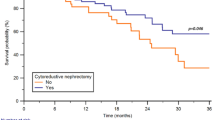
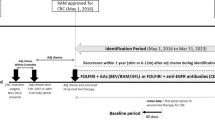
Abstract
Objectives
Treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) has become increasingly more complex over the last several years. Objective 1 is to which treatment option is immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or the combination of immunotherapy with targeted therapy the best for patients? Objective 2 is to study which regimens with the highest chance of cure/durable response and what is the optimal sequence in advanced RCC.
Materials and methods
Between 2016 and 2018, 6 adult patients admitted to our institute with RCC were reviewed. Clinical information, treatment and outcomes were retrieved for further analysis. This applies to all risk groups as determined by the International Metastatic RCC Database Consortium criteria. We have intended to provide the reader with a comprehensive and authoritative review of the broad subject of RCC.
Results
Immunotherapy-based regimens and the functioning of various growth-and survival-promoting kinases, specifically, receptor-associated tyrosine kinases have dramatically changed the treatment landscape of advanced RCC. Recent phase III trials have demonstrated a survival benefit for front-line ipilimumab plus nivolumab therapy, and immune checkpoint inhibition plus anti-vascular endothelial growth factor combination therapy in metastatic clear-cell RCC.
Conclusion
In renal cell carcinoma, rapid and successful drug development has resulted in multiple treatment options, requiring careful decision making for individual patients and have emphasized how newly developed therapies work.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Linehan WM, Pinto PA, Srinivasan R, Merino M, Choyke P, Choyke L et al (2007) Identification of the genes for kidney cancer: opportunity for disease-specific targeted therapeutics. Clin Cancer Res 13:671–679
Linehan WM, Pinto PA, Bratslavsky G, Pfaffenroth E, Merino M, Vocke CD et al (2009) Hereditary kidney cancer: unique opportunity for disease-based therapy. Cancer 115:2252–2261
Nickerson ML, Jaeger E, Shi Y, Durocher JA, Mahurkar S, Zaridze D et al (2008) Improved identification of Von Hippel-Lindau gene alterations in clear cell renal tumors. Clin Cancer Res 14(15):4726–4734
McDermott DF, Atkins MB (2013) Immune therapy for kidney cancer: a second dawn? Semin Oncol 40(4):492–498
Abel EJ, Culp SH, Tannir NM, Matin SF, Tamboli P, Jonasch E et al (2011) Primary tumor response to targeted agents in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol 59(1):10–15
Bex A, van der Veldt AA, Blank C, van den Eertwegh AJ, Boven E, Horenblas S et al (2009) Neoadjuvant sunitinib for surgically complex advanced renal cell cancer of doubtful resectability: initial experience with downsizing to reconsider cytoreductive surgery. World J Urol 27(4):533–539
Bex A, Van der Veldt AA, Blank C, Meijerink MR, Boven E, Haanen JB (2010) Progression of a caval vein thrombus in two patients with primary renal cell carcinoma on pretreatment with sunitinib. Acta Oncol 49(4):520–523
Haas NB, Manola J, Uzzo RG, Flaherty KT, Wood CG, Kane C et al (2016) Adjuvant sunitinib or sorafenib for high-risk, non-metastatic renal-cell carcinoma (ECOG-ACRIN E2805): a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet 387(10032):2008–2016
Ravaud A, Motzer RJ, Pandha HS, George DJ, Pantuck AJ, Patel A et al (2016) Adjuvant sunitinib in high-risk renal-cell carcinoma after nephrectomy. N Engl J Med 375(23):2246–2254
Gross-Goupil M, Kwon TG, Eto M, Ye D, Miyake H, Seo SI et al (2018) Axitinib versus placebo as an adjuvant treatment for renal cell carcinoma: results from the phase III. Randomized ATLAS Trial. Ann Oncol 29(12):2371–2378
Motzer RJ, Haas NB, Donskov F, Gross-Goupil M, Varlamov S, Kopyltsov E et al (2017) Randomized phase III trial of adjuvant pazopanib versus placebo after nephrectomy in patients with localized or locally advanced renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 35(35):3916–3923
Escudier B, Porta C, Schmidinger M, Rioux-Leclercq N, Bex A, Khoo V et al (2016) Renal cell carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 27(suppl 5):v58–v68
Flanigan RC, Salmon SE, Blumenstein BA, Bearman SI, Roy V, McGrath PC (2001) Nephrectomy followed by interferon alfa-2b compared with interferon alfa-2b alone for metastatic renal-cell cancer. N Engl J Med 345(23):1655–1659
Mickisch GH, Garin A, van Poppel H, de Prijck L, Sylvester R (2001) European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) Genitourinary Group. Radical nephrectomy plus interferon-alfa-based immunotherapy compared with interferon alfa alone in metastatic renal- cell carcinoma: a randomised trial. Lancet 358(9286):966–970
Méjean A, Ravaud A, Thezenas S, Colas S, Beauval JB, Bensalah K et al (2018) Sunitinib alone or after nephrectomy in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 379(5):417–427
Bex A, Mulders P, Jewett M, Wagstaff J, van Thienen JV, Blank CU et al (2018) Comparison of immediate vs deferred cytoreductive nephrectomy in patients with synchronous metastatic renal cell carcinoma receiving sunitinib: the SURTIME randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol 5:167–170 (Epub ahead of print)
Heng DY, Xie W, Regan MM, Harshman LC, Bjarnason GA, Vaishampayan UN et al (2013) External validation and comparison with other models of the International Metastatic Renal-Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium prognostic model: a population-based study. Lancet Oncol 14(2):141–148
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Cella D, Reeves J, Hawkins R, Guo J et al (2013) Pazopanib versus sunitinib in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 369(8):722–731
Motzer RJ, Nosov D, Eisen T, Bondarenko I, Lesovoy V, Lipatov O et al (2013) Tivozanib versus sorafenib as initial targeted therapy for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma:results from a phase III trial. J Clin Oncol 31(30):3791–3799
Choueiri TK, Halabi S, Sanford BL, Hahn O, Michaelson MD, Walsh MK et al (2017) Cabozantinib versus sunitinib as initial targeted therapy for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma of poor or intermediate risk: the Alliance A031203 CABOSUN Trial. J Clin Oncol 35(6):591–597
Motzer RJ, Tannir NM, McDermott DF, Arén Frontera O, Melichar B, Choueiri TK et al (2018) Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 378(14):1277–1290
McDermott DF, Lee JL, Szczylik C, Donskov F, Malik J, Alekseev BY et al (2018) Pembrolizumab monotherapy as first-line therapy in advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma: results from cohort A of KEYNOTE-427. J Clin Oncol 36S:ASCO#4500
Gabrilovich DI, Chen HL, Girgis KR, Cunningham HT, Meny GM, Nadaf S et al (1996) Production of vascular endothelial growth factor by human tumors inhibits the functional maturation of dendritic cells. Nat Med 2(10):1096–1103
Oyama T, Ran S, Ishida T, Nadaf S, Kerr L, Carbone DP et al (1998) Vascular endothelial growth factor affects dendritic cell maturation through the inhibition of nuclear factor-kappa B activation in hemopoietic progenitor cells. J Immunol 160(3):1224–1232
Goel S, Duda DG, Xu L, Munn LL, Boucher Y, Fukumura D et al (2011) Normalization of the vasculature for treatment of cancer and other diseases. Physiol Rev 91(3):1071–1121
Motz GT, Santoro SP, Wang LP, Garrabrant T, Lastra RR, Hagemann IS et al (2014) Tumor endothelium FasL establishes a selective immune barrier promoting tolerance in tumors. Nat Med 201420(6):607–615
Hodi FS, Lawrence D, Lezcano C, Wu X, Zhou J, Sasada T et al (2014) Bevacizumab plus ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. Cancer Immunol Res 2(7):632–642
Wallin JJ, Bendell JC, Funke R, Sznol M, Korski K, Jones S et al (2016) Atezolizumab in combination with bevacizumab enhances antigen-specific T-cell migration in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Nat Commun 30(7):12624
Gabrilovich DI, Nagaraj S (2009) Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as regulators of the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 9(3):162–174
Roland CL, Lynn KD, Toombs JE, Dineen SP, Udugamasooriya DG, Brekken RA (2009) Cytokine levels correlate with immune cell infiltration after anti-VEGF therapy in preclinical mouse models of breast cancer. PLoS One 4(11):e7669
Facciabene A, Peng X, Hagemann IS, Balint K, Barchetti A, Wang LP et al (2011) Tumour hypoxia promotes tolerance and angiogenesis via CCL28 and T(reg) cells. Nature 475(7355):226–230
Voron T, Colussi O, Marcheteau E, Pernot S, Nizard M, Pointet AL et al (2015) VEGF-A modulates expression of inhibitory checkpoints on CD8 + T cells in tumors. J Exp Med 212(2):139–148
Motzer R, Powles T, Atkins M, Escudier B, McDermott DF, Suarez C et al (2018) IMmotion151: a randomized phase III study of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab vs sunitinib in untreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 36:578 (Abstract 578)
Motzer RJ, Penkov K, Haanen J, Rini B, Albiges L, Campbell MT et al (2019) Avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 380(12):1103–1115
Rini BI, Plimack ER, Stus V, Gafanov R, Hawkins R, Nosov D et al (2019) Pembrolizumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 380(12):1116–1127
Rini BI, Huseni M, Atkins MB, McDermott DF, Powles TB, Escudier B et al (2018) Molecular correlates differentiate response to atezolizumab (atezo) + bevacizumab (bev) vs sunitinib (sun): results from a Phase III study (IMmotion151) in untreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC). Ann Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdy424.037
Choueiri TK, Escudier B, Powles T, Tannir NM, Mainwaring PN, Rini BI et al (2016) Cabozantinib versus everolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma (METEOR): final results from a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 17:917–927
McKay RR, Kroeger N, Xie W, Lee JL, Knox JJ, Bjarnason GA et al (2014) Impact of bone and liver metastases on patients with renal cell carcinoma treated with targeted therapy. Eur Urol 65(3):577–584
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Glen H, Michaelson MD, Molina A, Eisen T et al (2015) Lenvatinib, everolimus, and the combination in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a randomised, phase 2, open-label, multicentre trial. Lancet Oncol 16(15):1473–1482
Rini BI, Escudier B, Tomczak P, Kaprin A, Szczylik C, Hutson TE et al (2011) Comparative effectiveness of axitinib versus sorafenib in advanced renal cell carcinoma (AXIS): a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet 378:1931–1939
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Tomczak P, Hutson TE, Michaelson MD, Negrier S et al (2013) Axitinib versus sorafenib as second-line treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma: overall survival analysis and updated results from a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 14:552–562
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, McDermott DF, George S, Hammers HJ, Srinivas S et al (2015) Nivolumab versus everolimus in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 373(19):1803–1813
Seastone DJ, Elson P, Garcia JA, Chao ST, Suh JH, Angelov L et al (2014) Clinical outcome of stereotactic radiosurgery for central nervous system metastases from renal cell carcinoma. Clin Genitourin Cancer 12(2):111–116
Tawbi HA, Forsyth PA, Algazi A, Hamid O, Hodi FS, Moschos SJ et al (2018) Combined nivolumab and ipilimumab in melanoma metastatic to the brain. N Engl J Med 379(8):722–730
Marchioni M, Bandini M, Pompe RS, Tian Z, Martel T, Kapoor A et al (2017) Survival of metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients continues to improve over time, even in targeted therapy era. Int Urol Nephrol 49(12):2143–2149
Ravaud A, Oudard S, De Fromont M, Chevreau C, Gravis G, Zanetta S et al (2015) First-line treatment with sunitinib for type 1 and type 2 locally advanced or metastatic papillary renal cell carcinoma: a phase II study (SUPAP) by the French Genitourinary Group (GETUG)†. Ann Oncol 26:1123–1128
Bottaro DP, Rubin JS, Faletto DL, Chan AM, Kmiecik TE, Vande Woude GF et al (1991) Identification of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor as the c-met proto-oncogene product. Science 251:802–804
Dharmawardana PG, Giubellino A, Bottaro DP (2004) Hereditary papillary renal carcinoma type I. Curr Mol Med 4:855–868
Peruzzi B, Bottaro DP (2006) Targeting the c-Met signaling pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 12:3657–3660
Giubellino A, Linehan WM, Bottaro DP (2009) Targeting the Met signaling pathway in renal cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 9:785–793
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cetin, B., Kosar, A. Game of thrones: immunotherapy versus molecular targeted therapy in renal cell cancer scenarios. Int Urol Nephrol 51, 2107–2117 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-019-02264-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-019-02264-5