Abstract
Introduction
Erectile dysfunction (ED) was established to be linked to the risk factors of coronary artery disease such as metabolic syndrome, hypertension, diabetes, smoking, obesity and dyslipidemia.
Objective
To study the influence of smoking and obesity on penile hemodynamics in patients with erectile dysfunction.
Patients and methods
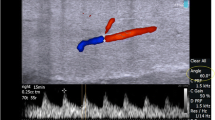
This prospective study was carried out on 130 patients above 40 years and suffering from ED for more than 6 months. Selected patients were divided into four groups: group 1 (nonsmokers/non-obese) N = 36, group 2 (nonsmokers/obese) N = 30, group 3 (smokers/non-obese) N = 34, group 4 (smokers and obese) N = 30. Other risk factors for ED were excluded except dyslipidemia. All patients were subjected to personal history, sexual history, history of medical disorders or operations, evaluation of erectile function using an abridged IIEF-5. Measuring of BMI, fasting lipid profile, blood sugar, TT, prolactin, and PSA was performed. Penile hemodynamics was evaluated using intracavernosal injection of 1 cc Bimix (papaverin + phentolamine) and penile duplex ultrasound measuring the peak systolic velocity (PSV), end diastolic velocity (EDV), resistive index (RI), and cavernosal artery diameter before and after injection.
Results
The mean ages of group 1, group 2, group 3 and group 4 were 50.92 ± 6.52, 55.20 ± 7.18, 50.88 ± 7.66 and 52.30 ± 7.61, respectively, with no statistically significant (p = 0.341). A statistically significant difference observed between mean value of PSV between group 1 and all other groups on both sides and between group 3 and 4. Also, our results recorded a statistically significant difference between mean value of EDV and RI between group 1 and all other groups on both sides. Concerning the change in the cavernosal artery diameter after ICI, there was a significant difference was seen between the following groups 1 and 4, 3 and 4 on both sides and between groups 1 and 2 at right side only. There was a statistically significant difference between the study groups concerning patient’s response to ICI (p value 0.000). A significant negative correlation between BMI and total testosterone was recorded (p = 0.001). Regarding the mean value of testosterone, a significant difference was observed between the different four groups (p = 0.002). And a statistically significant difference was reported between group 1 and group 2 (p = 0.004) and group 2 and group 3 (p = 0.007).
Conclusion
Both smoking and BMI are strong risk factors for ED and affect response to ICI and penile duplex parameters (PSV, EDV, RI). Smoking and BMI together cause more deterioration of penile duplex parameters and response to ICI. The effect of smoking on EDV and RI was more than BMI. The effect of BMI on PSV, response to ICI and testosterone levels was more than smoking.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hatzimouratidis K (2010) Epidemiology of male sexual dysfunction. Am J Mens Health 1(2):103–125
Rosen RC, Cappelleri JC, Smith MD (1999) Development and evaluation of an abridged, 5-item version of the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5) as a diagnostic tool for erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res 11:319–326
Billups KL, Bank AJ, Padma-Nathan H, Katz S, Williams R (2005) Erectile dysfunction is a marker for cardiovascular disease: results of the minority health institute expert advisory panel. J Sex Med 2:40–50
Mirone V, Imbimbo C, Bortolotti A, Di Cintio E, Colli E, Landoni M et al (2002) smoking as risk factor for erectile dysfunction: results from an Italian epidemiological study. Eur Urol 41:294–297
Wannamethee SG, Lowe GD, Shaper AG, Rumley A, Lennon L, Whincup PH (2005) Associations between cigarette smoking, pipe/cigar smoking, and smoking cessation, and haemostatic and inflammatory markers for cardiovascular disease. Eur Heart J 26:1765–1773
Levey HR, Rais-Babrami S, Gbiraldi E et al (2011) Body mass index predicts peak systolic velocity in cavernosal artery. J Sex Med 8(Suppl 1):4–48
Kim SH (2002) Doppler US evaluation of erectile dysfunction. Abdom Imaging 27:578–587
Ioakeimidis N, Vlachopoulos C, Rokkas K (2011) Relationship of asymmetric dimethylarginine with penile Doppler ultrasound parameters in men with vasculogenic erectile dysfunction. Eur Urol 5(9):948–955
Corona G, Mannucci E, Schulman C, Petrone L, Mansani R, Cilotti A et al (2006) Psychobiologic correlates of the metabolic syndrome and associated sexual dysfunction. Eur Urol 50:595–604
Rosen MP, Greenfield AJ, Walker TG, Grant P, Dubrow J, Bettman MA et al (1991) Cigarette smoking: an independent risk factor for atherosclerosis in the hypogastric-cavernous arterial bed of men with arteriogenic impotence. J Urol 145:759–763
Wu C, Zhang H, Gao Y, Tan A, Yang X, Lu Z, Zhang Y, Liao M, Wang M, Mo Z (2012) The association of smoking and erectile dysfunction: results from the Fangchenggang Area Male Health and Examination Survey (FAMHES). J Androl 33:59–65
Godtfredsen NS, Prescott E, Osler M, Vestbo J (2001) Predictors of smoking reduction and cessation in a cohort of Danish moderate and heavy smokers. Prev Med 33:46–52
Nguyen NT, Magno CP, Lane KT, Hinojosa MW, Lane JS (2007) Association of hypertension, diabetes dyslipidemia, and metabolic syndrome with obesity: findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999 to 2004. J Am Coll Surg 207:928–934
Roxo L, Virgolino A, Costa J, Alarcao V (2018) Understanding the relationship between BMI and sexual dysfunction: can DSM-5 shed light into this topic? Rev Int Androl 17:130–137
Jackson G (2007) Vascular risk factors and erectile dysfunction: ‘sexing-up’ the importance of lifestyle changes. Int J Clin Pract 61:1421–1422
Aversa A, Sarteschi LM (2007) The role of penile color-duplex ultrasound for the evaluation of erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med 4:1437–1447
Wiesmann F, Petersen SE, Leeson PM, Francis JM, Robson MD, Wang Q et al (2004) Global impairment of brachial, carotid, and aortic vascular function in young smokers: direct quantification by high resolution magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol 44:2056–2064
Rehill N, Beck CR, Yeo KR, Yeo WW (2006) The effect of chronic tobacco smoking on arterial stiffness. Br J Clin Pharmacol 61:767–773
EL Hanbly S, Abdel-Gaber S, Fathy H, EL-Bayoumi Y, Wald M, Niederberger CS (2004) Erectile dysfunction in smokers: a penile dynamic and vascular study from the Department of Andrology, Mansoura University, Mansoura, Egypt; and the Department of Urology, University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, Illinois. J Androl 25(6):991–995
Glina S, Reichet AC, Leao PP (1988) Impact of cigarette smoking on papaverine-induced erection. J Urol 140:523–524
Purvis K, Brekke I, Christiansen E (1996) Determinants of satisfactory rigidity after ICI with PGE1 in men with erectile failure. Int J Impot Res 8:9–16
McVary KT, Carrier S, Wessells H (2001) Smoking and erectile dysfunction: evidence based analysis. J Urol 166:1624–1632
Zohdy W, Kamal EE, Ibrahim Y (2007) Androgen deficiency and abnormal penile duplex parameters in obese men with erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med 4:797–808
Bacon CG, Mittleman MA, Kawachi I, Giovannucci E, Glasser DB, Rimm EB (2006) A prospective study of risk factors for erectile dysfunction. J Urol 176:217–221
Derby CA, Mohr BA, Goldstein I, Feldman HA, Johannes CB, McKinlay JB (2000) Modifiable risk factors and erectile dysfunction: can lifestlye changes modify risk? Urology 56:302–306
Ahn TY, Park JK, Lee SW, Hong JH, Park NC, Kim JJ et al (2007) Prevalence and risk factors for erectile dysfunction in Korean men: results of an epidemiological study. J Sex Med 4:1269–1276
Mulhall J, Teloken P, Brock G, Kim E (2006) Obesity, dyslipidemias and erectile dysfunction: a report of a subcommittee of the sexual medicine society of North America. J Sex Med 3:778–786
Feldman HA, Johannes CB, Derby CA, Kleinman KP, Mohr BA, Araujo AB (2000) Erectile dysfunction and coronary risk factors: prospective results from the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. Prev Med 30:328–338
Corona G, Mannucci E, Petrone L, Balercia G, Paggi F, Fisher AD et al (2007) NCEP-ATPIII-defined metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and prevalence of hypogonadism in male patients with sexual dysfunction. J Sex Med 4:1038–1045
Kaplan SA, Meehan AG, Shah A (2006) The age-related decrease in testosterone is significantly exacerbated in obese men with the metabolic syndrome. What are the implications for the relatively high incidence of erectile dysfunction observed in these men? J Urol 176:1524–1527
Laaksonen DE, Niskanen L, Punnonen K, Tuomainen TP, Valkonen VP, Salonen JK (2005) The metabolic syndrome and smoking in relation to hypogonadism in middle-aged men: a prospective cohort study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90:712–719
Esposito K, Giugliano F, Di Palo C, Giugliano G, Marfella R, D’Andrea F et al (2004) Effect of lifestyle changes on erectile dysfunction in obese men: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 291:2978–2984
Funding
No funding received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
The ethical committee, Faculty of Medicine, approved our study; Cairo University.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azab, S.S., Salem, A., Ismail, N.N. et al. Penile hemodynamics study in erectile dysfunction men: the influence of smoking obesity on the parameters of penile duplex. Int Urol Nephrol 52, 1015–1025 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02405-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02405-1