2 in protection against renal disease. Curr Med Chem 24(33):3583–3605. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867324666170511120814
Zhou Z, Liu C, Chen S, Zhao H, Zhou K, Wang W, Yuan Y, Li Z, Guo Y, Shen Z, Mei X (2017) Activation of the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway by probucol contributes to inhibiting inflammation and neuronal apoptosis after spinal cord injury. Oncotarget 8(32):52078–52093. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.19107
Izumi Y, Kataoka H, Inose Y, Akaike A, Koyama Y, Kume T (2018) Neuroprotective effect of an Nrf2-ARE activator identified from a chemical library on dopaminergic neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 818:470–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.11.023
Karin M, Yamamoto Y, Wang QM (2004) The IKK NF-kappa B system: a treasure trove for drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3(1):17–26. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd1279
Nagashima K, Sasseville VG, Wen D, Bielecki A, Yang H, Simpson C, Grant E, Hepperle M, Harriman G, Jaffee B, Ocain T, Xu Y, Fraser CC (2006) Rapid TNFR1-dependent lymphocyte depletion in vivo with a selective chemical inhibitor of IKKbeta. Blood 107(11):4266–4273. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2005-09-3852
Bellezza I, Mierla AL, Minelli A (2010) Nrf2 and NF-kappaB and their concerted modulation in cancer pathogenesis and progression. Cancers 2(2):483–497. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers2020483
Lu H, Ouyang W, Huang C (2006) Inflammation, a key event in cancer development. Mol Cancer Res MCR 4(4):221–233. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.mcr-05-0261
Surh YJ, Kundu JK, Na HK, Lee JS (3001s) Redox-sensitive transcription factors as prime targets for chemoprevention with anti-inflammatory and antioxidative phytochemicals. J Nutr 135(12 Suppl):2993s–3001s. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/135.12.2993S
Chang J, Zhang Y, Li Y, Lu K, Shen Y, Guo Y, Qi Q, Wang M, Zhang S (2018) NrF2/ARE and NF-kappaB pathway regulation may be the mechanism for lutein inhibition of human breast cancer cell. Fut Oncol (London, England) 14(8):719–726. https://doi.org/10.2217/fon-2017-0584
Liu GH, Qu J, Shen X (2008) NF-kappaB/p65 antagonizes Nrf2-ARE pathway by depriving CBP from Nrf2 and facilitating recruitment of HDAC3 to MafK. Biochem Biophys Acta 1783(5):713–727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2008.01.002
Yu M, Li H, Liu Q, Liu F, Tang L, Li C, Yuan Y, Zhan Y, Xu W, Li W, Chen H, Ge C, Wang J, Yang X (2011) Nuclear factor p65 interacts with Keap1 to repress the Nrf2-ARE pathway. Cell Signal 23(5):883–892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.01.014
Ishola IO, Akinyede AA, Adeluwa TP, Micah C (2018) Novel action of vinpocetine in the prevention of paraquat-induced parkinsonism in mice: involvement of oxidative stress and neuroinflammation. Metab Brain Dis 33(5):1493–1500. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0256-9
Wadie W, El-Tanbouly DM (2017) Vinpocetine mitigates proteinuria and podocytes injury in a rat model of diabetic nephropathy. Eur J Pharmacol 814:187–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.08.027
Fattori V, Borghi SM, Guazelli CFS, Giroldo AC, Crespigio J, Bussmann AJC, Coelho-Silva L, Ludwig NG, Mazzuco TL, Casagrande R, Verri WA Jr (2017) Vinpocetine reduces diclofenac-induced acute kidney injury through inhibition of oxidative stress, apoptosis, cytokine production, and NF-kappaB activation in mice. Pharmacol Res 120:10–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2016.12.039
Hoesel B, Schmid JA (2013) The complexity of NF-kappaB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol Cancer 12:86. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-12-86
Gilmore TD (2006) Introduction to NF-kappaB: players, pathways, perspectives. Oncogene 25(51):6680–6684. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209954
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank Wuhan Central Hospital, Wuhan, Hubei, China, for the project support. This work was supported by the Wuhan Municipal Health Commission (No. WZ16A01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LD and YY helped design and implement animal experiments. WY, YG, and JX provided technical support in cell experiments. The first draft of the manuscript was written by WS and all authors commented on the previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical approval
The animal study was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) and the ABSL-3 Institutional Biosafety Committee (IBC). All experiments were performed in strict accordance with the recommendations of the National Institutes of Health Laboratory Animal Care and Use Guidelines.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, W., Yin, W., Ding, L. et al. Vinpocetine reduces cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury through inhibition of NF–κB pathway and activation of Nrf2/ARE pathway in rats. Int Urol Nephrol 52, 1389–1401 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02485-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02485-z