Abstract
Purpose
Protein-energy wasting, characterized by decreased muscle mass, is one of the strongest predictors of mortality in patients on maintenance hemodialysis (MHD). As people get older, their muscle strength usually declines faster than muscle mass. However, the association between lower-limb muscle strength and all-cause mortality remains unclear. We aimed to evaluate risk factors for decreased upper-limb muscle strength in MHD patients and its impact on patient survival.
Methods
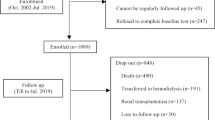
The cross-sectional part of the study included 174 MHD patients. Subsequently, they were followed up for 52 weeks. Biceps muscle strength, anthropometry, body composition, dietary intake, daily steps, and biochemical indicators of malnutrition and inflammation were evaluated. Risk factors for muscle weakness were screened by multiple linear regression analysis, and patient survival was analyzed by Kaplan–Merier and Cox multivariate analysis.
Results
The 174 MHD patients (93 men; 63.05 ± 12.29 years) were classified as a young (< 65 years, n = 97) group and an elderly group (≥ 65 years, n = 77). Gender, daily steps, muscle mass, 25(OH)D level and IL-6 in young group, and muscle mass, 25(OH)D, daily steps, and NT-proBNP in elderly group were associated with the decreased biceps muscle strength. The survival rate in high muscle strength group was significantly higher than that in low muscle strength group (P = 0.002). The association between low muscle strength and high mortality risk remained strong in the fully adjusted model.
Conclusion
Risk factors of muscle weakness were different between young and elderly MHD patients. There was a strong correlation between strong biceps muscle strength and high patient survival.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Data that support the findings of this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
References
Fouque D, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kopple J, Cano N, Chauveau P, Cuppari L, Franch H, Guarnieri G, Ikizler TA, Kaysen G, Lindholm B, Massy Z, Mitch W, Pineda E, Stenvinkel P, Trevino-Becerra A, Wanner C (2008) A proposed nomenclature and diagnostic criteria for protein-energy wasting in acute and chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 73(4):391–398
Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kopple JD (2001) Relative contributions of nutrition and inflammation to clinical outcome in dialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 38(6):1343–1350
Mehrotra R, Kopple JD (2001) Nutritional management of maintenance dialysis patients: why aren't we doing better? Annu Rev Nutr 21:343–379
Kopple JD (1997) McCollum Award Lecture, 1996: protein-energy malnutrition in maintenance dialysis patients. Am J Clin Nutr 65(5):1544–1557
Kalantar-Zadeh K, Ikizler TA, Block G, Avram MM, Kopple JD (2003) Malnutrition-inflammation complex syndrome in dialysis patients: causes and consequences. Am J Kidney Dis 42(5):864–881
Carrero JJ, Chmielewski M, Axelsson J, Snaedal S, Heimburger O, Barany P, Suliman ME, Lindholm B, Stenvinkel P, Qureshi AR (2008) Muscle atrophy, inflammation and clinical outcome in incident and prevalent dialysis patients. Clin Nutr 27(4):557–564
Heimburger O, Qureshi AR, Blaner WS, Berglund L, Stenvinkel P (2000) Hand-grip muscle strength, lean body mass, and plasma proteins as markers of nutritional status in patients with chronic renal failure close to start of dialysis therapy. Am J Kidney Dis 36(6):1213–1225
Goodpaster BH, Park SW, Harris TB, Kritchevsky SB, Nevitt M, Schwartz AV, Simonsick EM, Tylavsky FA, Visser M, Newman AB (2006) The loss of skeletal muscle strength, mass, and quality in older adults: the health, aging and body composition study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 61(10):1059–1064
Hughes VA, Frontera WR, Wood M, Evans WJ, Dallal GE, Roubenoff R, Fiatarone Singh MA (2001) Longitudinal muscle strength changes in older adults: influence of muscle mass, physical activity, and health. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 56(5):B209–217
Isoyama N, Qureshi AR, Avesani CM, Lindholm B, Barany P, Heimburger O, Cederholm T, Stenvinkel P, Carrero JJ (2014) Comparative associations of muscle mass and muscle strength with mortality in dialysis patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 9(10):1720–1728
Holick MF (2009) Vitamin D status: measurement, interpretation, and clinical application. Ann Epidemiol 19(2):73–78
Holick MF (2007) Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J Med 357(3):266–281
Ravani P, Malberti F, Tripepi G, Pecchini P, Cutrupi S, Pizzini P, Mallamaci F, Zoccali C (2009) Vitamin D levels and patient outcome in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 75(1):88–95
Krassilnikova M, Ostrow K, Bader A, Heeger P, Mehrotra A (2014) Low dietary intake of vitamin D and vitamin D deficiency in hemodialysis patients. J Nephrol Ther 4(3):1
Gordon PL, Doyle JW, Johansen KL (2012) Association of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D levels with physical performance and thigh muscle cross-sectional area in chronic kidney disease stage 3 and 4. J Ren Nutr 22(4):423–433
Zhang Q, Li M, Zhang T, Chen J (2016) Effect of vitamin D receptor activators on glomerular filtration rate: a meta-analysis and systematic review. PLoS ONE 11(1):e0147347
Xie H, Cheng C, Tao Y, Zhang J, Robert D, Jia J, Su Y (2020) Quality of life in Chinese family caregivers for elderly people with chronic diseases. Health Qual Life Outcomes 14(1):99
Liao CC, Li CR, Lee SH, Liao WC, Liao MY, Lin J, Yeh CJ, Lee MC (2020) Social support and mortality among the aged people with major diseases or ADL disabilities in Taiwan: a national study. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 60(2):317–321
Al-Qaoud TM, Nitsch D, Wells J, Witte DR, Brunner EJ (2011) Socioeconomic status and reduced kidney function in the Whitehall II Study: role of obesity and metabolic syndrome. Am J Kidney Dis 58(3):389–397
Bansal N, Zelnick LR, Himmelfarb J, Chertow GM (2018) Bioelectrical impedance analysis measures and clinical outcomes in CKD. Am J Kidney Dis 72(5):662–672
Wilson FP, Xie D, Anderson AH, Leonard MB, Reese PP, Delafontaine P, Horwitz E, Kallem R, Navaneethan S, Ojo A, Porter AC, Sondheimer JH, Sweeney HL, Townsend RR, Feldman HI, Investigators CS (2014) Urinary creatinine excretion, bioelectrical impedance analysis, and clinical outcomes in patients with CKD: the CRIC study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 9(12):2095–2103
Termorshuizen F, Dekker FW, van Manen JG, Korevaar JC, Boeschoten EW, Krediet RT, Group NS (2004) Relative contribution of residual renal function and different measures of adequacy to survival in hemodialysis patients: an analysis of the Netherlands Cooperative Study on the Adequacy of Dialysis (NECOSAD)-2. J Am Soc Nephrol 15(4):1061–1070
Qureshi AR, Alvestrand A, Danielsson A, Divino-Filho JC, Gutierrez A, Lindholm B, Bergstrom J (1998) Factors predicting malnutrition in hemodialysis patients: a cross-sectional study. Kidney Int 53(3):773–782
Biasioli S, Foroni R, Petrosino L, Cavallini L, Zambello A, Cavalcanti G, Talluri T (1993) Effect of aging on the body composition of dialyzed subjects: comparison with normal subjects. ASAIO J 39(3):M596–601
Kaizu Y, Ohkawa S, Odamaki M, Ikegaya N, Hibi I, Miyaji K, Kumagai H (2003) Association between inflammatory mediators and muscle mass in long-term hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 42(2):295–302
Delmonico MJ, Harris TB, Visser M, Park SW, Conroy MB, Velasquez-Mieyer P, Boudreau R, Manini TM, Nevitt M, Newman AB, Goodpaster BH, Health A (2009) Longitudinal study of muscle strength, quality, and adipose tissue infiltration. Am J Clin Nutr 90(6):1579–1585
Newman AB, Kupelian V, Visser M, Simonsick EM, Goodpaster BH, Kritchevsky SB, Tylavsky FA, Rubin SM, Harris TB (2006) Strength, but not muscle mass, is associated with mortality in the health, aging and body composition study cohort. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 61(1):72–77
Matsuzawa R, Hoshi K, Yoneki K, Harada M, Watanabe T, Shimoda T, Yamamoto S, Matsunaga A (2017) Exercise training in elderly people undergoing hemodialysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Kidney Int Rep 2(6):1096–1110
Chen JL, Godfrey S, Ng TT, Moorthi R, Liangos O, Ruthazer R, Jaber BL, Levey AS, Castaneda-Sceppa C (2010) Effect of intra-dialytic, low-intensity strength training on functional capacity in adult haemodialysis patients: a randomized pilot trial. Nephrol Dial Transplant 25(6):1936–1943
London GM, Guerin AP, Verbeke FH, Pannier B, Boutouyrie P, Marchais SJ, Metivier F (2007) Mineral metabolism and arterial functions in end-stage renal disease: potential role of 25-hydroxyvitamin D deficiency. J Am Soc Nephrol 18(2):613–620
Matias PJ, Ferreira C, Jorge C, Borges M, Aires I, Amaral T, Gil C, Cortez J, Ferreira A (2009) 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3, arterial calcifications and cardiovascular risk markers in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24(2):611–618
Drechsler C, Pilz S, Obermayer-Pietsch B, Verduijn M, Tomaschitz A, Krane V, Espe K, Dekker F, Brandenburg V, Marz W, Ritz E, Wanner C (2010) Vitamin D deficiency is associated with sudden cardiac death, combined cardiovascular events, and mortality in haemodialysis patients. Eur Heart J 31(18):2253–2261
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes CKDMBDWG (2009) KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis, evaluation, prevention, and treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD). Kidney Int Suppl (113):S1–S130
Boudville N, Inderjeeth C, Elder GJ, Glendenning P (2010) Association between 25-hydroxyvitamin D, somatic muscle weakness and falls risk in end-stage renal failure. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 73(3):299–304
Bataille S, Landrier JF, Astier J, Giaime P, Sampol J, Sichez H, Ollier J, Gugliotta J, Serveaux M, Cohen J, Darmon P (2016) The "dose-effect" relationship between 25-hydroxyvitamin D and muscle strength in hemodialysis patients favors a normal threshold of 30 ng/mL for plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D. J Ren Nutr 26(1):45–52
Hewitt NA, O'Connor AA, O'Shaughnessy DV, Elder GJ (2013) Effects of cholecalciferol on functional, biochemical, vascular, and quality of life outcomes in hemodialysis patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 8(7):1143–1149
Mori A, Nishino T, Obata Y, Nakazawa M, Hirose M, Yamashita H, Uramatsu T, Shinzato K, Kohno S (2013) The effect of active vitamin D administration on muscle mass in hemodialysis patients. Clin Drug Investig 33(11):837–846
Roubicek T, Bartlova M, Krajickova J, Haluzikova D, Mraz M, Lacinova Z, Kudla M, Teplan V, Haluzik M (2009) Increased production of proinflammatory cytokines in adipose tissue of patients with end-stage renal disease. Nutrition 25(7–8):762–768
Zhang W, He J, Zhang F, Huang C, Wu Y, Han Y, Zhang W, Zhao Y (2013) Prognostic role of C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 in dialysis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Nephrol 26(2):243–253
Bologa RM, Levine DM, Parker TS, Cheigh JS, Serur D, Stenzel KH, Rubin AL (1998) Interleukin-6 predicts hypoalbuminemia, hypocholesterolemia, and mortality in hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 32(1):107–114
Molsted S, Eiken P, Andersen JL, Eidemak I, Harrison AP (2014) Interleukin-6 and vitamin D status during high-intensity resistance training in patients with chronic kidney disease. Biomed Res Int 2014:176190
Booth RA, Hill SA, Don-Wauchope A, Santaguida PL, Oremus M, McKelvie R, Balion C, Brown JA, Ali U, Bustamam A, Sohel N, Raina P (2014) Performance of BNP and NT-proBNP for diagnosis of heart failure in primary care patients: a systematic review. Heart Fail Rev 19(4):439–451
Sivalingam M, Vilar E, Mathavakkannan S, Farrington K (2015) The role of natriuretic peptides in volume assessment and mortality prediction in Haemodialysis patients. BMC Nephrol 16:218
Das SR, Drazner MH, Dries DL, Vega GL, Stanek HG, Abdullah SM, Canham RM, Chung AK, Leonard D, Wians FH Jr, de Lemos JA (2005) Impact of body mass and body composition on circulating levels of natriuretic peptides: results from the Dallas Heart Study. Circulation 112(14):2163–2168
Chen SF, Li YJ, Song HM, Wu P, Zhang XS, Cui CL (2016) Impact of protein nutritional status on plasma BNP in elderly patients. J Nutr Health Aging 20(9):937–943
Anker SD, Chua TP, Ponikowski P, Harrington D, Swan JW, Kox WJ, Poole-Wilson PA, Coats AJ (1997) Hormonal changes and catabolic/anabolic imbalance in chronic heart failure and their importance for cardiac cachexia. Circulation 96(2):526–534
Acknowledgements
This work was partly presented as a poster at the annual meeting of the American Society of Nephrology, Oct 31–Nov 5, 2017, New Orleans, LA, and has been published in an abstract form (J Am Soc Nephrol 28, 2017:723). Part of this work was also accepted as an oral communication during the XIX International Congress on Nutrition and Metabolism in Renal Disease held in Genoa (Italy) on June 29, 2018.
Funding
This work was supported by the China Natural Science Foundation (81570665, 81400745), State Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (81730017), Program for Outstanding Medical Academic Leader (2019LJ03) and Shanghai Science and Technology Committee (17411950700). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QZ, JZ and WZ collected and interpreted the data; QZ and MW analyzed data and prepared figures; BH and MZ helped with data interpretation; QZ wrote and edited the manuscript. JC designed research and wrote the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declared no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee (the ethics committee of Huashan Hospital 2016–193) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11255_2020_2468_MOESM1_ESM.doc
Supplementary Figure 1: Kaplan–Meier curves for non-mortal cardiovascular events according to the presence of high or low biceps muscle strength (A) and in different age groups (B) (DOC 147 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Zhang, J., Zhang, W. et al. Risk factors for decreased upper-limb muscle strength and its impact on survival in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Int Urol Nephrol 52, 1143–1153 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02468-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02468-0