Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of the study was to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of core biopsy in small renal masses ≤ 4 cm in response to the rising prevalence of renal masses.
Methods
Data from 129 consecutive patients who underwent biopsies of solid renal masses of ≤ 4 cm were prospectively collected between September 2014 and January 2017. In cases with inconclusive biopsies, a repeat biopsy was recommended. Histology from surgical specimens was used as gold standard to evaluate the accuracy of renal biopsies.
Results
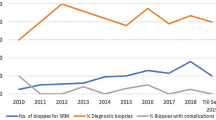
The initial biopsies revealed malignancy in 77 patients (59.7%) and benign histology in 35 patients (27.1%), whereas 17 (13.2%) were inconclusive. Fifty-six patients with malignant histology underwent either partial or radical nephrectomy according to the physicians’ recommendation, while two patients with benign histology requested surgery. In all cases, the biopsy diagnosis was confirmed upon final histopathology. Of the inconclusive cases, six underwent repeat biopsies all with benign histology. Further, three patients opted for immediate partial nephrectomy with benign oncocytoma in two and renal cell carcinoma in the third. The remaining eight patients opted for follow-up CT scans with no sign of progression with a minimum of 6-month follow-up. No biopsy related complications were reported in the first 30 days after RTB. Overall, the treatment strategy changed in 45 of 129 (35%) patients due to biopsy results. This was either due to benign findings or due to the discovery of non-renal cell cancers.
Conclusion
Core needle biopsies of solid renal masses ≤ 4 cm have excellent accuracy and may be used to select the correct treatment. Importantly, they may serve to prevent overtreatment of benign tumors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chow WH, Devesa SS, Warren JL et al (1999) Rising incidence of renal cell cancer in the United States. JAMA 281:1628–1631
Hollingsworth JM, Miller DC, Daignault S et al (2006) Rising incidence of small renal masses: a need to reassess treatment effect. J Natl Cancer Inst 98:1331–1334
Pierorazio PM, Hyams ES, Tsai S et al (2013) Multiphasic enhancement patterns of small renal masses (≤ 4 cm) on preoperative computed tomography: utility for distinguishing subtypes of renal cell carcinoma, angiomyolipoma, and oncocytoma. Urology 81:1265–1271
Israel GM, Hindman N, Bosniak MA (2004) Evaluation of cystic renal masses: comparison of CT and MR imaging by using the Bosniak classification system. Radiology 231:365–371
Gerst S, Hann LE, Li D et al (2011) Evaluation of renal masses with contrast-enhanced ultrasound: initial experience. AJR Am J Roentgenol 197:897–906
Lindkvist Pedersen C, Winck-Flyvholm L, Dahl C et al (2014) High rate of benign histology in radiologically suspect renal lesions. Dan Med J 61:A4932
Ljungberg B, Bensalah K, Canfield S et al (2015) EAU Guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: 2014 update. Eur Urol 67:913–924
Schemper M, Smith TL (1996) A note on quantifying follow-up in studies of failure time. Control Clin Trials 17:343–346
Wang X, Lv Y, Xu Z et al (2018) Accuracy and safety of ultrasound-guided percutaneous needle core biopsy of renal masses: a single center experience in China. Medicine 97:e0178
Schieda N, Al-Subhi M, Flood TA et al (2014) Diagnostic accuracy of segmental enhancement inversion for the diagnosis of renal oncocytoma using biphasic computed tomography (CT) and multiphase contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Eur Radiol 24:2787–2794
Woo S, Suh CH, Cho JY et al: Diagnostic performance of CT for diagnosis of fat-poor angiomyolipoma in patients with renal masses: a systematic review and meta-analysis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2017: W1–W11
Richard PO, Jewett MAS, Bhatt JR et al (2015) Renal tumor biopsy for small renal masses: a single-center 13-year experience. Eur Urol 68:1007–1013
Richard PO, Jewett MAS, Tanguay S et al (2017) Safety, reliability and accuracy of small renal tumour biopsies: results from a multi-institution registry. BJU Int 119:543–549
Herts BR (2000) Imaging guided biopsies of renal masses. Curr Opin Urol 10:105–109
Rybicki FJ, Shu KM, Cibas ES et al (2003) Percutaneous biopsy of renal masses: sensitivity and negative predictive value stratified by clinical setting and size of masses. AJR Am J Roentgenol 180:1281–1287
Leveridge MJ, Finelli A, Kachura JR et al (2011) Outcomes of small renal mass needle core biopsy, nondiagnostic percutaneous biopsy, and the role of repeat biopsy. Eur Urol 60:578–584
Lebret T, Poulain JE, Molinie V et al (2007) Percutaneous core biopsy for renal masses: indications, accuracy and results. J Urol 178:1184–1188
Neuzillet Y, Lechevallier E, Andre M et al (2004) Accuracy and clinical role of fine needle percutaneous biopsy with computerized tomography guidance of small (less than 4.0 cm) renal masses. J Urol 171:1802–1805
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The present study was carried out with the approval of the Danish Patient Safety Authority; Case No. 3-3013-1567/1/.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azawi, N.H., Tolouee, S.A., Madsen, M. et al. Core needle biopsy clarify the histology of the small renal masses and may prevent overtreatment. Int Urol Nephrol 50, 1205–1209 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-018-1885-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-018-1885-y