Abstract
Purpose
Urinary kidney injury molecule-1 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 are significance factors in the diagnosis and intervention of diabetic kidney diseases. This study determined levels of these proteins in diabetic patients with varying degrees of kidney disease and assessed their relationship with risk factors associated with diabetic kidney diseases.
Methods
A total of 185 patients with type 2 diabetes were divided into three groups [low risk (n = 47), moderate risk (n = 63), and high risk (n = 75)] based on the severity of diabetic kidney disease according to kidney disease: improving global outcomes guidelines. Both urinary kidney injury molecule-1 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 levels were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Student`s t test, analysis of variance, and Spearman’s correlation were used for statistical analysis.
Results
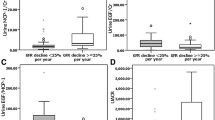
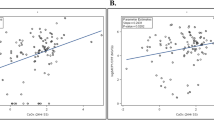
The kidney injury molecule-1-to-creatinine ratio (P = 0.035) and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1-to-creatinine ratio (P < 0.001) increased significantly with the increase in kidney disease severity and varied according to different albuminuria statuses and estimated glomerular-filtration rates. The monocyte chemoattractant protein-1-to-creatinine ratio showed a significant correlation with hemoglobin A1c (P = 0.002) and inflammatory marker levels (interleukin-6, P = 0.005; tumor necrosis factor-α, P < 0.001).
Conclusion
Urinary levels of both kidney injury molecule-1 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 represent distinguishing markers for the evaluation of diabetic kidney disease progression according to the associated degrees of albuminuria or/and the estimated glomerular-filtration rate. In addition, correlations between urinary monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and glycemic and inflammatory marker levels revealed the role of hyperglycemia and chronic inflammation in the pathogenesis of diabetic kidney disease.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
International Diabetes Federation (2017) IDF diabetes atlas, 8th edn. International Diabetes Federation, Brussels. https://www.diabetesatlas.org. Accessed 9 Oct 2018
SCOT Data (2017) Dialysis in the Kindom of Saudi Arabia. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 28:949–957
Bhattacharjee N, Barma S, Konwar N, Dewanjee S, Manna P (2016) Mechanistic insight of diabetic nephropathy and its pharmacotherapeutic targets: an update. Eur J Pharmacol 791:8–24
Ichimura T, Bonventre JV, Bailly V, Wei H, Hession CA, Cate RL, Sanicola M (1998) Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), a putative epithelial cell adhesion molecule containing a novel immunoglobulin domain, is up-regulated in renal cells after injury. J Biol Chem 273:4135–4142
Van Timmeren MM, van den Heuvel MC, Bailly V, Bakker SJ, van Goor H, Stegeman CA (2007) Tubular kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) in human renal disease. J Pathol 212:209–217
Vaidya VS, Waikar SS, Ferguson MA, Collings FB, Sunderland K, Gioules C, Bradwin G, Matsouaka R, Betensky RA, Curhan GC, Bonventre JV (2008) Urinary biomarkers for sensitive and specific detection of acute kidney injury in humans. Clin Transl 1:200–208
Bangstad HJ, Seljeflot I, Berg TJ, Hanssen KF (2009) Renal tubulointerstitial expansion is associated with endothelial dysfunction and inflammation in type 1 diabetes. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 69:138–144
Vaidya VS, Ferguson MA, Bonventre JV (2008) Biomarkers of acute kidney injury. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 48:463–493
Fu WJ, Xiong SL, Fang YG, Wen S, Chen ML, Deng RT, Zheng L, Wang SB, Pen LF, Wang Q (2012) Urinary tubular biomarkers in short-term type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a cross-sectional study. Endocrine 41:82–88
El-Ashmawy NE, El-Zamarany EA, Khedr NF, Abd El-Fattah AI, Eltoukhy SA (2015) Kidney injury molecule-1 (Kim-1): an early biomarker for nephropathy in type II diabetic patients. Into J Diabetes Dev Ctries 35:431–438
Banba N, Nakamura T, Matsumura M, Kuroda H, Hattori Y, Kasai K (2000) Possible relationship of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 with diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 58:684–690
Wang QY, Chen FQ (2009) Clinical significance and different levels of urinary monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 83:215–219
Tashiro K, Koyanagi I, Saitoh A, Shimizu A, Shike T, Ishiguro C, Koizumi M, Funabiki K, Horikoshi S, Shirato I, Tomino Y (2002) Urinary levels of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) and interleukin-8 and renal injuries in patients with type 2 diabetic nephropathy. J Clin Lab Anal 16:1–4
Ibrahim S, Rashed L (2008) Correlation of urinary monocyte chemoattractant protein- 1 with other parameters of renal injury in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Saudi J Kid Dis Transpl 19:911–917
Tilak P, Khashim Z, Kumpatla S, Babu M, Viswanathan V (2010) Clinical significance of urinary Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (uMCP-1) in Indian type 2 diabetic patients at different stages of diabetic nephropathy. Int J Diabetes Mellit 2:15–19
World Medical Association (2013) World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human patients. JAMA 310:2191–2194
Al-Rubeaan K, Siddiqui K, Alghonaim M, Youssef AM, AlNaqeb D (2018) The Saudi Diabetic Kidney Disease study (Saudi-DKD): clinical characteristics and biochemical parameters. Ann Saudi Med 38:46–56
National Kidney Foundation (2012) KDOQI clinical practice guideline for diabetes and CKD: 2012 update. Am J Kidney Dis 60:850–886
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) (2013) Chapter 1: definition and classification of CKD. Kidney Int Suppl 3:19–62
Ketteler M, Block GA, Evenepoel P, Fukagawa M, Herzog CA, McCann L, Moe SM, Shroff R, Tonelli MA, Toussaint ND, Vervloet MG, Leonard MB, (2018) Diagnosis, evaluation, prevention, and treatment of chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder: synopsis of the kidney disease: improving global outcomes 2017 clinical practice guideline update. Ann Intern Med 168:422–430
Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang YL, Castro AF 3rd, Feldman HI, Kusek JW, Eggers P, Van Lente F, Greene T, Coresh J, CKD-EPI (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration) (2009) A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med 150:604–612
The Oxford Centre for Diabetes. Endocrinology and metabolism. Diabetes trial unit. HOMA calculator. https://www.dtu.ox.ac.uk/ToolsSoftware/. Accessed 13 Nov 2016.
Harjutsalo V, Groop PH (2014) Epidemiology and risk factors for diabetic kidney disease. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 21:260–266
Bonventre JV (2009) Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1): a urinary biomarker and much more. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24:3265–3268
Han WK, Bailly V, Abichandani R, Thadhani R, Bonventre JV (2002) Kidney Injury Molecule-1 (KIM-1): a novel biomarker for human renal proximal tubule injury. Kidney Int 62:237–244
van Timmeren MM, Bakker SJ, Vaidya VS, Bailly V, Schuurs TA, Damman J, Stegeman CA, Bonventre JV, van Goor H (2006) Tubular kidney injury molecule-1 in protein-overload nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 29:F456–F464
Kim SS, Song SH, Kim IJ, Yang JY, Lee JG, Kwak IS, Kim YK (2012) Clinical implication of urinary tubular markers in the early stage of nephropathy with type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 97:251–257
Kin Tekce B, Tekce H, Aktas G, Sit M (2014) Evaluation of the urinary kidney injury molecule-1 levels in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Clin Invest Med 37:E377–E383
Ucakturk A, Avci B, Genc G, Ozkaya O, Aydin M (2016) Kidney injury molecule-1 and neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin in normoalbuminuric diabetic children. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 29:145–151
Tesch GH (2008) MCP-1/CCL2: a new diagnostic marker and therapeutic target for progressive renal injury in diabetic nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 294:F697–701
Morii T, Fujita H, Narita T, Shimotomai T, Fujishima H, Yoshioka N, Imai H, Kakei M, Ito S (2003) Association of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 with renal tubular damage in diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Complicat 17:11–15
Gupta S, Gambhir JK, Kalra O, Gautam A, Shukla K, Mehndiratta M, Agarwal S, Shukla R (2013) Association of biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress with the risk of chronic kidney disease in Type 2 diabetes mellitus in North Indian population. J Diabetes Complicat 27:548–552
Shoukry A, Sel-A Bdeer, El-Sokkary RH (2015) Urinary monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and vitamin D-binding protein as biomarkers for early detection of diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mol Cell Biochem 408:25–35
Zoja C, Benigni A, Remuzzi G (2004) Cellular responses to protein overload: key event in renal disease progression. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 13:31–37
Mora C, Navarro JF (2005) The role of inflammation as a pathogenic factor in the development of renal disease in diabetes. Curr Diab Rep 5:399–401
Bian ZM, Elner SG, Yoshida A, Elner VM (2004) Differential involvement of phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt in human RPE MCP-1 and IL-8 expression. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45:1887–1896
Yap HL, Frankel AH, Tam FWK (2017) MCP-1: a potential target for diabetic microvascular complications? Open Urol Nephrol J 5:00171
Ha H, Yu MR, Choi YJ, Kitamura M, Lee HB (2002) Role of high glucose-induced nuclear factor-kappaB activation in monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression by mesangial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:894–902
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to members of the research unit at the University Diabetes Center for their help with patient recruitment and to the staff at the Strategic Center for Diabetes Research, College of Medicine, King Saud University, Saudi Arabia, for performing routine biochemical and biomarker analyses for this study.
Funding
This study was funded by King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology (KACST; Grant for Project No. A-T-34–194).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siddiqui, K., Joy, S.S. & Al-Rubeaan, K. Association of urinary monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) and kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) with risk factors of diabetic kidney disease in type 2 diabetes patients. Int Urol Nephrol 51, 1379–1386 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-019-02201-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-019-02201-6