Abstract
Purpose
Segmental bioimpedance analysis (BIA) can identify fluid volume changes in the arms of patients on hemodialysis (HD) after vascular access surgery. We investigated whether the difference in fluid volumes between the arms of the patients using segmental BIA is associated with vascular access outcome.
Methods
Body composition measurements were taken for 127 patients on HD with segmental, multi-frequency BIA equipment (InBody 1.0, Biospace Co. Ltd, Seoul, Korea). The difference in fluid volume between the arms of the patients was calculated from the fluid volume of the arm with the vascular access minus that of the other. The primary outcome was the loss of vascular access patency within 3 months of BIA measurement.
Results
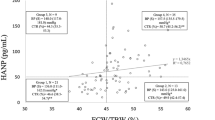
The median absolute and relative inter-arm fluid volume differences were 150 ml [interquartile range (IQR) 90–250 ml] and 9.6% (IQR 4.9–14.4%), respectively. Within 3 months of BIA measurement, 38 patients (30.0%) experienced vascular access failure. When the patients were divided into three groups based on the tertiles of relative inter-arm fluid volume differences (lowest tertile: < 6.8%; middle tertile: 6.8–12.7%; highest tertile: > 12.7%), greater difference in relative inter-arm fluid volume differences was associated with higher vascular access failure rates (14 vs. 28 vs. 48%, p value for trend across tertiles = 0.003).
Conclusions
We conclude that segmental BIA may be used as a tool that can predict vascular access failure in patients on HD by calculating the relative difference in fluid volume between the arms of the patients with and without vascular access.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kassam H, Sun Y, Adeniyi M, Agaba EI, Martinez M, Servilla KS, Raj DS, Murata GH, Tzamaloukas AH (2011) Hospitalizations before and after initiation of chronic hemodialysis. Hemodial Int 15(3):341–349
Lok CE, Foley R (2013) Vascular access morbidity and mortality: trends of the last decade. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 8(7):1213–1219
Viecelli AK, Mori TA, Roy-Chaudhury P, Polkinghorne KR, Hawley CM, Johnson DW, Pascoe EM, Irish AB (2017) The pathogenesis of hemodialysis vascular access failure and systemic therapies for its prevention: optimism unfulfilled. Semin Dial Nov 26 [epub ahead of print]
NKF, KDOQI (2006) 2006 Update vascular access. Guideline 4: detection of access dysfunction: monitoring, surveillance, and diagnostic testing. Am J Kidney Dis 48(1):S176–S247
Leivaditis K, Panagoutsos S, Roumeliotis A, Liakopoulos V, Vargemezis V (2014) Vascular access for hemodialysis: postoperative evaluation and function monitoring. Int Urol Nephrol 46(2):403–409
Polkinghorne KR, Lau KK, Saunder A, Atkins RC, Kerr PG (2006) Does monthly native arteriovenous fistula blood-flow surveillance detect significant stenosis—a randomized controlled trial. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21(9):2498–2506
Ram SJ, Nassar R, Work J, Abreo K, Dossabhoy NR, Paulson WD (2008) Risk of hemodialysis graft thrombosis: analysis of monthly flow surveillance. Am J Kidney Dis 52(5):930–938
Sergi G, Bussolotto M, Perini P, Calliari I, Giantin V, Ceccon A, Scanferla F, Bressan M, Moschini G, Enzi G (1994) Accuracy of bioelectrical impedance analysis in estimation of extracellular space in healthy subjects and in fluid retention states. Ann Nutr Metab 38(3):158–165
Frankenfield DC, Cooney RN, Smith JS, Rowe WA (1999) Bioelectrical impedance plethysmographic analysis of body composition in critically injured and healthy subjects. Am J Clin Nutr 69(3):426–431
Barbosa-Silva MC, Barros AJ, Wang J, Heymsfield SB, Pierson RN Jr (2005) Bioelectrical impedance analysis: population reference values for phase angle by age and sex. Am J Clin Nutr 82(1):49–52
Basile C, Vernaglione L, Di Iorio B, Bellizzi V, Chimienti D, Lomonte C, Rubino A, D’Ambrosio N (2007) Development and validation of bioimpedance analysis prediction equations for dry weight in hemodialysis patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2(4):675–680
Davies SJ, Davenport A (2014) The role of bioimpedance and biomarkers in helping to aid clinical decision-making of volume assessments in dialysis patients. Kidney Int 86(3):489–496
Antlanger M, Hecking M, Haidinger M, Werzowa J, Kovarik JJ, Paul G, Eigner M, Bonderman D, Hörl WH, Säemann MD (2013) Fluid overload in hemodialysis patients: a cross-sectional study to determine its association with cardiac biomarkers and nutritional status. BMC Nephrol 2(14):266
Rosenberger J, Kissova V, Majernikova M, Straussova Z, Boldizsar J (2014) Body composition monitor assessing malnutrition in the hemodialysis population independently predicts mortality. J Ren Nutr 24(3):172–176
Woodrow G, Oldroyd B, Smith MA, Turney JH (1997) The effect of arteriovenous fistulae in haemodialysis patients on whole body and segmental bioelectrical impedance. Nephrol Dial Transplant 12(3):524–527
Park J, Yang WS, Kim SB, Park SK, Lee SK, Park JS, Chang JW (2009) Usefulness of segmental bioimpedance ratio to determine dry body weight in new hemodialysis patients: a pilot study. Am J Nephrol 29(1):25–30
Ling CH, de Craen AJ, Slagboom PE, Gunn DA, Stokkel MP, Westendorp RG, Maier AB (2011) Accuracy of direct segmental multi-frequency bioimpedance analysis in the assessment of total body and segmental body composition in middle-aged adult population. Clin Nutr 30(5):610–615
Zhu F, Schneditz D, Wang E, Martin K, Morris AT, Levin NW (1998) Validation of changes in extracellular volume measured during hemodialysis using a segmental bioimpedance technique. ASAIO J 44(5):M541–M545
Zhu F, Schneditz D, Levin NW (1999) Sum of segmental bioimpedance analysis during ultrafiltration and hemodialysis reduces sensitivity to changes in body position. Kidney Int 56(2):692–699
Codognotto M, Piazza M, Frigatti P, Piccoli A (2008) Influence of localized edema on whole-body and segmental bioelectrical impedance. Nutrition 24(6):569–574
Schoeller DA, Alon A, Manekas D, Mixson LA, Lasseter KC, Noonan GP, Bolognese JA, Heymsfield SB, Beals CR, Nunes I (2012) Segmental bioimpedance for measuring amlodipine-induced pedal edema: a placebo-controlled study. Clin Ther 34(3):580–592
Suehiro K, Morikage N, Yamashita O, Harada T, Ueda K, Samura M, Tanaka Y, Takeuchi Y, Nakamura K, Hamano K (2016) Distribution of extracellular fluid in legs with venous edema and lymphedema. Lymphat Res Biol 14(3):156–161
Nescolarde L, Yanguas J, Lukaski H, Alomar X, Rosell-Ferrer J, Rodas G (2013) Localized bioimpedance to assess muscle injury. Physiol Meas 34(2):237–245
Kenworthy P, Grisbrook TL, Phillips M, Gittings P, Wood FM, Gibson W, Edgar DW (2017) Bioimpedance spectroscopy: a technique to monitor interventions for swelling in minor burns. Burns 43(8):1725–1735
Booth J, Pinney J, Davenport A (2011) The effect of vascular access modality on changes in fluid content in the arms as determined by multifrequency bioimpedance. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26(1):227–231
Panorchan K, Nongnuch A, El-Kateb S, Goodlad C, Davenport A (2015) Does the presence of an arteriovenous fistula alter changes in body water following hemodialysis as determined by multifrequency bioelectrical impedance assessment? Hemodial Int 19(4):484–489
Lee SW, Song JH, Kim GA, Lee KJ, Kim MJ (2001) Assessment of total body water from anthropometry-based equations using bioelectrical impedance as reference in Korean adult control and haemodialysis subjects. Nephrol Dial Transplant 16(1):91–97
Krivitski NM (1995) Theory and validation of access flow measurement by dilution technique during hemodialysis. Kidney Int 48(1):244–250
Kraemer M, Rode C, Wizemann V (2006) Detection limit of methods to assess fluid status changes in dialysis patients. Kidney Int 69(9):1609–1620
Hur E, Usta M, Toz H, Asci G, Wabel P, Kahvecioglu S, Kayikcioglu M, Demirci MS, Ozkahya M, Duman S, Ok E (2013) Effect of fluid management guided by bioimpedance spectroscopy on cardiovascular parameters in hemodialysis patients: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Kidney Dis 61(6):957–965
Kalantar-Zadeh K, Ikizler TA, Block G, Avram MM, Kopple JD (2003) Malnutrition-inflammation complex syndrome in dialysis patients: causes and consequences. Am J Kidney Dis 42(5):864–881
Marcelli D, Usvyat LA, Kotanko P, Bayh I, Canaud B, Etter M, Gatti E, Grassmann A, Wang Y, Marelli C, Scatizzi L, Stopper A, van der Sande FM, Kooman J, MONitoring Dialysis Outcomes (MONDO) Consortium (2015) Body composition and survival in dialysis patients: results from an international cohort study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 10(7):1192–1200
Demirci C, Aşcı G, Demirci MS, Özkahya M, Töz H, Duman S, Sipahi S, Erten S, Tanrısev M, Ok E (2016) Impedance ratio: a novel marker and a powerful predictor of mortality in hemodialysis patients. Int Urol Nephrol 48(7):1155–1162
Garagarza C, João-Matias P, Sousa-Guerreiro C, Amaral T, Aires I, Ferreira C, Jorge C, Gil C, Ferreira A (2013) Nutritional status and overhydration: can bioimpedance spectroscopy be useful in haemodialysis patients? Nefrologia 33(5):667–674
Kim HJ, Ko EJ, Lee Y, Jung H (2016) Association of vascular access flow and volume status on fistula arm by bio-impedance analysis in hemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 31(Suppl. 1):i273
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the 2017 education, research and student guidance grant funded by Jeju National University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Jeju National University Hospital Institutional Review Board in agreement with the Declaration of 1964 Helsinki.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, H., Seo, H.M., Kim, J.Y. et al. Prediction of hemodialysis vascular access failure using segmental bioimpedance analysis parameters. Int Urol Nephrol 50, 947–953 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-018-1827-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-018-1827-8