Abstract
Purpose
The aim of our study was to assess the correlation between serum endocan level and erectile dysfunction (ED).
Methods
A total of 92 patients were reviewed in this study after institutional review board approval. The patients’ characteristics were recorded, including age, body mass index, blood pressure, smoking history, serum creatinine, glucose, lipid profile, total testosterone, and Beck Depression Inventory scores. ED was evaluated with the Sexual Health Inventory for Men (SHIM) questionnaire and classified as severe, moderate, or mild. Scores of > 18 indicate normal erectile function and were recruited for the control group.
Results
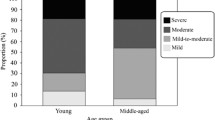
Sixty-three patients with a median age of 56 years in the ED group and 29 patients with a median age of 55 years in the control group were compared. ED was classified as severe in 20, moderate in 25, and mild in 18 patients. A significant difference was determined between the severe ED group and the control group for serum endocan levels (p < 0.001). A significant negative correlation between the SHIM score and endocan levels (rho − 0.65; p < 0.01), age and SHIM score (rho − 0.32; p = 0.04), BMI and SHIM score (rho − 0.25; p = 0.03), and BMI and total testosterone (rho − 0.16; p = 0.04) was determined upon Spearman’s correlation analysis. A positive correlation was also determined between total testosterone and SHIM score (rho 0.50; p = 0.04). Patients’ age (p = 0.037) and serum endocan level (p = 0.029) were determined as significant in the multivariate analysis.
Conclusion
This study demonstrated the presence of an association between plasma endocan levels and ED. Endocan may be used as a new diagnostic marker for the severity of ED.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pohjantahti-Maaroos H, Palomaki A, Hartikainen J (2011) Erectile dysfunction, physical activity and metabolic syndrome: differences in markers of atherosclerosis. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 11:36–44
Smith LJ, Mulhall JP, Deveci S, Monaghan N, Reid MC (2007) Sex after seventy: a pilot study of sexual function in older persons. J Sex Med 4(5):1247–1253
Feldman HA, Goldstein I, Hatzichristou DG, Krane RJ, McKinlay JB (1994) Impotence and its medical and psychosocial correlates: results of the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Urol 151(1):54–61
Ayta IA, McKinlay JB, Krane RJ (1999) The likely worldwide increase in erectile dysfunction between 1995 and 2025 and some possible policy consequences. BJU Int 84(1):50–56
Elzanaty S, Rezanezhad B, Willenheimer R, Borgquist R (2016) Association between erectile function and biomarkers of subclinical atherosclerosis: a study based on middle-aged healty men from the general population. Curr Urol 9(3):119–123
Afsar B, Takir M, Kostek O, Covic A, Kanbay M (2014) Endocan: a new molecule playing a role in the development of hypertension and chronic kidney disease. J Clin Hypertens 16(12):914–916
Yang J, Yang Q, Yu S, Zhang X (2015) Endocan: a new marker for cancer and a target for cancer therapy. Biomed Rep 3(3):279–283
Aitkenhead M, Wang SJ, Nakatsu MN, Mestas J, Heard C, Hughes CC (2002) Identification of endothelial cell genes expressed in an in vitro model of angiogenesis: induction of ESM-1, (beta) ig-h3, and NrCAM. Microvasc Res 63(2):159–171
Arslan B, Onuk O, Hazar I, Aydin M, Cilesiz NC, Eroglu A et al (2017) Prognostic value of endocan in prostate cancer: clinicopathologic association between serum endocan levels and biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectmy. Tumori 103(2):204–208
Scherpereel A, Depontieu F, Grigoriu B, Cavestri B, Tsicopoulos A, Gentina T et al (2006) Endocan, a new endothelial marker in human sepsis. Crit Care Med 34(2):532–537
Roumeguere T, Van Antwerpen P, Fathi H, Rousseau A, Vanhamme L, Franck T et al (2017) Relationship between oxidative stres and erectile function. Free Radic Res 51(11–12):924–931
Nguyen HMT, Gabrielson AT, Hellstrom WJG (2017) Erectile dysfunction in young men-a review of the prevalence and risk factors. Sex Med Rev 5(4):508–520
Sarrazin S, Adam E, Lyon M, Depontieu F, Motte V, Landolfi C et al (2006) Endocan or endothelial cell specific molecule-1 (ESM-1): a potential novel endothelial cell marker and a new target for cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1765(1):25–37
Balta S, Mikhailidis DP, Demirkol S, Ozturk C, Kurtoglu E, Demir M et al (2014) Endocan-a novel inflammatory indicator in newly diagnosed patients with hypertension:a pilot study. Angiology 65(9):773–777
Kose M, Emet S, Akpinar TS, Kocaaga M, Çakmak R, Akarsu M et al (2014) Serum endocan level and the severity of coronary artery disease: a pilot study. Angiology 66(8):727–731
Karabakan M, Bozkurt A, Akdemir S, Gunay M, Keskin E (2017) Significance of serum endothelial cell specific molecule-1 (Endocan) level in patients with erectile dysfunction: a pilot study. Int J Impot Res 29(4):175–178
Akarsu M, Atalay HA, Canat L, Ozcan M, Arman Y, Aydın S et al (2018) Endocan is markedly overexpressed in severe erectile dysfunction. Andrologia. https://doi.org/10.1111/and.12912
Komarova YA, Mehta D, Malik AB (2007) Dual regulation of endothelial junctional permeability. Sci STKE 412:re8
Finigan JH, Dudek SM, Singleton PA, Chiang ET, Jacobson JR, Camp SM et al (2005) Activated protein C mediates novel lung endothelial barrier enhancement: role of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor transactivation. J Biol Chem 280(17):17286–17293
McLaughlin JN, Shen L, Holinstat M, Brooks JD, Dibenedetto E, Hamm HE (2005) Functional selectivity of G protein signaling by agonist peptides and thrombin fort he protease-activated receptor-1. J Biol Chem 280(26):25048–25059
Lee W, Ku SK, Kim SW, Bae JS (2014) Endocan elicits severe vascular inflammatory responses in vitro and vivo. J Cell Physiol 229(5):620–630
Regieli JJ, Jukema JW, Doevendans PA, Zwinderman AH, Kastelein JJ, Grobbee DE et al (2009) Paraoxonase variants relate to 10-year risk in coronary artery disease: impact of a high-density lipoprotein-bound antioxidant in secondary prevention. J Am Coll Cardiol 54(14):1238–1245
Menon P, Kocher ON, Aird WC (2011) Endothelial cell specific molecule-1 (ESM-1), a novel secreted proteoglycan stimulates vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. Circulation 124:A15455
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Onuk, Ö., Arslan, B., Gezmis, T.C. et al. Is the plasma endocan level a reliable predictor for the severity of erectile dysfunction?. Int Urol Nephrol 50, 1577–1582 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-018-1946-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-018-1946-2