Abstract
Objective
Levels of urinary prostatic exosomal protein (PSEP) were detected to evaluate the clinical potential of PSEP as a diagnostic marker of chronic prostatitis (CP).
Materials and methods
The level of urinary PSEP was measured in 412 cases by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit, including 202 controls and 210 CP cases. Of the CP patients, 116 cases met the definition of the USA National Institutes of Health category III (NIH-III), with 60 cases of NIH-IIIA and 56 cases of NIH-IIIB. The ages, body mass indexes (BMI), white blood cell (WBC) levels in expressed prostatic secretions (EPS), lecithin body counts in EPS, urine PSEP levels both before and after prostate massage obtained from the CP patients and NIH-CPSI scores were analyzed.
Results
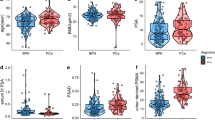
In the diagnosis of CP, the PSEP contents in the urine samples before and after prostate massage manifested a sensitivity of 86.93% vs. 61.06%, and a total coincidence rate of 85.24% vs. 61.06%, respectively. The area under the ROC curve was 0.926 vs. 0.709 for the before and after massage PSEP contents, respectively. Besides, during the follow-up of patients with CP, the improvement in symptoms was not correlated with the level changes of PSEP.
Conclusion
Measurement of PSEP levels for the clinical diagnosis of CP is objective and painless. It could be a novel, simple, and noninvasive method for the diagnosis of CP. However, differences in fluid intake may result in a concentration or dilution of urine, which would ultimately affect the judgment of PSEP results.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Collins MM, Stafford RS, O’Leary MP, Barry MJ (1998) How common is prostatitis? A national survey of physician visits. J Urol 159(4):1224–1228
Clemens JQ, Meenan RT, O’Keeffe Rosetti MC, Kimes T, Calhoun EA (2007) Prevalence of and risk factors for prostatitis: population based assessment using physician assigned diagnoses. J Urol 178(4 Pt 1):1333–1337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2007.05.140
Wang J, Yan D, Liang K, Xu Z (2016) A randomized controlled trial of levofloxacin, terazosin, and combination therapy in patients with category III chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Int Urol Nephrol 48(1):13–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-015-1147-1
McNaughton CM, Pontari MA, O’Leary MP, Calhoun EA, Santanna J, Landis JR, Kusek JW, Litwin MS, Chronic Prostatitis Collaborative Research N (2001) Quality of life is impaired in men with chronic prostatitis: the Chronic Prostatitis Collaborative Research Network. Journal of general internal medicine 16(10):656–662. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1497.2001.01223.x
Nickel JC, Nyberg LM, Hennenfent M (1999) Research guidelines for chronic prostatitis: consensus report from the first National Institutes of Health International Prostatitis Collaborative Network. Urology 54(2):229–233
Mo MQ, Long LL, Xie WL, Chen S, Zhang WH, Luo CQ, Deng LW (2014) Sexual dysfunctions and psychological disorders associated with type IIIa chronic prostatitis: a clinical survey in China. Int Urol Nephrol 46(12):2255–2261. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-014-0810-2
Polackwich AS, Shoskes DA (2016) Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: a review of evaluation and therapy. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 19(2):132–138. https://doi.org/10.1038/pcan.2016.8
Aalberts M, Stout TA, Stoorvogel W (2014) Prostasomes: extracellular vesicles from the prostate. Reproduction 147(1):R1–14. https://doi.org/10.1530/REP-13-0358
Bjartell A, Montironi R, Berney DM, Egevad L (2011) Tumour markers in prostate cancer II: diagnostic and prognostic cellular biomarkers. Acta Oncol 50(Suppl 1):76–84. https://doi.org/10.3109/0284186X.2010.531284
Graddis TJ, McMahan CJ, Tamman J, Page KJ, Trager JB (2011) Prostatic acid phosphatase expression in human tissues. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 4(3):295–306
Cho SY, Choi K, Jeon JH, Kim CW, Shin DM, Lee JB, Lee SE, Kim CS, Park JS, Jeong EM, Jang GY, Song KY, Kim IG (2010) Differential alternative splicing of human transglutaminase 4 in benign prostate hyperplasia and prostate cancer. Exp Mol Med 42(4):310–318. https://doi.org/10.3858/emm.2010.42.4.031
Zeng Y, Zhang J, Chen Y-H, Onco Biomedical Technology Suzhou CO. L (2015) Establishment of ELISA detection method for prostate exosomal protein and its primary evaluation. Prac J med Pham 32(10):885–888
Nopparat J, Zhang J, Lu JP, Chen YH, Zheng D, Neufer PD, Fan JM, Hong H, Boykin C, Lu Q (2015) delta-Catenin, a Wnt/beta-catenin modulator, reveals inducible mutagenesis promoting cancer cell survival adaptation and metabolic reprogramming. Oncogene 34(12):1542–1552. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.89
Pontari MA, Ruggieri MR (2008) Mechanisms in prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. The J Urol 179(5 Suppl):S61–S67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2008.03.139
Lotti F, Corona G, Mondaini N, Maseroli E, Rossi M, Filimberti E, Noci I, Forti G, Maggi M (2014) Seminal, clinical and colour-Doppler ultrasound correlations of prostatitis-like symptoms in males of infertile couples. Andrology 2(1):30–41. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2047-2927.2013.00156.x
Nickel JC (2003) Recommendations for the evaluation of patients with prostatitis. World J Urol 21(2):75–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-003-0328-1
Pons-Rejraji H, Artonne C, Sion B, Brugnon F, Canis M, Janny L, Grizard G (2011) Prostasomes: inhibitors of capacitation and modulators of cellular signalling in human sperm. Int J Androl 34(6 Pt 1):568–580. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2605.2010.01116.x
Stewart AB, Anderson W, Delves G, Lwaleed BA, Birch B, Cooper A (2004) Prostasomes: a role in prostatic disease? BJU Int 94(7):985–989. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2004.05091.x
Minelli A, Ronquist G, Carlsson L, Mearini E, Nilsson O, Larsson A (2005) Antiprostasome antibody titres in benign and malignant prostate disease. Anticancer Res 25(6C):4399–4402
Utleg AG, Yi EC, Xie T, Shannon P, White JT, Goodlett DR, Hood L, Lin B (2003) Proteomic analysis of human prostasomes. Prostate 56(2):150–161. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.10255
Yin L, Tang Y, Pan A, Yang L, Zhu X, Liu Y (2019) The application of IL-10 and TNF-alpha in expressed prostatic secretions and prostatic exosomal protein in urine in the diagnosis of patients with chronic prostatitis. Medicine 98(33):e16848. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000016848
Watanabe T, Inoue M, Sasaki K, Araki M, Uehara S, Monden K, Saika T, Nasu Y, Kumon H, Chancellor MB (2011) Nerve growth factor level in the prostatic fluid of patients with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome is correlated with symptom severity and response to treatment. BJU Int 108(2):248–251. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2010.09716.x
Wei X, Zhang G, Yuan H, Ding X, Li S, Zhang X, Hou J (2011) Detection and quantitation of soluble B7-H3 in expressed prostatic secretions: a novel marker in patients with chronic prostatitis. J Urol 185(2):532–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2010.09.104
Soric T, Selimovic M, Bakovic L, Simurina T, Selthofer R, Dumic J (2017) Clinical and biochemical influence of prostatic stones. Urol Int 98(4):449–455. https://doi.org/10.1159/000455161
Li X, Jiang T, Liu F, Shao X, Xu Y, Sheng W, Sun W (2018) Clinical evaluation of urine prostatic exosomal protein in the diagnosis of chronic prostatitis. Urol Int 100(1):112–118. https://doi.org/10.1159/000479188
Acknowledgements
The presented research was financially supported by the National Science Foundation for Young Scientists (81400757 and 81802827), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31430028, 81630019 and 81870519), Scientific Research Foundation of the Institute for Translational Medicine of Anhui Province (2017ZHYX02), the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province, China (KJ2019A0277) and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (2017A030313800).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CL, SF, LZ and XZ designed this experiment. XF, LZ and MZ performed the research and analyzed the data. XF and MZ wrote the manuscript, and then HH, SF, LZ and CL revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
The research contents and research programs were reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University. (anyiyifuyuanlunshen-kuai-PJ-2019-09-11).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, X., Zhang, M., Zhang, L. et al. The clinical value of the prostatic exosomal protein expression in the diagnosis of chronic prostatitis: a single-center study. Int Urol Nephrol 52, 225–232 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-019-02313-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-019-02313-z