Abstract
Background
The aim of this study was to assess the effects of smoking on albuminuria risk in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
A literature search was conducted using MEDLINE, EMBASE, and China National Knowledge Infrastructure from the established date to October 2017. Summary relative risks (SRR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were computed utilizing a random effect inverse variance method.
Results
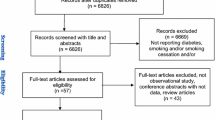
This meta-analysis included a total of 19 relevant observational studies (four prospective cohort, seven case–control, and eight cross-sectional studies), reporting 105,031 participants and 23,366 albuminuria events. Compared with never-smokers with T2DM, the SRRs of albuminuria were 1.43 (95% CIs 1.27–1.61) for ever-smokers, 2.61 (95% CIs 1.86–3.64) for current smokers, and 1.86 (95% CIs 1.37–2.52) for former smokers. Considerable heterogeneity was observed among these studies, and study design was a significant modifier for this association. There were significantly elevated risk associations for microalbuminuria (SRRs = 1.24, 95% CIs 1.05–1.46) and for macroalbuminuria (SRRs = 1.65, 95% CIs 1.03–2.66), respectively.
Conclusions
Our systematic review and meta-analysis indicates that cigarette smoking might be a potential factor for the development of albuminuria in adults with T2DM. Future studies are required to investigate the association between smoking cessation and intensity and incident albuminuria in adults with T2DM.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keen H, Chlouverakis C, Fuller J et al (1969) The consomitants of raised blood sugar: studies in newly-detected hyperglycaemics. II. Urinary albumin excretion, blood pressure and their relation to blood sugar levels. Guys Hosp Rep 118(2):247–254
Viberti GC, Hill RD, Jarrett RJ et al (1982) Microalbuminuria as a predictor of clinical nephropathy in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Lancet 1(8287):1430–1432
Mogensen CE (1984) Microalbuminuria predicts clinical proteinuria and early mortality in maturity-onset diabetes. N Engl J Med 310(6):356–360
Bakris GL, Molitch M (2014) Microalbuminuria as a risk predictor in diabetes: the continuing saga. Diabetes Care 37(3):867–875
Tebbe U, Bramlage P, Thoenes M et al (2009) Prevalence of microalbuminuria and its associated cardiovascular risk: German and Swiss results of the recent global i-SEARCH survey. Swiss Med Wkly 139(33–34):473–480
Ahn JH, Yu JH, Ko SH et al (2014) Prevalence and determinants of diabetic nephropathy in Korea: Korea national health and nutrition examination survey. Diabetes Metab J 38(2):109–119
Thompson JL, Allen P, Cunningham-Sabo L et al (2002) Environmental, policy, and cultural factors related to physical activity in sedentary American Indian women. Women Health 36(2):59–74
Radcliffe NJ, Seah JM, Clarke M et al (2017) Clinical predictive factors in diabetic kidney disease progression. J Diabetes Investig 8(1):6–18
Xue R, Gui D, Zheng L et al (2017) Mechanistic insight and management of diabetic nephropathy: recent progress and future perspective. J Diabetes Res 2017:1839809
Linneberg A, Jacobsen RK, Skaaby T et al (2015) Effect of smoking on blood pressure and resting heart rate: a mendelian randomization meta-analysis in the CARTA consortium. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 8(6):832–841
Li WH, Wang MP, Lam TH et al (2017) Brief intervention to promote smoking cessation and improve glycemic control in smokers with type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Sci Rep 7:45902
Yeom H, Lee JH, Kim HC et al (2016) The association between smoking tobacco after a diagnosis of diabetes and the prevalence of diabetic nephropathy in the Korean male population. J Prev Med Public Health 49(2):108–117
Zhang W, Yang Z, Li X et al (2015) The functional Q84R polymorphism of TRIB3 gene is associated with diabetic nephropathy in Chinese type 2 diabetic patients. Gene 555(2):357–361
Furukawa S, Yamamoto S, Todo Y et al (2014) Association between subclinical hypothyroidism and diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocr J 61(10):1011–1018
Wolf G, Busch M, Muller N et al (2011) Association between socioeconomic status and renal function in a population of German patients with diabetic nephropathy treated at a tertiary centre. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26(12):4017–4023
Hsu CC, Hwang SJ, Tai TY et al (2010) Cigarette smoking and proteinuria in Taiwanese men with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med 27(3):295–302
Parving HH, Lewis JB, Ravid M et al (2006) Prevalence and risk factors for microalbuminuria in a referred cohort of type II diabetic patients: a global perspective. Kidney Int 69(11):2057–2063
Hou XH, Wang JH, Feng P et al (2005) A case control study on the risk factors of proteinuria in patients with type 2 diabetes. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 26(1):39–43
Herrera-Pombo JL, Aguilar-Diosdado M, Hawkins F et al (2005) Is increasing urinary albumin a better marker for microvascular than for macrovascular complication of type 2 diabetes mellitus? Nephron Clin Pract 101(3):c116–c121
Cederholm J, Eliasson B, Nilsson PM et al (2005) Microalbuminuria and risk factors in type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 67(3):258–266
Tam TK, Cheng LP, Lau DM et al (2004) The prevalence of microalbuminuria among patients with type II diabetes mellitus in a primary care setting: cross-sectional study. Hong Kong Med J 10(5):307–311
Kohler KA, McClellan WM, Ziemer DC et al (2002) Smoking and microalbuminuria: a case-control study in African-Americans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 25(1):243–245
Pijls LT, de Vries H, Kriegsman DM et al (2001) Determinants of albuminuria in people with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 52(2):133–143
Yokoyama H, Okudaira M, Otani T et al (1998) High incidence of diabetic nephropathy in early-onset Japanese NIDDM patients. Risk analysis. Diabetes Care. 21(7):1080–1085
Klein R, Klein BE, Moss SE et al (1995) Ten-year incidence of gross proteinuria in people with diabetes. Diabetes 44(8):916–923
Al-Rubeaan K, Youssef AM, Subhani SN et al (2014) Diabetic nephropathy and its risk factors in a society with a type 2 diabetes epidemic: a Saudi National Diabetes Registry-based study. PLoS ONE 9(2):e88956. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0088956
Liu L, Zheng T, Wang F et al (2010) Pro12Ala polymorphism in the PPARG gene contributes to the development of diabetic nephropathy in Chinese type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 33(1):144–149. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc09-1258
Aekplakorn W, Srivanichakorn S, Sangwatanaroj S (2009) Microalbuminuria and metabolic risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes in primary care setting in Thailand. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 84(1):92–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2008.12.020
Unnikrishnan RI, Rema M, Pradeepa R et al (2007) Prevalence and risk factors of diabetic nephropathy in an urban South Indian population: the Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (CURES 45). Diabetes Care 30(8):2019–2024. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc06-2554
Amini M, Safaei H, Aminorroaya A (2007) The incidence of microalbuminuria and its associated risk factors in type 2 diabetic patients in Isfahan, Iran. Rev Diabet Stud 4(4):242–248. https://doi.org/10.1900/RDS.2007.4.242
Su S, Wang W, Sun T et al (2017) Smoking as a risk factor for diabetic nephropathy: a meta-analysis. Int Urol Nephrol 49(10):1801–1807. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-017-1638-3
Jiang N, Huang F, Zhang X (2017) Smoking and the risk of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Oncotarget 8(54):93209–93218. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.21478
Kramer HJ, Nguyen QD, Curhan G et al (2003) Renal insufficiency in the absence of albuminuria and retinopathy among adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA 289(24):3273–3277. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.289.24.3273
Yokoyama H, Sone H, Oishi M et al (2009) Prevalence of albuminuria and renal insufficiency and associated clinical factors in type 2 diabetes: the Japan Diabetes Clinical Data Management study (JDDM15). Nephrol Dial Transplant 24(4):1212–1219. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfn603
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC et al (2000) Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 283(15):2008–2012
Ovbiagele B (2008) Microalbuminuria: risk factor and potential therapeutic target for stroke? J Neurol Sci 271(1–2):21–28
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7(3):177–188
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ et al (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327(7414):557–560. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
Begg CB, Mazumdar M (1994) Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 50(4):1088–1101
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M et al (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315(7109):629–634
Chen Y, Zhi Y, Li C et al (2016) HDL cholesterol and risk of diabetic nephropathy in patient with type 1 diabetes: a meta-analysis of cohort studies. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 122:84–91
Barua RS, Ambrose JA (2013) Mechanisms of coronary thrombosis in cigarette smoke exposure. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 33(7):1460–1467
Caimi G, Hopps E, Montana M et al (2014) Nitric oxide metabolites (nitrite and nitrate) in several clinical condition. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 56(4):359–369
Salvatore SP, Troxell ML, Hecox D et al (2015) Smoking-related glomerulopathy: expanding the morphologic spectrum. Am J Nephrol 41(1):66–72
Baggio B, Budakovic A, Dalla Vestra M et al (2002) Effects of cigarette smoking on glomerular structure and function in type 2 diabetic patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 13(11):2730–2736
Jose MJ, Varkey V, Chandni R et al (2016) The Role of Smoking as a Modifiable Risk Factor in Diabetic Nephropathy. J Assoc Physicians India 64(7):34–38
Lan L, Han Y, Ren W et al (2015) Advanced glycation endproducts affect the cytoskeletal structure of rat glomerular endothelial cells via the Rasrelated C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 11(6):4321–4326
Pala L, Cresci B, Manuelli C et al (2005) Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 and low affinity VEGF binding sites on human glomerular endothelial cells: biological effects and advanced glycosilation end products modulation. Microvasc Res 70(3):179–188
Chuahirun T, Simoni J, Hudson C et al (2004) Cigarette smoking exacerbates and its cessation ameliorates renal injury in type 2 diabetes. Am J Med Sci 327(2):57–67
Phisitkul K, Hegazy K, Chuahirun T et al (2008) Continued smoking exacerbates but cessation ameliorates progression of early type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Am J Med Sci 335(4):284–291. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAJ.0b013e318156b799
Launay JM, Del Pino M, Chironi G et al (2009) Smoking induces long-lasting effects through a monoamine-oxidase epigenetic regulation. PLoS ONE 4(11):e7959
Hellemons ME, Agarwal PK, van der Bij W et al (2011) Former smoking is a risk factor for chronic kidney disease after lung transplantation. Am J Transplant 11(11):2490–2498
Bowlin SJ, Morrill BD, Nafziger AN et al (1996) Reliability and changes in validity of self-reported cardiovascular disease risk factors using dual response: the behavioral risk factor survey. J Clin Epidemiol 49(5):511–517
Orth SR, Stockmann A, Conradt C et al (1998) Smoking as a risk factor for end-stage renal failure in men with primary renal disease. Kidney Int 54(3):926–931. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.1998.00067.x
Authors’ contribution
Xu Haili and Lian jing participated in the design of this manuscript. Xu Haili, Jinliu Suo, and Lian jing participated in abstracting the data and performing statistical analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, H., Suo, J. & Lian, J. Cigarette smoking and risk of albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Int Urol Nephrol 50, 911–922 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-018-1825-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-018-1825-x