Abstract
Purpose
The association between Helicobacter pylori (HP) infection and duration of dialysis in dialysis patients is conflicting, this meta-analysis was conducted to elucidate the association between duration of dialysis and HP infection status in dialysis patients, and subgroup study was conducted to explore its influencing factors. Furthermore, our study aims to provide advice on the treatment of dialysis patients.
Methods
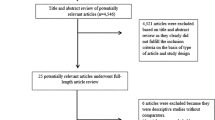
Articles published up to 30 September 2018 were searched from PubMed, Embase, Sinomed, Medline, China Knowledge Resource Integrated Database (CNKI) and Wang fang database. Two researchers independently identified whether studies met the eligibility criteria. The adjusted relative risk (RR) or the weighted mean difference (WMD) and their 95% CI were estimated. I2 was performed to evaluate the statistical heterogeneity. Publication bias was evaluated using Egger’s test and a funnel plot.
Results
Fourteen studies were included involving 2087 dialysis patients, 815 of them were HP positive, 1272 of them were HP negative. Quantitative data and qualitative data were analyzed, respectively. For quantitative data, statistical differences were observed in the association between HP infection and duration of dialysis (P = 0.008), also in the hemodialysis subgroup (P = 0.006). After stratifying by detection methods, differences still existed in groups with different detection methods (P = 0.001, P = 0.033). For qualitative data, there was no statistical difference in the association between HP infection rate and duration of dialysis (P = 0.295). Furthermore, we found that the age was higher in HP positive patients than in HP negative patients (P < 0.001).
Conclusion
Our meta-analysis found that HP infection rate was negatively correlated with accumulative dialysis time, and methods of HP detection did not influence the association between HP infection and accumulative dialysis time. We also found that age was the risk factor of HP infection in dialysis patients. Further studies need to be performed to elucidate the mechanism of the correlation between HP infection and duration of dialysis, to explore which timing period of dialysis is most susceptible to HP infection, then, improve the prognosis of patients with renal diseases.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atich M, Hafez F, Samanch H (2016) A comparison between hybrid therapy and standard triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication in patients with uremia: a randomized clinical trial. Middle East J Dig Dis 6(1):39. https://doi.org/10.15171/mejdd.2016.05
Su-Ping WANG, Ye-Meng CHU, Xiao-Jun WU et al (2015) The role of toll-like receptor 4 in atherosclerosis induced by Helicobacter pylori infection. Chin J Arterioscler 23(8):855–858
Xu Y, Wang Q, Liu Y et al (2016) Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and carotid atherosclerosis in patients with vascular dementia. J Neurol Sci 362:73–77
Sugimoto M, Sakai K, Kita M et al (2009) Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in long-term hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 75:96–103
Chang WC, Jo Y-I, Park H-S et al (2010) Helicobacter pylori eradication with a 7-day low-dose triple therapy in hemodialysis patient. Clin Exp Nephrol 14:469–473. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-010-0319-7
Khedmat H, Ahmadzad-Asl M, Amini M et al (2007) Gastro-duodenal lesions and Helicobacter pylori infection in uremic patients and renal transplant recipients. Transplant Proc 39:1003–1007
Fabian G, Szigeti N, Kovacs T et al (2000) An unusual multiplex cause of severe gastrointestinal bleeding in a hemodialysis patient. Nephrol Dial Transplant 15:1869–1871
Zhou F, Zhong X, Chen J et al (2015) Helicobacter pylori infection associated with type 2 diabetic nephropathy in patients with dyspeptic symptoms. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 110:328–334
Ozgur O, Boyacioglu S, Ozdogan M et al (1997) Helicobacter pylori infection in hemodialysis patients and renal transplant recipients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 12:289–291
Karn W, Charat T, Pitchaphon N et al (2017) Association of Helicobacter pylori with chronic kidney diseases: a meta-analysis. Springer, Berlin
Fumitaka N, Masahiro S, Hiroshi O et al (2004) Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori antibodies in long-term dialysis patients. Nephrology 9:73–76
Rasmi Y, Farshid S, Makhdomi K et al (2012) Effect of duration on hemodialysis on prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transplant 23:489–492
Sugimoto M, Sahara S, Ichikawa H et al (2017) Natural course of Helicobacter pylori infection in Japanese hemodialysis patients. Digestion 95(4):302–309
Fakhrossadat M, Mandana R (2008) Endoscopic findings and Helicobacter pylori in children on long-term hemodialysis. Pak J Biol Sci 11:1840–1843
Yıldız A, Beşışık F, Akkaya V et al (1999) Helicobacter pylori antibodies in hemodialysis patients and renal transplant recipients. Clin Transplant 13:13–16
Neslihan S, Emine K, Salih H et al (1996) Helicobacter pylori antibodies in patients on chronic hemodialysis. Nephron 72:725–726
Nakajima F, Sakaguchi M, Amemoto K et al (2002) Helicobacter pylori in patients receiving long-term dialysis. Am J Nephrol 22:468–472
Lui SL, Wong WM, Suk YN et al (2005) Seroprevalence of Helicobacter pylori in Chinese patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Nephrology 10:21–24
Khazaei MR, Imanieh MH, Al-Hashemi GH (2008) Gastrointestinal evaluation in pediatric kidney transplantation candidates. Iran J Kidney Dis 2(1):40–45
Ibrahiem SA, Abdullah KAH (2012) Gastroduodenal lesions in peritoneal dialysis patients: the role of Helicobacter pylori infection. Nephrol Rev 4:12–17
Ke YJ, Wang Y, Zheng D et al (2015) The correlation between Helicobacter pylori infection and patients with long-term hemodialysis. Chin J Crit Care Med 8:92–95
Gür G, Boyacioglu S, Gül C et al (1999) Impact of Helicobacter pylori infection on serum gastrin in hemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 14(11):2688–2691
Mojgan J, Hamid RS, Jamshid V et al (2010) Association of Helicobacter pylori infection and serum albumin in patients on hemodialysis. Iran J Kidney Dis 4:312–316
Antoniou S, Dimitriadis A, Kliridou M, Pavlitou K, Batzili H, Malaka E (1997) Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori antibodies in CAPD patients. Nephron 75(3):358–359
Wang AY, Ninomiya T, Al-Kahwa A et al (2014) Effect of hemodiafiltration or hemofiltration compared with hemodialysis on mortality and cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Am J Kidney Dis 63(6):968–978
Mohamad RT, Saberi Far M, Soleimani A et al (2013) Evaluation of noninvasive tests for diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection in hemodialysis patients. J Nephropathol 2(4):249–253
Shirazian S, Radhakrishnan J (2010) Gastrointestinal disorders and renal failure: exploring the connection. Nat Rev Nephrol 6(8):480–492
Moriyama T, Matsumoto T, Hirakawa K et al (2010) Helicobacter pylori status and esophagogastroduodenal mucosal lesions in patients with end-stage renal failure on maintenance hemodialysis. J Gastroenterology 45(5):515–522
Gu M, Xiao S, Pan X et al (2013) Helicobacter pylori infection in dialysis patients: a meta-analysis. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2013:1–10
Nakysa H, Mitra M, Elham T et al (2011) Helicobacter pylori infection in pediatric candidates for kidney transplantation. Iran J Kidney Dis 5:124–129
Fatma EM, Abdulah K, Mohamed AW et al (1997) Helicobacter pylori and uremic gastritis: a histopathologic study and a correlation with endoscopic and bacteriologic findings. Am J Nephrol 17:165–171
Azar B, Hamid N (2005) Helicobacter pylori lgG specific antibodies in association with serum albumin in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Pak J Nutr 4:265–269
Fabrizi F, Martin P, Dixit V et al (1999) Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori in chronic hemodialysis patients using the new RIBA H. pylori SIA. Nephrol Dial Transplant 14:1929–1933
Hsu CH, Hu HY, Huang N et al (2016) Early eradication has a lower risk of peptic ulcer bleeding in Helicobacter pylori infected chronic kidney disease patients. Eur J Intern Med 33:112–117
Hagymasi K, Tulassay Z (2014) Helicobacter pylori infection: new pathogenetic and clinical aspects. World J Gastroenterol 20(21):6386–6399
Hwang IR, Kodama T, Kikuchi S et al (2002) Effect of interleukin 1 polymorphisms on gastric mucosal interleukin 1 beta production in Helicobacter pylori infection. Gastroentology 123:1793–1803
Acknowledgements
The authors declare that there exist no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LC designed the study and revised the manuscript, K-JL collected and analyzed the data and wrote first draft of the manuscript. All authors had participated to approve the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, KJ., Chen, L. Association between duration of dialysis and Helicobacter pylori infection in dialysis patients: a meta-analysis. Int Urol Nephrol 51, 1361–1370 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-019-02205-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-019-02205-2