Abstract
Background
Although there were studies to investigate the risk factors for acute kidney injury (AKI) after surgery, most of them focused on one specific type of surgeries. The risk factors for postoperative AKI in patients undergoing all surgeries in intensive care units (ICU) have not been reported.
Methods
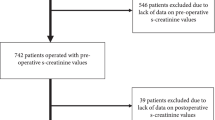
Data from 1731 patients undergoing surgery in 30 ICUs of 28 tertiary hospitals in Beijing from March to August 2012 were prospectively collected. AKI was defined and staged by the KDIGO criteria. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to assess independent risk factors for postoperative AKI.
Results
Postoperative AKI occurred in 44.8% of patients (stage 1 54.8%; stage 2 21.9%, stage 3 23.3%). Cardiovascular surgery was identified as an independent factor for postoperative AKI as well as emergency surgery [odds ratio (OR) 1.403], nephrotoxic drugs (OR 1.303), APACHE II score (OR 1.055), SOFA score (OR 1.115), duration for positive fluid balance (OR 1.165), use of diuretics (OR 2.293), sepsis (OR 1.501), and CKD (OR 4.517). AKI stage 3 versus stages 1–2 was associated with higher mortality in ICU, hospital, and 28-day follow-up after cardiovascular, abdominal, limb, and chest surgeries, while this was not observed after neurosurgery or other surgeries.
Conclusion
Risk factors for AKI in ICU patients after different types of surgery were identified. This might be the first step to reduce the high incidence of AKI after surgery. The presence of AKI in ICU patients was associated with higher mortality after most types of surgery, but not after neurosurgery.
Trial registration
ChiCTR-ONC-11001875.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AKI:
-
Acute kidney injury
- ICU:
-
Intensive care unit
- RRT:
-
Renal replacement therapy
- KDIGO:
-
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes
- SCr:
-
Serum creatinine
- GFR:
-
Glomerular filtration rate
- MDRD:
-
Modification of diet in renal disease
- ACCP/SCCM:
-
American College of Chest Physicians and the Society of Critical Care Medicine
- ICD:
-
International classification of diseases
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- CKD:
-
Chronic kidney disease
- DIC:
-
Disseminated intravascular coagulation
- APACHE:
-
Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation
- SOFA:
-
Sequential Organ Failure Assessment
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- IQR:
-
Interquartile range
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- NYHA:
-
New York Heart Association
- ENT:
-
Ears, nose, and throat
- MAP:
-
Mean arterial pressure
- CHF:
-
Congestive heart failure
- MODS:
-
Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome
References
Grams ME, Sang Y, Coresh J, Ballew S, Matsushita K, Molnar MZ, Szabo Z, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kovesdy CP (2016) Acute kidney injury after major surgery: a retrospective analysis of veterans health administration data. Am J Kidney Dis 67:872–880
Thiele RH, Isbell JM, Rosner MH (2015) AKI associated with cardiac surgery. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 10:500–514
Englberger L, Suri RM, Connolly HM, Li Z, Abel MD, Greason KL, Dearani JA, Schaff HV (2013) Increased risk of acute kidney injury in patients undergoing tricuspid valve surgery. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 43:993–999
Hobson C, Ozrazgatbaslanti T, Kuxhausen A, Thottakkara P, Efron PA, Moore FA, Moldawer LL, Segal MS, Bihorac A (2015) Cost and mortality associated with postoperative acute kidney injury. Ann Surg 261:1207–1214
Petäjä L, Vaara S, Liuhanen S, Suojaranta-Ylinen R, Mildh L, Nisula S, Korhonen AM, Kaukonen KM, Salmenperä M, Pettilä V (2016) Acute Kidney Injury After Cardiac Surgery by Complete KDIGO Criteria Predicts Increased Mortality. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 31:827–836
Deng Y, Yuan J, Chi R, Ye H, Zhou D, Wang S, Mai C, Nie Z, Wang L, Zhai Y (2017) The incidence, risk factors and outcomes of postoperative acute kidney injury in neurosurgical critically III patients. Sci Rep 7:4245
Romagnoli S, Zagli G, Tuccinardi G, Tofani L, Chelazzi C, Villa G, Cianchi F, Coratti A, Gaudio ARD, Ricci Z (2016) Postoperative acute kidney injury in high-risk patients undergoing major abdominal surgery. J Crit Care 35:120–125
Saydy N, Mazine A, Stevens LM, Jeamart H, Demers P, Pagé P, Lamarche Y, Elhamamsy I (2017) Differences and similarities in risk factors for postoperative acute kidney injury between younger and older adults undergoing cardiac surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 155:256–265
Tang X, Chen D, Yu S, Yang L, Mei C (2017) Acute kidney injury burden in different clinical units: data from nationwide survey in China. PLoS ONE 12:e0171202
Kellum JA, Lameire N, Group KAGW (2013) Diagnosis, evaluation, and management of acute kidney injury: a KDIGO summary (Part 1). Crit Care 17:204
Glodowski SD, Wagener G (2015) New insights into the mechanisms of acute kidney injury in the intensive care unit. J Clin Anesth 27:175–180
Ma YC, Zuo L, Chen JH, Luo Q, Yu XQ, Li Y, Xu JS, Huang SM, Wang LN, Huang W (2006) Modified glomerular filtration rate estimating equation for Chinese patients with chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:2937–2944
Goolsby MJ (2003) National kidney foundation guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Ann Intern Med 139:137–147
Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra FB, Dellinger RP, Fein AM, Knaus WA, Schein RMH, Sibbald WJ (1992) Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. Chest 101:1644–1655
Knaus WA, Draper EA, Wagner DP, Zimmerman JE (1985) APACHE II: a severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med 13:818–829
Lee JH, Hwang SY, Kim HR, Kim YW, Kang MJ, Cho KW, Lee DW, Kim YH (2016) Effectiveness of the sequential organ failure assessment, acute physiology and chronic health evaluation II, and simplified acute physiology score II prognostic scoring systems in paraquat-poisoned patients in the intensive care unit. Hum Exp Toxicol 36:431–437
Vincent JL, Moreno R, Takala J, Willatts S, Mendonça AD, Bruining H, Reinhart CK, Suter PM, Thijs LG (1996) The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. Intensive Care Med 22:707–710
Gameiro J, Neves JB, Rodrigues N, Bekerman C, Melo MJ, Pereira M, Teixeira C, Mendes I, Jorge S, Rosa R (2016) Acute kidney injury, long-term renal function and mortality in patients undergoing major abdominal surgery: a cohort analysis. Clin Kidney J 9:192–200
Teixeira C, Rosa R, Rodrigues N, Mendes I, Peixoto L, Dias S, Melo MJ, Pereira M, Bicha CH, Lopes JA (2014) Acute kidney injury after major abdominal surgery: a retrospective cohort analysis. Crit Care Res Pract 2014:132175
Jöbsis JJ, Alabbas A, Milner R, Reilly C, Mulpuri K, Mammen C (2017) Acute kidney injury following spinal instrumentation surgery in children. World J Nephrol 6:79–85
Yu P, Wang W, Wang J, Li Y, Feng D (2017) Incidence and risk factors of in-hospital mortality from AKI after non-cardiovascular operation: a nationwide survey in China. Sci Rep 7:13953
Kolli H, Rajagopalam S, Patel N, Ranjan R, Venuto R, Lohr J, Arora P (2010) Mild acute kidney injury is associated with increased mortality after cardiac surgery in patients with eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m(2). Ren Fail 32:1066–1072
Elmistekawy E, Mcdonald B, Hudson C, Ruel M, Mesana T, Chan V, Boodhwani M (2014) Clinical impact of mild acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery. Ann Thorac Surg 98:815–822
Biteker M, Dayan Aİ, Tekkeşin Aİ, Can MM, Taycı i, İlhan E, Şahin G (2014) Incidence, risk factors, and outcomes of perioperative acute kidney injury in noncardiac and nonvascular surgery. Am J Surg 207:53–59
Abelha FJ, Botelho M, Fernandes V, Barros H (2009) Determinants of postoperative acute kidney injury. Crit Care 13:R79
Kheterpal S, Tremper KK, Heung M, Rosenberg AL, Englesbe M, Shanks AM Jr, Campbell DA (2009) Development and validation of an acute kidney injury risk index for patients undergoing general surgery: results from a national data set. Anesthesiology 110:505–515
Boubacar Ba EH, Leye PA, Traoré MM, Ndiaye PI, Gaye I, Bah MD, Fall ML, Diouf E (2017) Intra-anesthetic arterial hypotension in elderly patients during emergency surgery: what are the risk factors? Pan Afr Med J 26:242
Nielson E, Hennrikus E, Lehman E, Mets B (2014) Angiotensin axis blockade, hypotension, and acute kidney injury in elective major orthopedic surgery. J Hosp Med 9:283–288
Pankhurst T, Mani D, Ray D, Jham S, Borrows R, Coleman JJ, Rosser D, Ball S (2014) Acute kidney injury following unselected emergency admission: role of the inflammatory response, medication and co-morbidity. Nephron Clin Pract 126:81–89
Xu JR, Zhuang YM, Liu L, Shen B, Wang YM, Luo Z, Teng J, Wang CS, Ding XQ (2017) Reversible preoperative renal dysfunction does not add to the risk of postoperative acute kidney injury after cardiac valve surgery. Ther Clin Risk Manag 13:1499–1505
Nisula S, Kaukonen KM, Vaara ST, Korhonen AM, Poukkanen M, Karlsson S, Haapio M, Inkinen O, Parviainen I, Suojaranta-Ylinen R (2013) Incidence, risk factors and 90-day mortality of patients with acute kidney injury in Finnish intensive care units: the FINNAKI study. Intensive Care Med 39:420–428
Huang TM, Wu VC, Young GH, Lin YF, Shiao CC, Wu PC, Li WY, Yu HY, Hu FC, Lin JW (2016) Preoperative proteinuria predicts adverse renal outcomes after coronary artery bypass grafting. J Am Soc Nephrol 22:156–163
Ding LH, Liu D, Xu M, Wu M, Liu H, Tang RN, Ma KL, Chen PS, Liu BC (2015) TLR2-MyD88-NF-κB pathway is involved in tubulointerstitial inflammation caused by proteinuria. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 69:114–120
Dreischulte T, Morales DR, Bell S, Guthrie B (2015) Combined use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with diuretics and/or renin-angiotensin system inhibitors in the community increases the risk of acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 88:396–403
Coleman A, Chai MO (2014) Development of acute kidney injury following a course of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Mag Online Library 6:126–132
Lin SY, Tang SC, Tsai LK, Yeh SJ, Shen LJ, Wu FL, Jeng JS (2015) Incidence and risk factors for acute kidney injury following mannitol infusion in patients with acute stroke: a retrospective cohort study. Medicine 94:e2032
Andreucci M, Faga T, Pisani A, Sabbatini M, Michael A (2014) Acute kidney injury by radiographic contrast media: pathogenesis and prevention. Biomed Res Int 2014:362725
Wu X, Zhang W, Ren H, Chen X, Xie J, Chen N (2014) Diuretics associated acute kidney injury: clinical and pathological analysis. Ren Fail 36:1051–1055
Krzych ŁJ, Czempik P (2016) Loop Diuretics and Mortality in Patients with Acute Kidney Injury. In: Landoni G, Pisano A, Zangrillo A, Bellomo R (eds) Reducing mortality in acute kidney injury. Springer, Cham, pp 175–184
White LE, Hassoun HT, Bihorac A, Moore LJ, Sailors RM, Mckinley BA, Valdivia A, Moore FA (2013) Acute kidney injury is surprisingly common and a powerful predictor of mortality in surgical sepsis. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 75:432–438
Seely KA, Holthoff JH, Burns ST, Wang Z, Thakali KM, Gokden N, Rhee SW, Mayeux PR (2011) Hemodynamic changes in the kidney in a pediatric rat model of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 301:F209–F217
Xu C, Chang A, Hack BK, Eadon MT, Alper SL, Cunningham PN (2014) TNF-mediated damage to glomerular endothelium is an important determinant of acute kidney injury in sepsis. Kidney Int 85:72–81
Gomez H, Ince C, Backer DD, Pickkers P, Payen D, Hotchkiss J, Kellum JA (2014) A unified theory of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury: inflammation, microcirculatory dysfunction, bioenergetics and the tubular cell adaptation to injury. Shock 41:3–11
Salahuddin N, Sammani M, Hamdan A, Joseph M, Alnemary Y, Alquaiz R, Maghrabi K (2015) Positive fluid balance is an independent risk factor for acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: results of a prospective, cross-sectional study. Crit Care 19:1–201
de Oliveira FS, Freitas FG, Ferreira EM, De CI, Bafi AT, de Azevedo LC, Machado FR (2015) Positive fluid balance as a prognostic factor for mortality and acute kidney injury in severe sepsis and septic shock. J Crit Care 30:97–101
Moore E, Tobin A, Reid D, Santamaria J, Paul E, Bellomo R (2015) The impact of fluid balance on the detection, classification and outcome of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 29:1229–1235
Bellomo R, Kellum JA, Ronco C (2007) Defining and classifying acute renal failure: from advocacy to consensus and validation of the RIFLE criteria. Intensive Care Med 33:409–413
Reddy SLC, Grayson AD, Griffiths EM, Pullan DM, Rashid A (2007) Logistic risk model for prolonged ventilation after adult cardiac surgery. Ann Thorac Surg 84:528–536
Koyner JL, Murray PT (2008) Mechanical ventilation and lung-kidney interactions. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 3:562–570
Park M, Coca SG, Nigwekar SU, Garg AX, Garwood S, Parikh CR (2010) Prevention and treatment of acute kidney injury in patients undergoing cardiac surgery: a systematic review. Am J Nephrol 31:408–418
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by a grant from the Beijing Municipal Science & Technology Commission, a government fund used to improve healthcare quality (No. D101100050010058). It offered financial support for data collection. Also, in the final revision stage of the essay, I would like to thank Yanling Hu who added a lot of valuable suggestions and guidance.
Funding
This study was funded by a grant from the Beijing Municipal Science & Technology Commission, a government fund used to improve healthcare quality (No. D101100050010058).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Author contribution
YZ designed and carried out the study, performed the statistical analysis, and drafted the manuscript. LJ was involved in design and in acquisition of data and helped to revise the manuscript critically for important content. WB checked the whole data. The Beijing Acute Kidney Injury Trial (BAKIT) Workgroup participated in acquisition and interpretation of data. XX conceived of the study, participated in its design, and helped to revise manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Availability of data and material
The datasets generated during the current study are available in the Beijing Acute Kidney Injury Trial (BAKIT) workgroup repository.
Consent publication
All individual participants included in the study consent for publication.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Jiang, L., Wang, B. et al. Epidemiological characteristics of and risk factors for patients with postoperative acute kidney injury: a multicenter prospective study in 30 Chinese intensive care units. Int Urol Nephrol 50, 1319–1328 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-018-1828-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-018-1828-7